The OSI Model Explained — 7 Layers
The Open Systems Interconnection Model (OSI) is a conceptual framework that standardizes the different functions of a network. Created by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), the OSI model divides these functions into 7 layers, which work together to facilitate network communication.
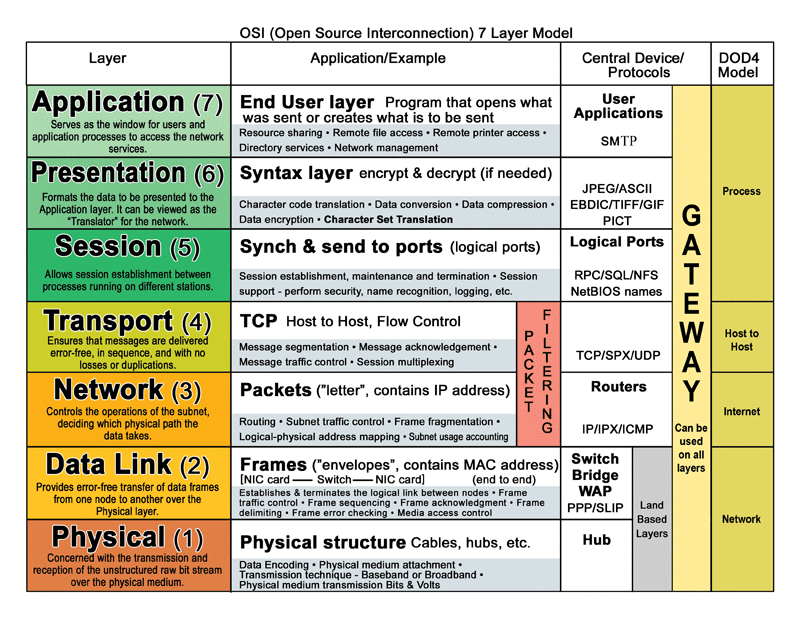 Image from : https://blog.smartbuildingsacademy.com/what-is-the-osi-model
Image from : https://blog.smartbuildingsacademy.com/what-is-the-osi-model
Layer 7 - Application
 Image from : https://www.lifewire.com/layers-of-the-osi-model-illustrated-818017
Image from : https://www.lifewire.com/layers-of-the-osi-model-illustrated-818017
- Function: Provides network services directly to end-user applications.
- Responsibilities:
- User interface for network services (e.g., browsing, emailing)
- Handles high-level protocols and requests
- Identifies communication partners
- Common Protocols: HTTP, HTTPS, SMTP, DNS, FTP
Layer 6 – Presentation Layer
 Image from : https://www.lifewire.com/layers-of-the-osi-model-illustrated-818017
Image from : https://www.lifewire.com/layers-of-the-osi-model-illustrated-818017
- Function: Ensures data is in a usable format and properly encoded/decoded.
- Responsibilities:
- Data translation (e.g., EBCDIC ↔ ASCII)
- Encryption and decryption (e.g., TLS/SSL)
- Data compression
- Common Protocols/Formats: SSL/TLS, JPEG, MPEG
Layer 5 – Session Layer
 Image from : https://www.lifewire.com/layers-of-the-osi-model-illustrated-818017
Image from : https://www.lifewire.com/layers-of-the-osi-model-illustrated-818017
- Function: Manages sessions (conversations) between applications.
- Responsibilities:
- Establish, maintain, and terminate connections
- Handle dialog control (half/full duplex)
- Perform synchronization and checkpoints
- Common Protocols: NetBIOS, RPC, SAP
Layer 4 – Transport Layer
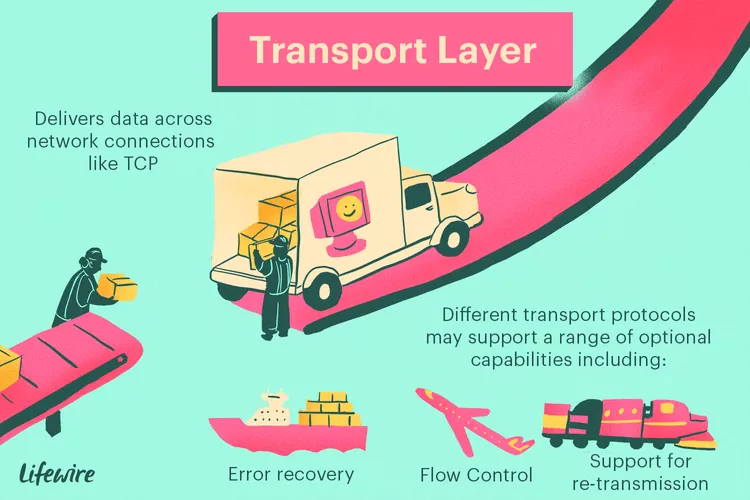 Image from : https://www.lifewire.com/layers-of-the-osi-model-illustrated-818017
Image from : https://www.lifewire.com/layers-of-the-osi-model-illustrated-818017
- Function: Provides reliable or fast delivery of data across networks.
- Responsibilities:
- Segmentation and reassembly of data
- Flow control and error handling
- Port addressing to deliver data to correct applications
- Common Protocols: TCP (reliable), UDP (faster, no guarantees)
Layer 3 – Network Layer
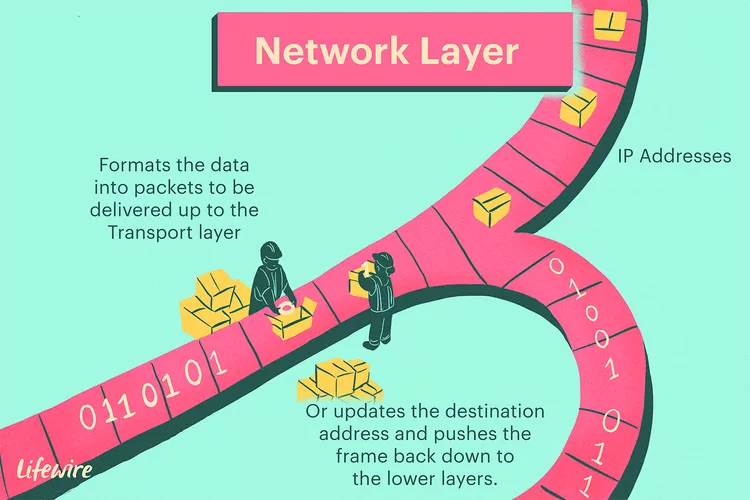 Image from : https://www.lifewire.com/layers-of-the-osi-model-illustrated-818017
Image from : https://www.lifewire.com/layers-of-the-osi-model-illustrated-818017
- Function: Handles routing and logical addressing.
- Responsibilities:
- IP addressing
- Path determination and packet forwarding
- Routing between networks
- Common Protocols: IP, ICMP, OSPF, BGP
Layer 2 – Data Link Layer
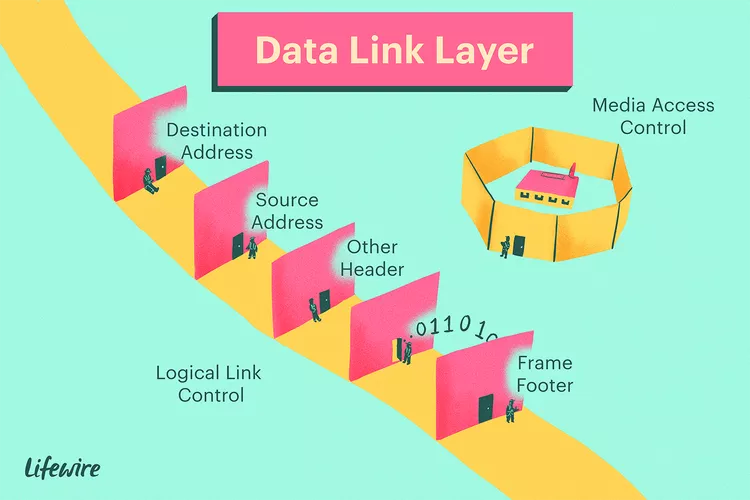 Image from : https://www.lifewire.com/layers-of-the-osi-model-illustrated-818017
Image from : https://www.lifewire.com/layers-of-the-osi-model-illustrated-818017
- Function: Facilitates reliable node-to-node communication on the same network segment.
- Responsibilities:
- Framing of raw bits into frames
- MAC addressing and physical addressing
- Error detection (CRC) and flow control
- Common Protocols/Technologies: Ethernet, ARP, PPP, 802.11 (Wi-Fi)
Layer 1 – Physical Layer
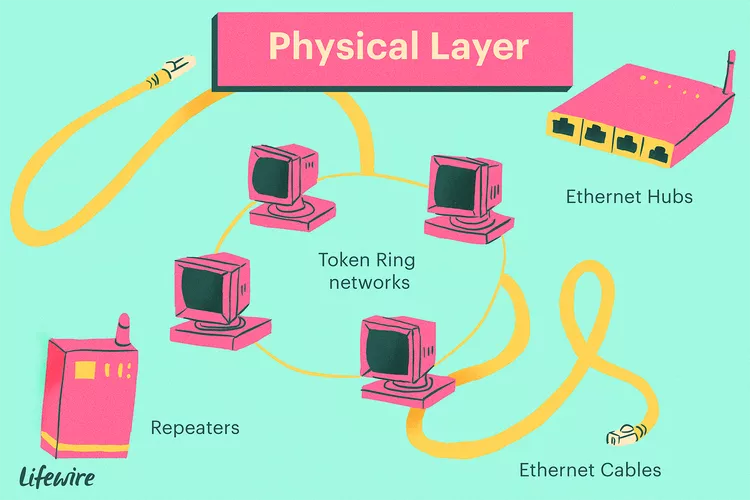 Image from : https://www.lifewire.com/layers-of-the-osi-model-illustrated-818017
Image from : https://www.lifewire.com/layers-of-the-osi-model-illustrated-818017
- Function: Transmits raw bitstreams over physical media.
- Responsibilities:
- Defines physical characteristics (cables, voltage levels)
- Converts frames into signals (electrical, optical, or wireless)
- Synchronization of bits
- Examples: Fiber optics, Ethernet cables, hubs, radio frequencies