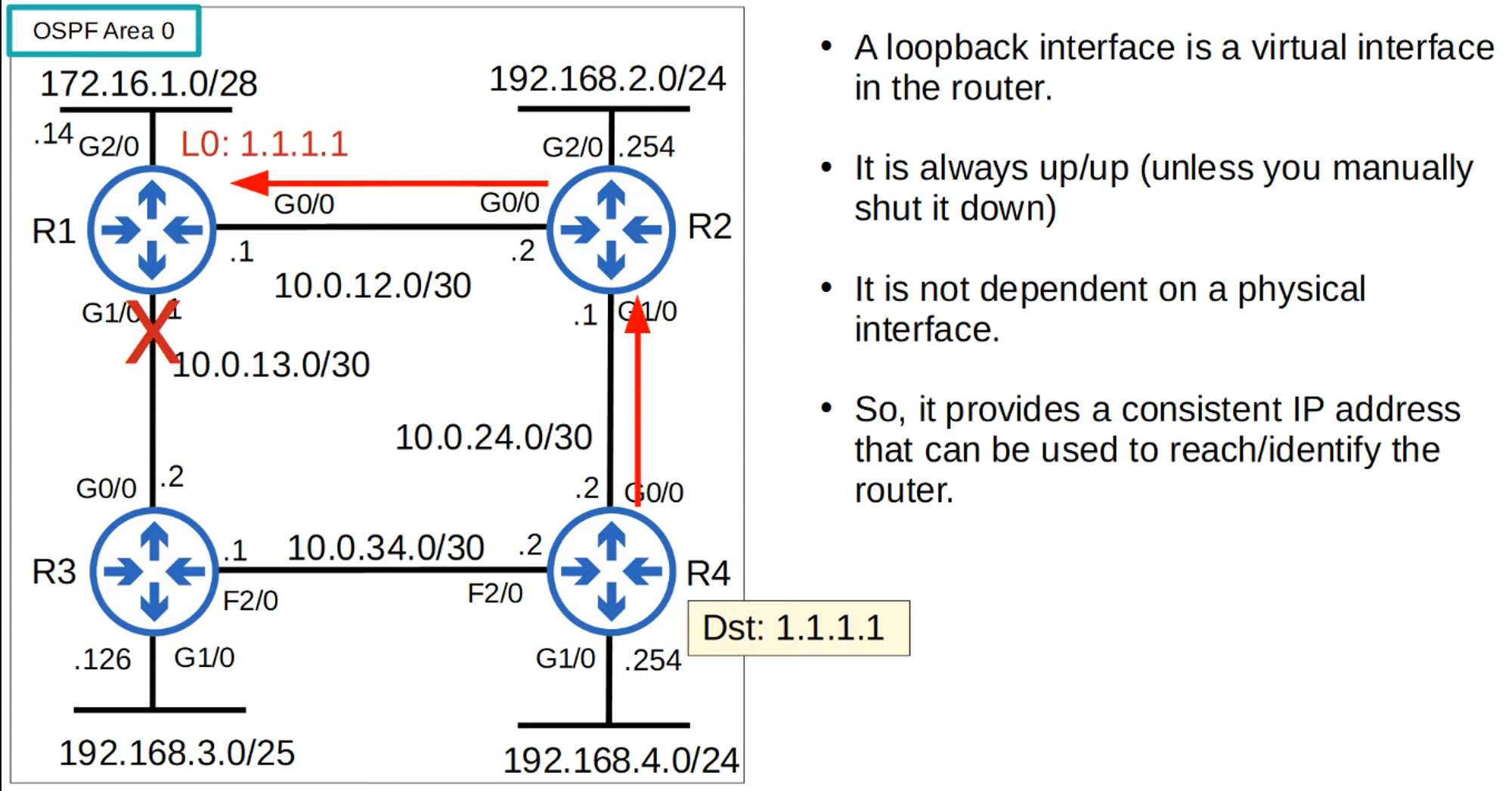
LOOPBACK INTERFACES
- Loopback Interface: A virtual interface in the router.
- Always UP/UP: It remains up unless manually shut down.
- Independent of Physical Interface: Provides a consistent IP address for identifying or reaching the router.
OSPF NETWORK TYPES
- OSPF Network Type: Refers to the connection type between OSPF neighbors (e.g., Ethernet).
- Three Main OSPF Network Types:
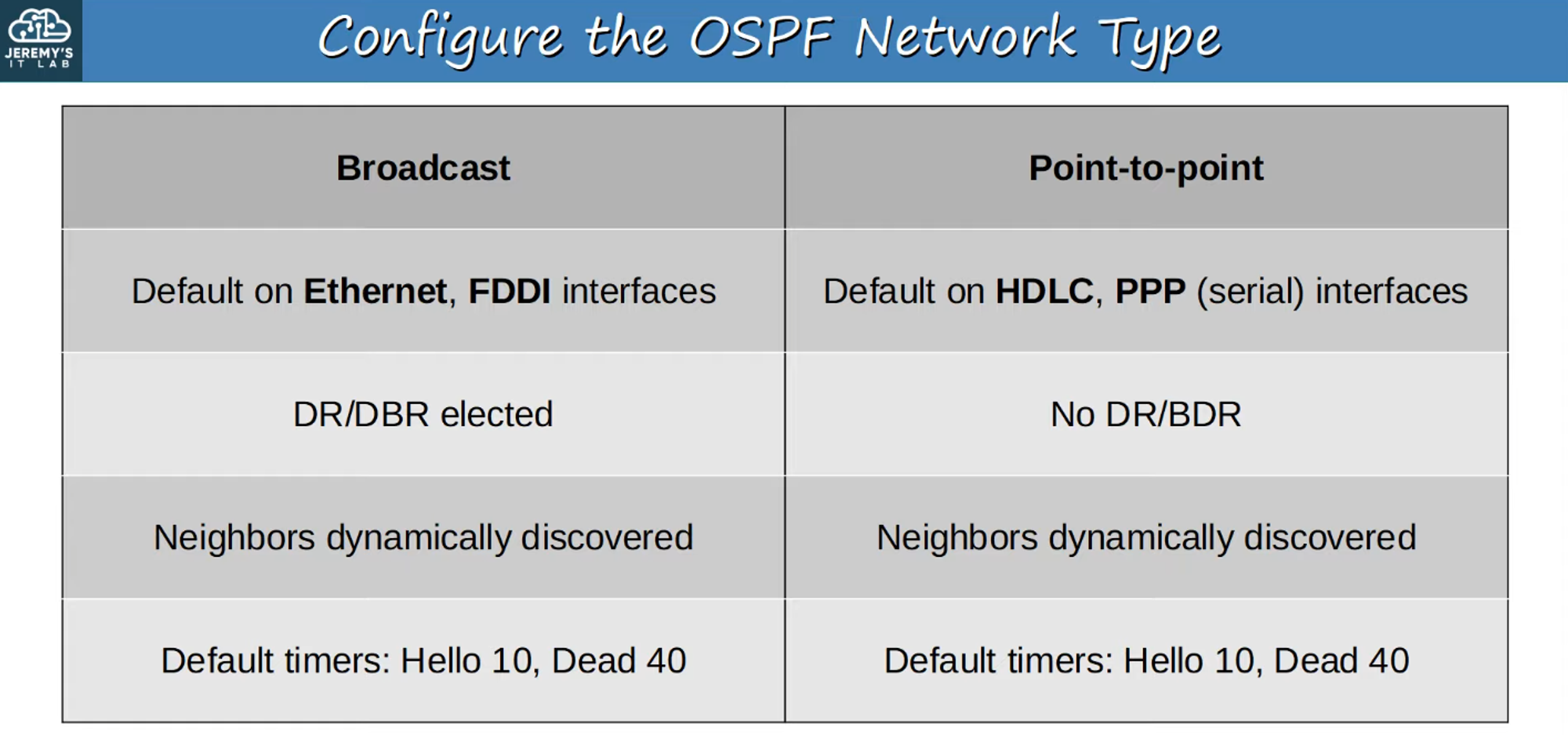
- Broadcast: Default on Ethernet and FDDI interfaces.
- Point-to-Point: Default on PPP and HDLC interfaces.
- Non-Broadcast: Default on Frame Relay and X.25 interfaces.
💡 CCNA focuses on Broadcast and Point-to-Point types.
OSPF BROADCAST NETWORK TYPE
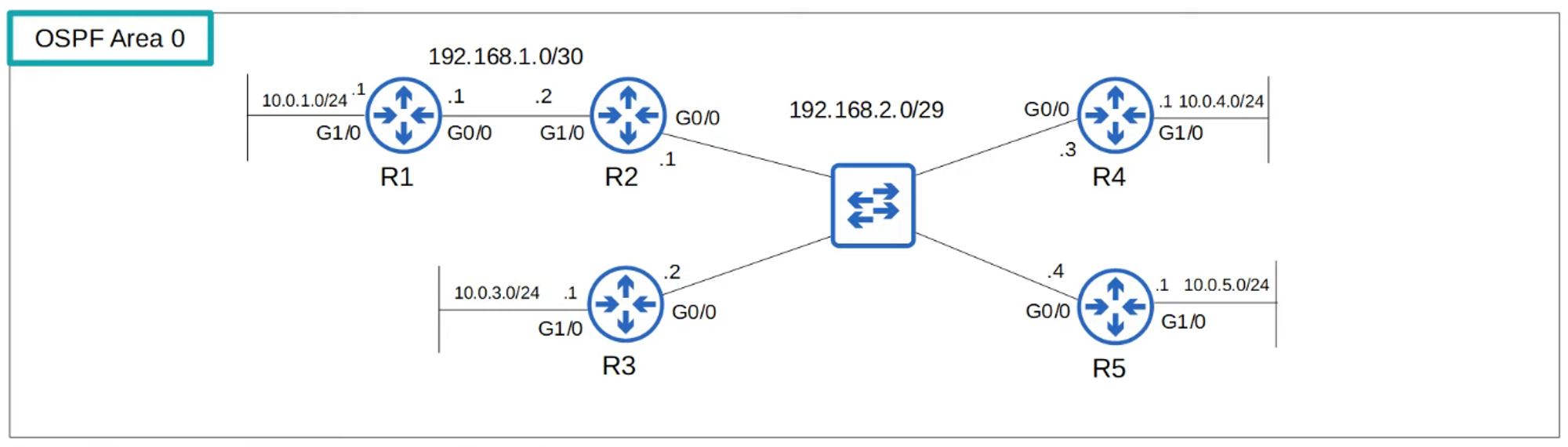
- Default on Ethernet and FDDI interfaces.
- Dynamic Neighbor Discovery: Uses OSPF “Hello” messages via multicast address 224.0.0.5.
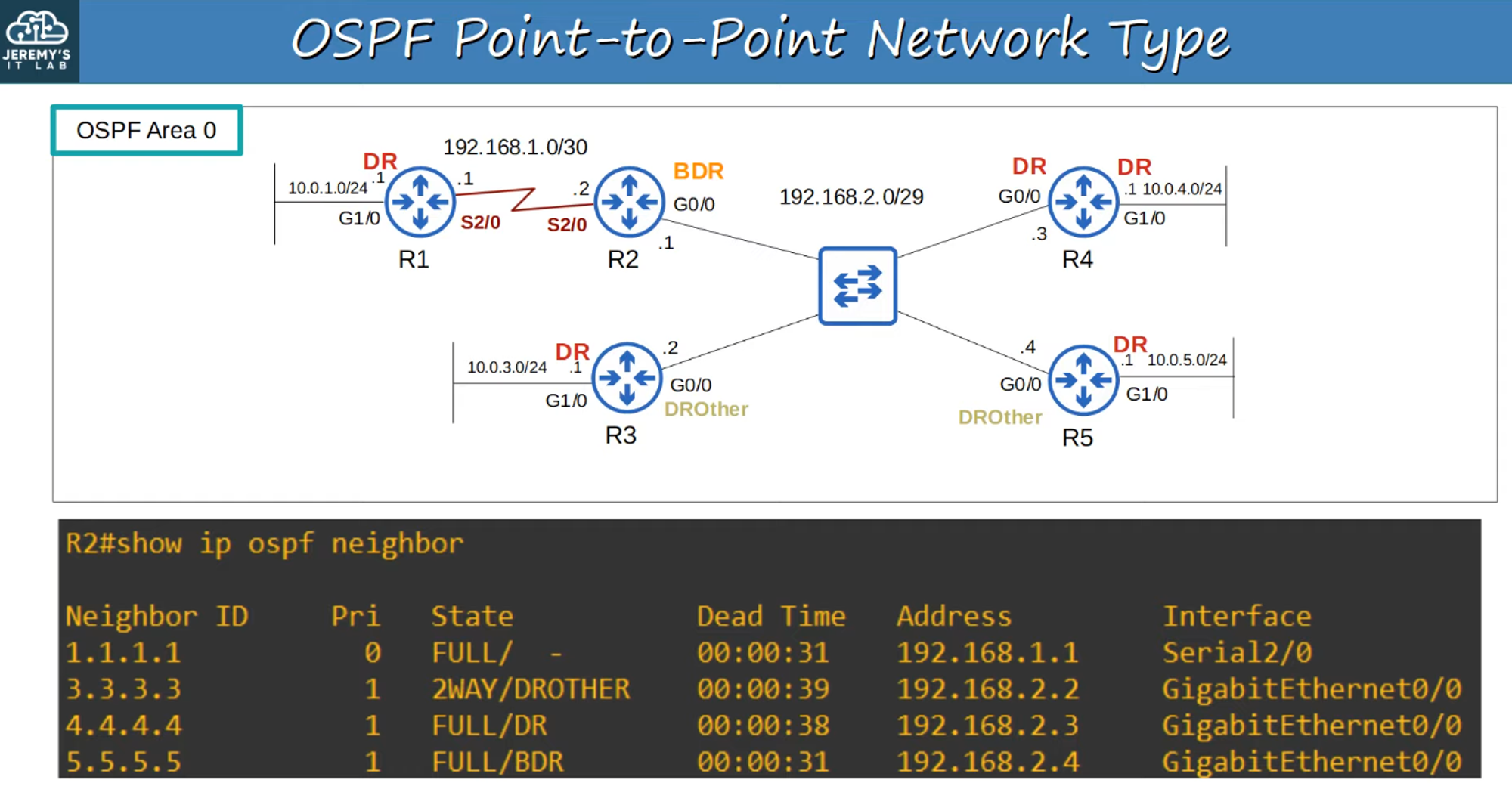
- DR and BDR Election:
- DR (Designated Router) and BDR (Backup Designated Router) are elected on each subnet.
- Non-DR/BDR routers become DROthers.
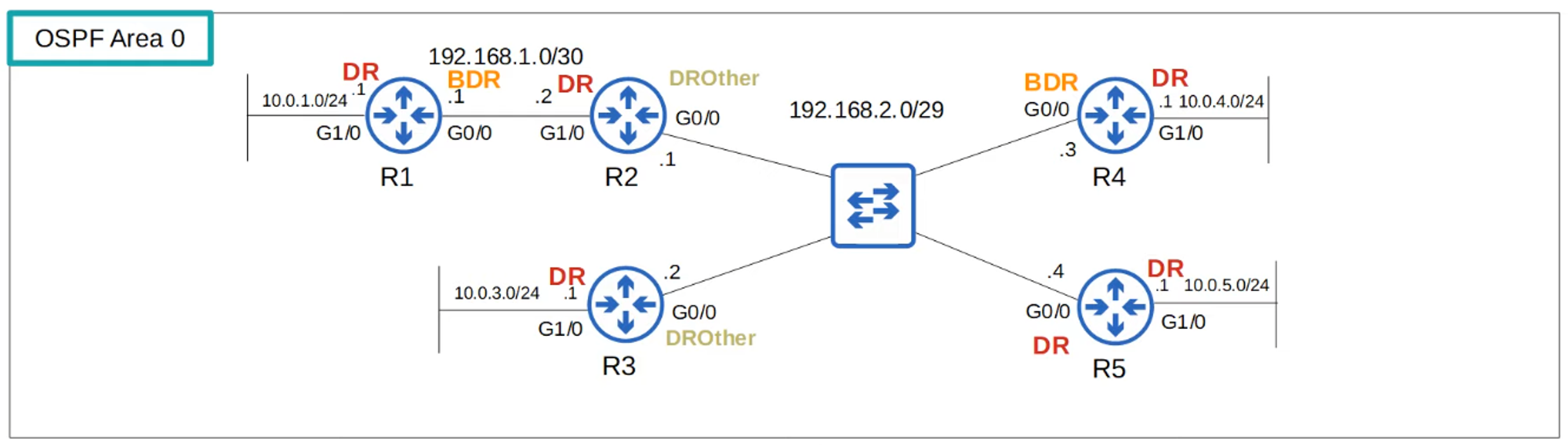
Election Order:
- Highest OSPF Interface Priority.
- Highest OSPF Router ID.
-
Default OSPF Interface Priority is “1” on all interfaces.
-
To change OSPF Priority:
R2(config-if)# ip ospf priority <priority number>
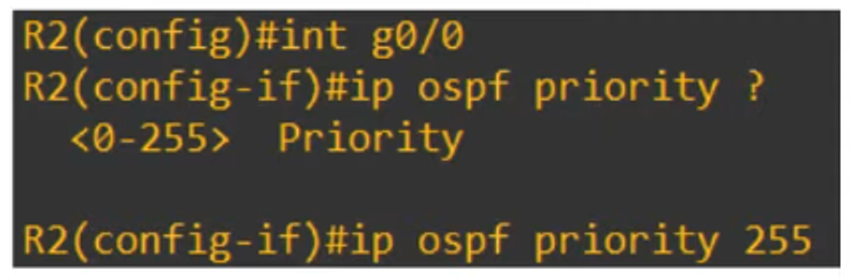
-
Priority of 0: Router cannot be DR/BDR.
-
Non-preemptive Election: DR/BDR roles remain until OSPF is reset, interface fails, or is shut down.
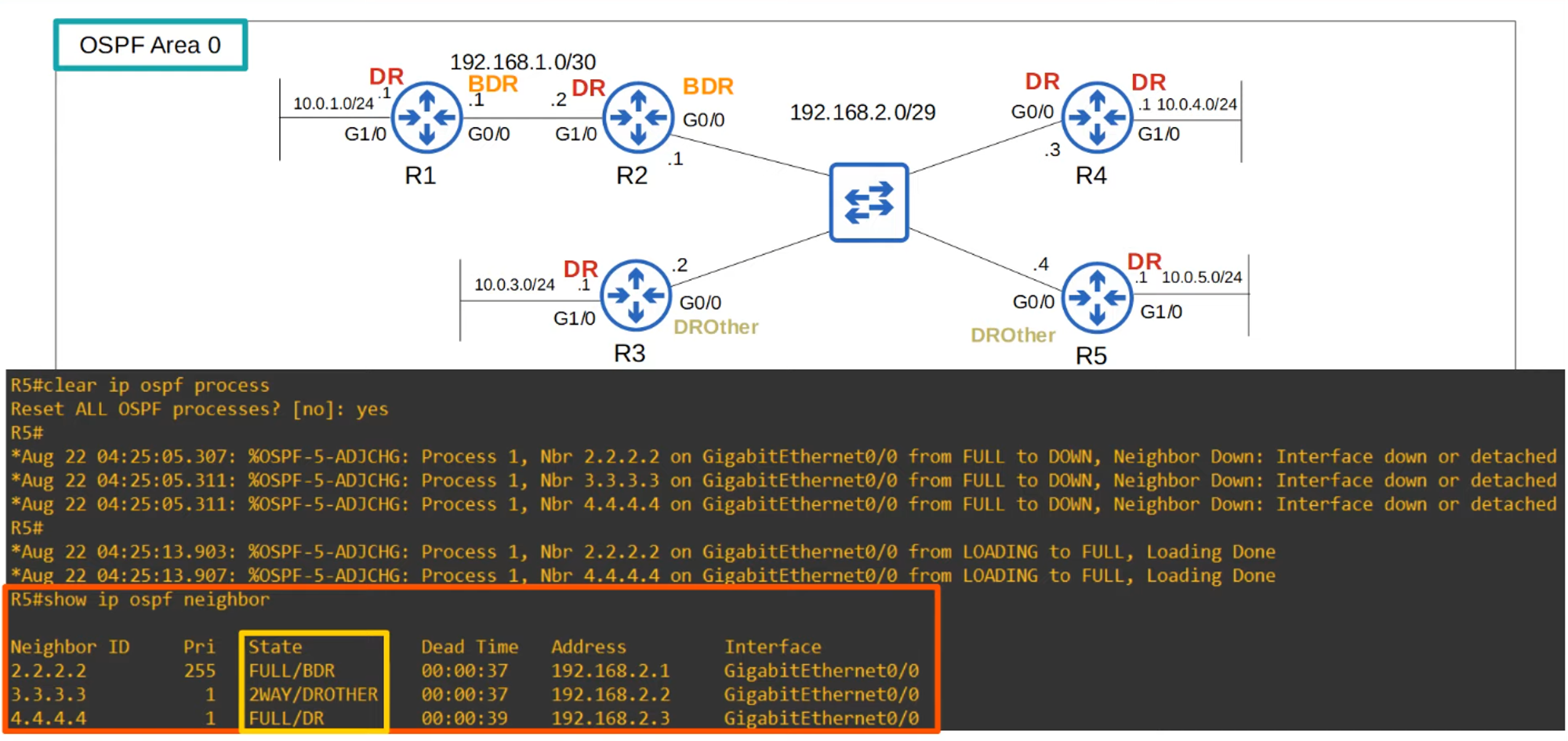
- Full Adjacency: Only with DR and BDR. DROthers do not exchange LSAs with each other, reducing LSA floods.
💡 Messages to DR/BDR: Multicast to 224.0.0.6.

OSPF POINT-TO-POINT NETWORK TYPE
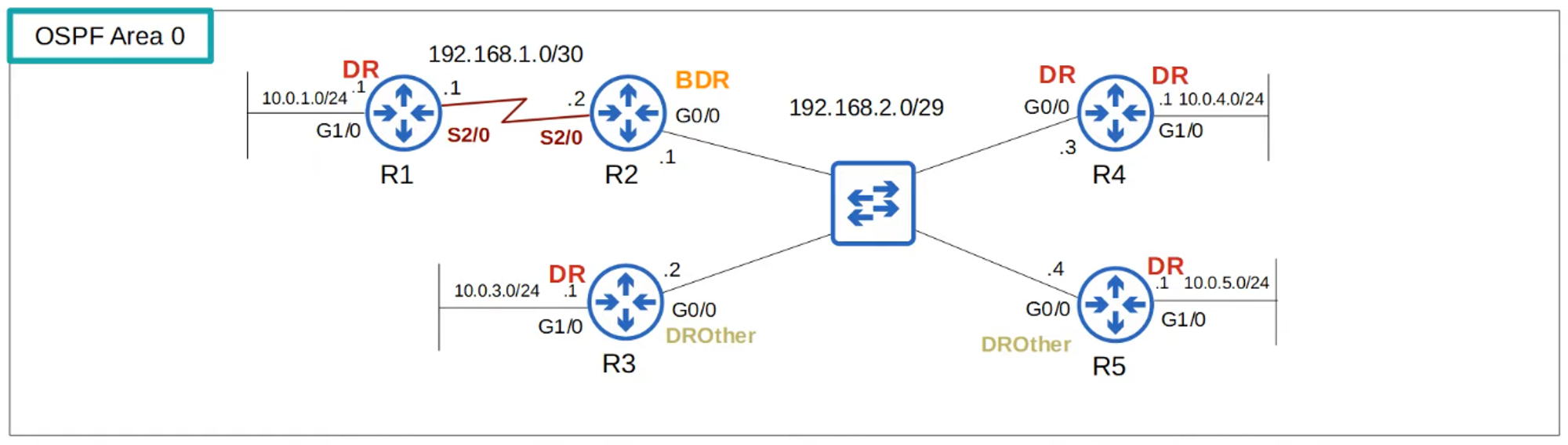
- Default on Serial Interfaces using PPP and HDLC encapsulations.
- Dynamic Neighbor Discovery: Uses OSPF “Hello” messages via multicast address 224.0.0.5.
- No DR/BDR Election: As it’s a direct connection, the two routers form a full adjacency with each other.
Serial Interfaces
-
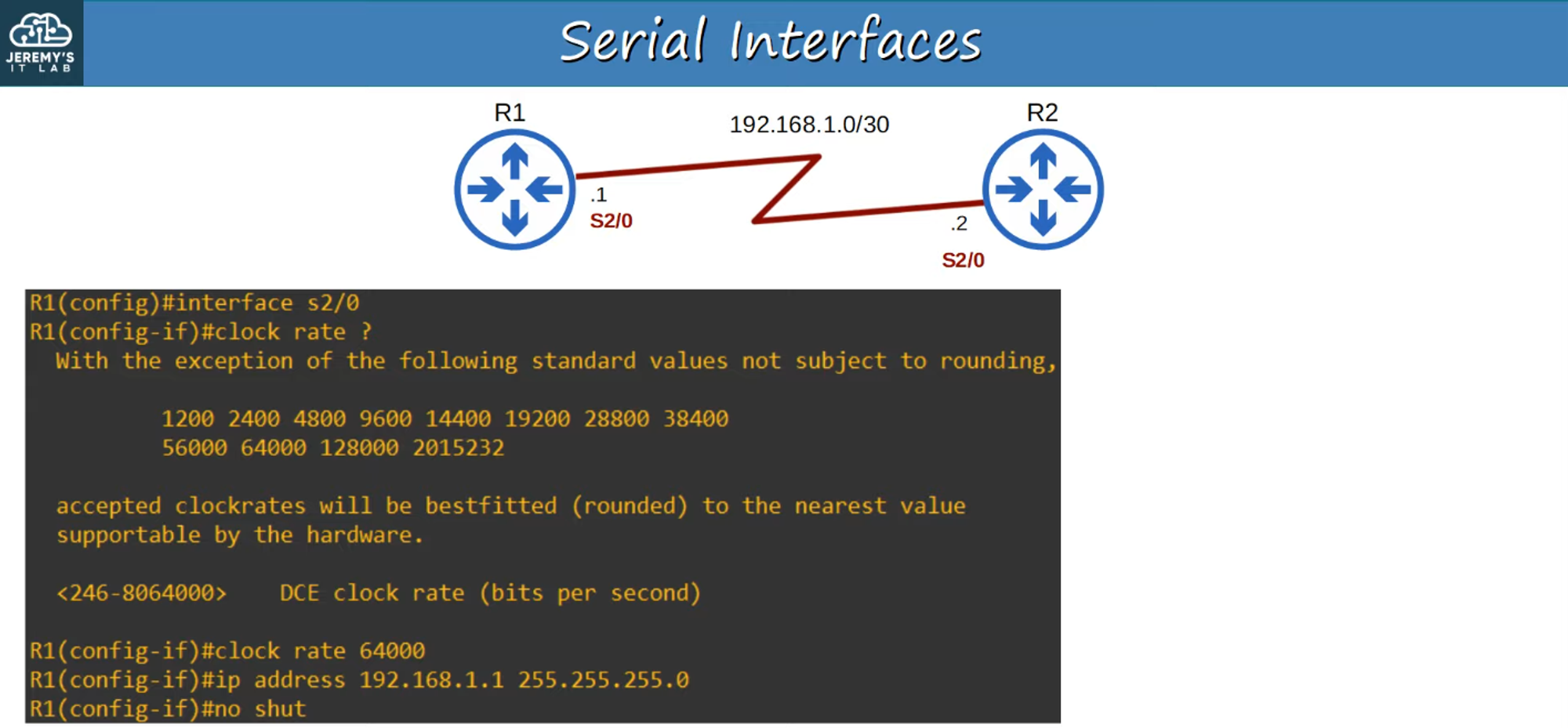
DCE and DTE: One side of the serial connection functions as DCE, the other as DTE.
-
Clock Rate: Only the DCE side specifies the clock rate (speed) of the connection.
-
Ethernet Interfaces: Use the “speed” command for operating speed.
-
Serial Interfaces: Use the “clock rate” command.
R1(config-if)# clock rate <bits-per-second>
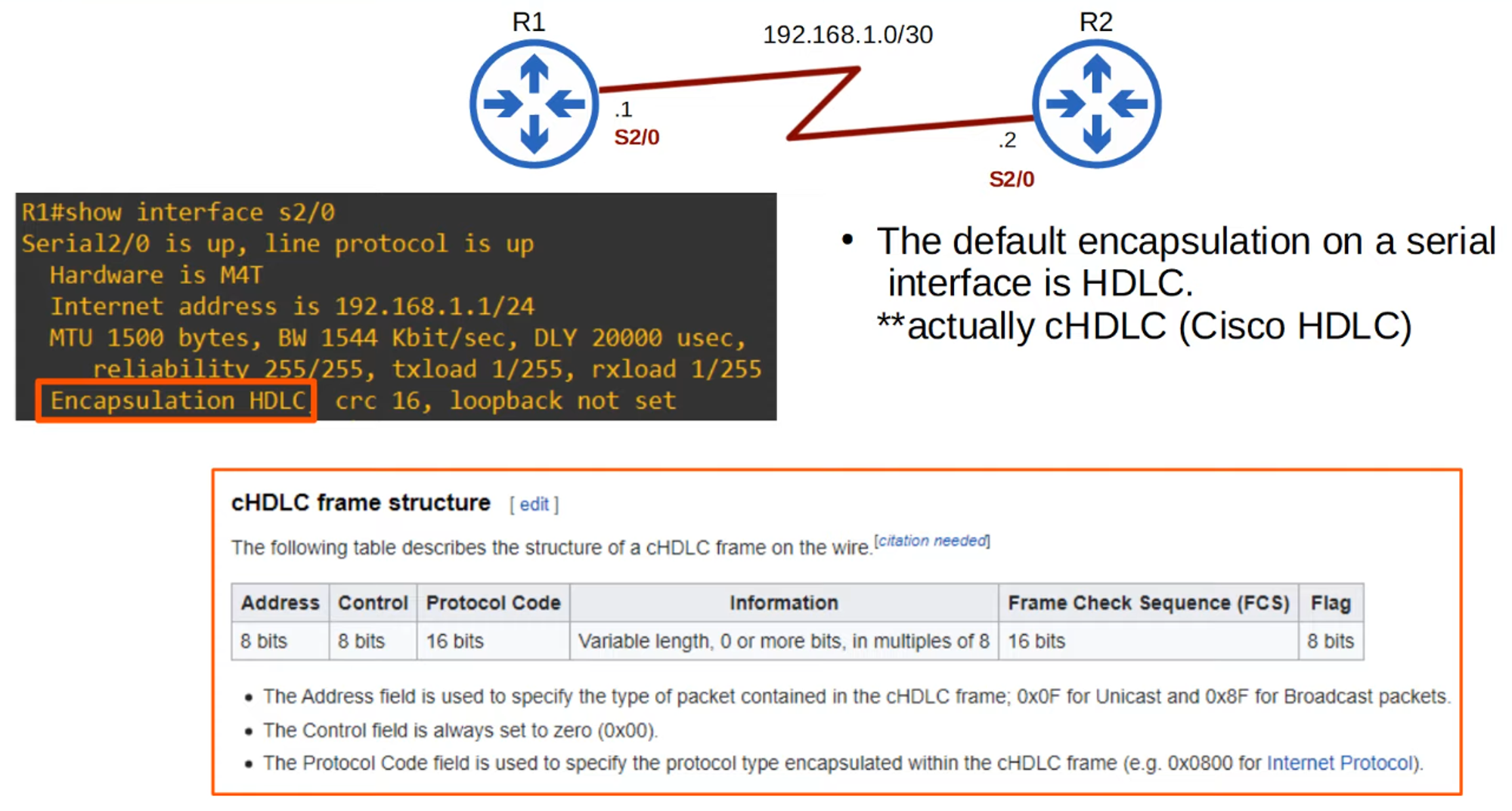
- Encapsulation Type: Must match on both ends, or the interface will go down.
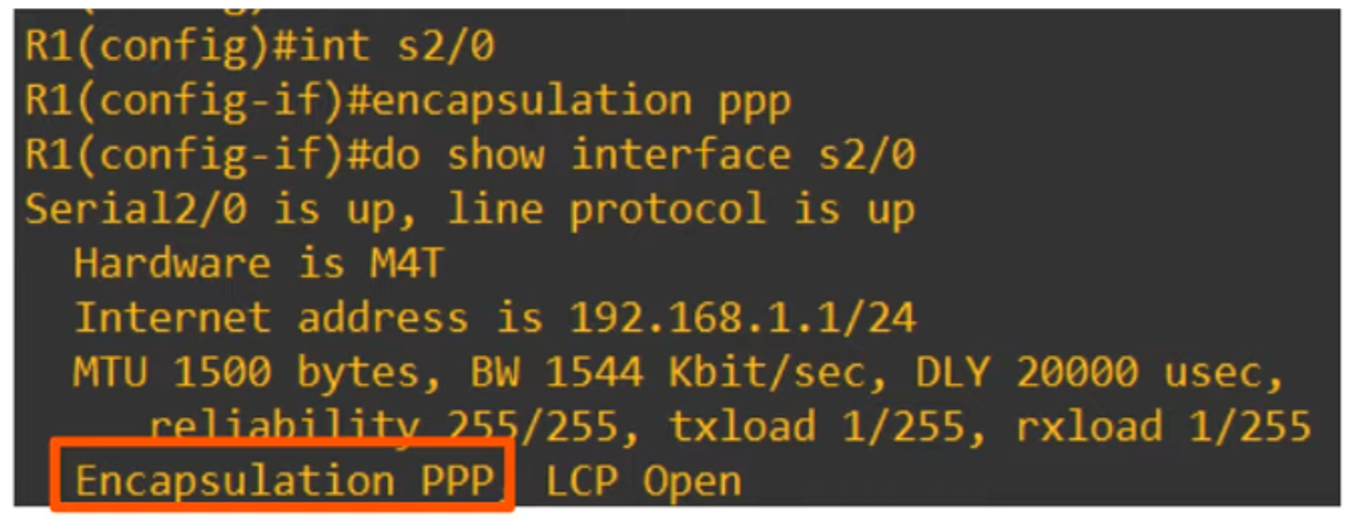
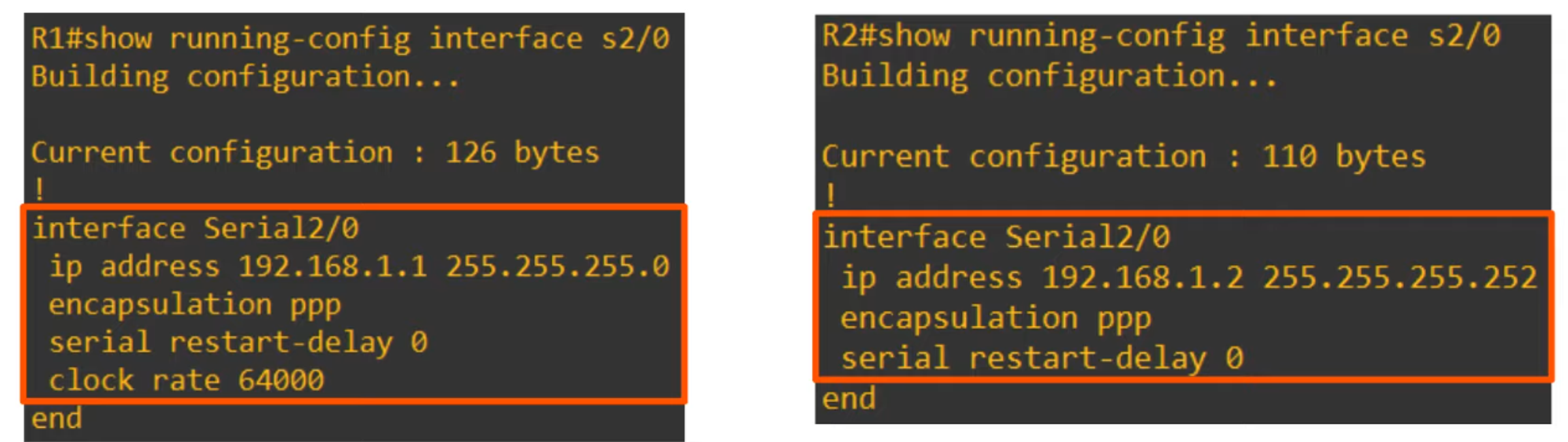
Summary of Serial Interfaces:
-
Default encapsulation is HDLC.
-
Configure PPP encapsulation with:
R1(config-if)# encapsulation ppp -
Identify which side is DCE/DTE:
R1# show controllers <interface-id>
-
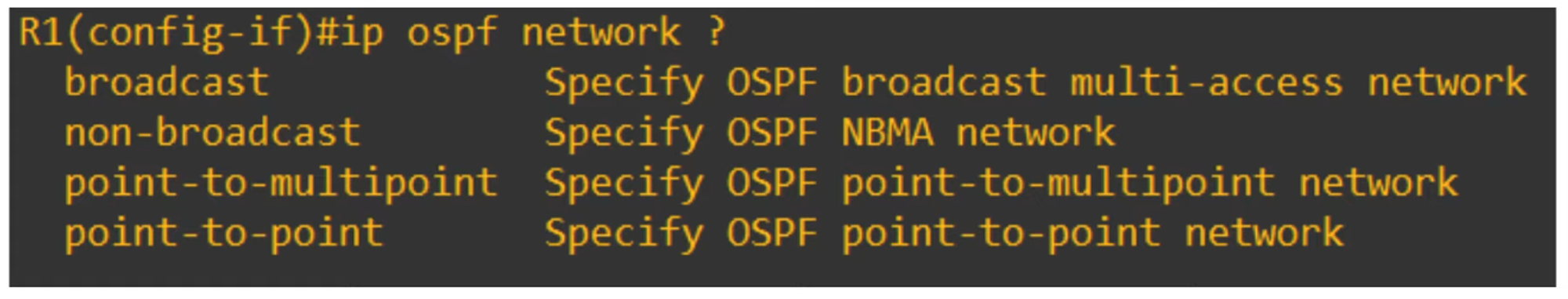
Configure the OSPF Network Type on an Interface:
R1(config-if)# ip ospf network <network type>
💡 Note: Not all network types work on all link types (e.g., a serial link cannot use the Broadcast network type).
OSPF NEIGHBOR/ADJACENCY REQUIREMENTS
- Area Number Must Match.
- Interfaces Must Be in the Same Subnet.
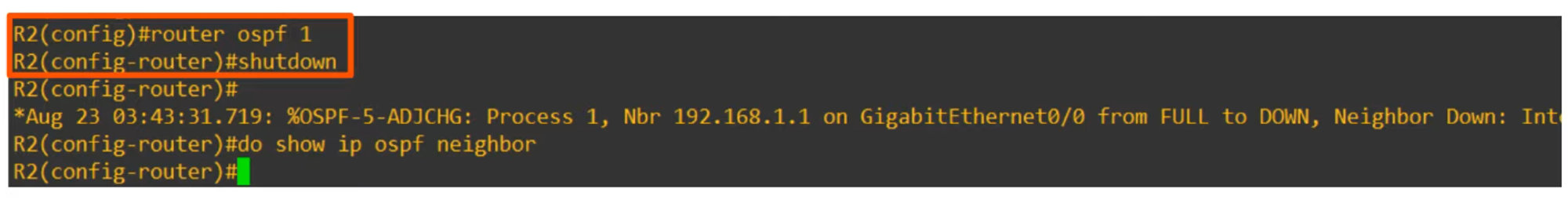
- OSPF Process Must Not Be Shut Down.
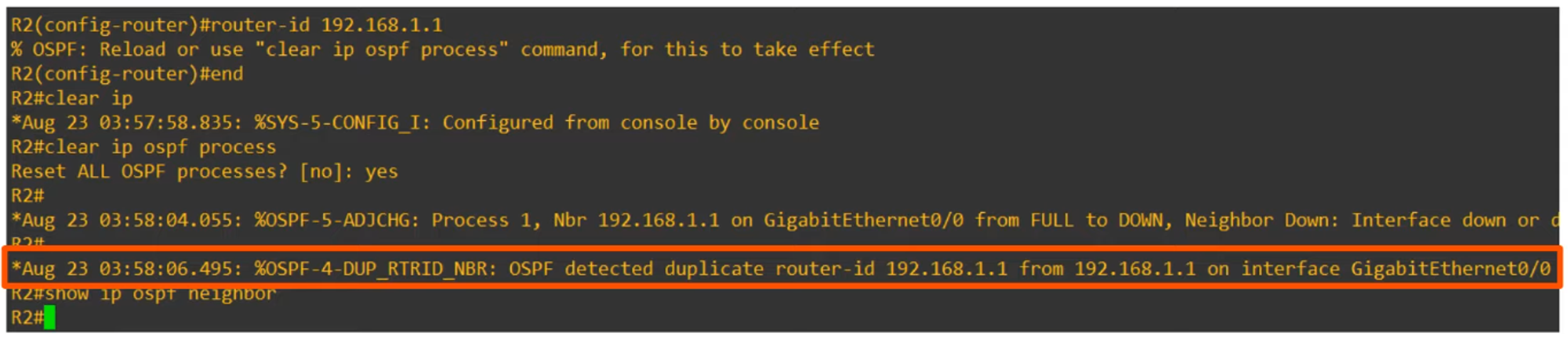
- OSPF Router ID Must Be Unique.
- Hello and Dead Timers Must Match.
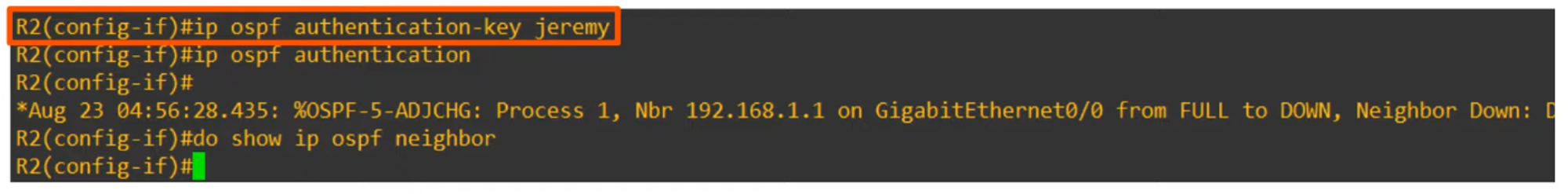
- Authentication Settings Must Match.
SPECIAL REQUIREMENTS
-
IP MTU Settings Must Match.
- IP MTU: Maximum size of an IP packet that can be sent from an interface.
- If settings don’t match, routers can still become OSPF neighbors, but OSPF will not operate properly.
-
OSPF Network Type Must Match.
- Mismatched types will appear to work, but neighbors won’t appear in routing information.
OSPF LSA TYPES
- The OSPF LSDB (Link-State Database) is made up of LSAs (Link-State Advertisements).
- Key LSA Types for CCNA:
- Type 1 (Router LSA): Generated by every OSPF router, identifies the router using its Router ID, and lists networks attached to the router’s OSPF-activated interfaces.
- Type 2 (Network LSA): Generated by the DR of each multi-access network (e.g., Broadcast network type), lists routers attached to the multi-access network.
- Type 5 (AS-External LSA): Generated by ASBRs to describe routes to destinations outside of the AS (OSPF domain).