API REVIEW
- An API (Application Programming Interface) is a software interface that allows two applications to communicate with each other.
- APIs are essential not just for network automation but for all kinds of applications
- In SDN Architecture, APIs are use to communicate between apps and the SDN controller (via the NBI) and between the SDN controller and the network devices (via the SBI)
- The NBI typically uses REST APIs
- NETCONF and RESTCONF are popular Southbound APIs
CRUD OPERATIONS AND HTTP VERBS
-
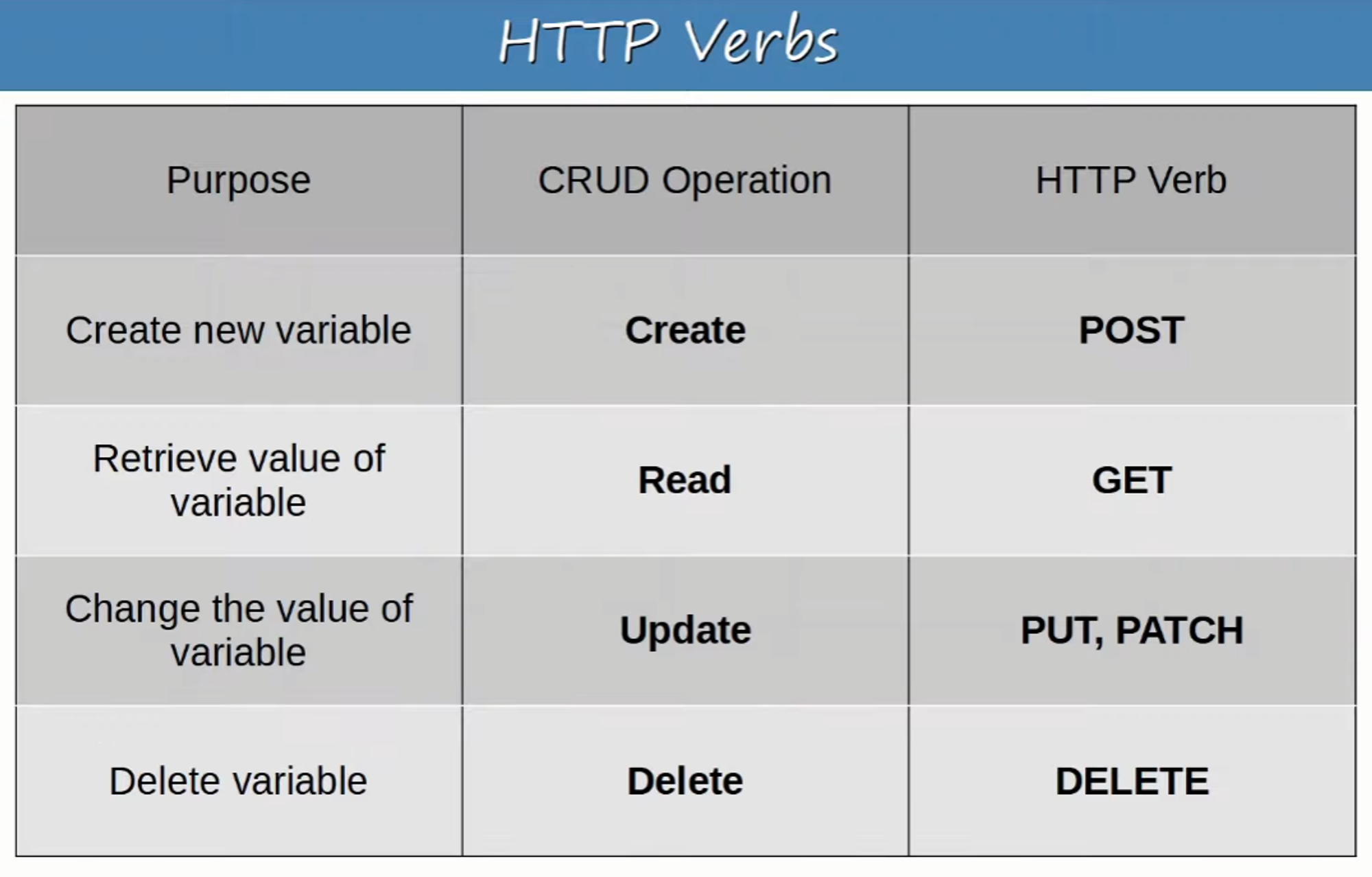
CRUD ( CREATE, READ, UPDATE, DELETE) refers to the operations we perform using REST APIs
-
CREATE :
- Used to CREATE new variables and set their initial values
- Example: create a variable “ip_address” and set the value to “10.1.1.1”
- Used to CREATE new variables and set their initial values
-
READ :
- Used to READ the value of a variable
- Example: Read the value of variable “ip_address” (”10.1.1.1”)
- Used to READ the value of a variable
-
UPDATE :
- Used to CHANGE / UPDATE the value of a variable
- Example: Change the value of “ip_address” from “10.1.1.1” to “10.2.3.4”
- Used to CHANGE / UPDATE the value of a variable
-
DELETE :
- Used to DELETE variables
- Example: Delete variable “ip_address”
- Used to DELETE variables
-
HTTP uses verbs (aka. methods) that map to these CRUD operations
-
REST APIs typically use HTTP
HTTP REQUEST :
- When an HTTP client sends a request to an HTTP server, the HTTP header includes information like this:
- An HTTP Verb (ie: GET)
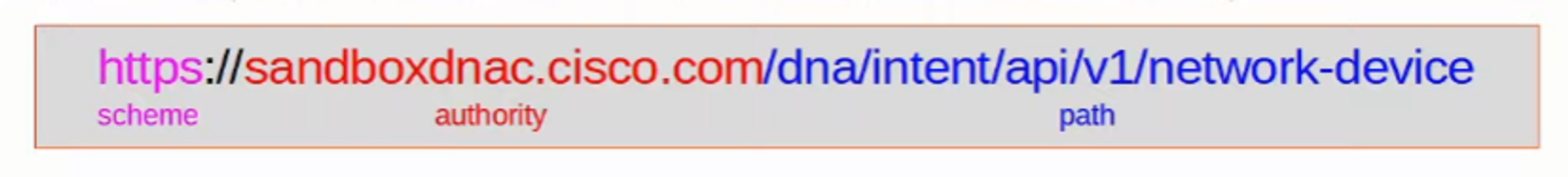
- A URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) indicating the resource it is trying to access

An example of a URI (demonstrated later)
- The HTTP request can include additional headers which pass additional information to the server.
Check the list at https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers

-
An example would be an ACCEPT header, which informs the server about the types(s) of data that can be sent back to the client.
- Example: Accept: application/json or Accept: application/xml
-
You can also view standard HTTP header fields with some examples at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_HTTP_header_fields
-
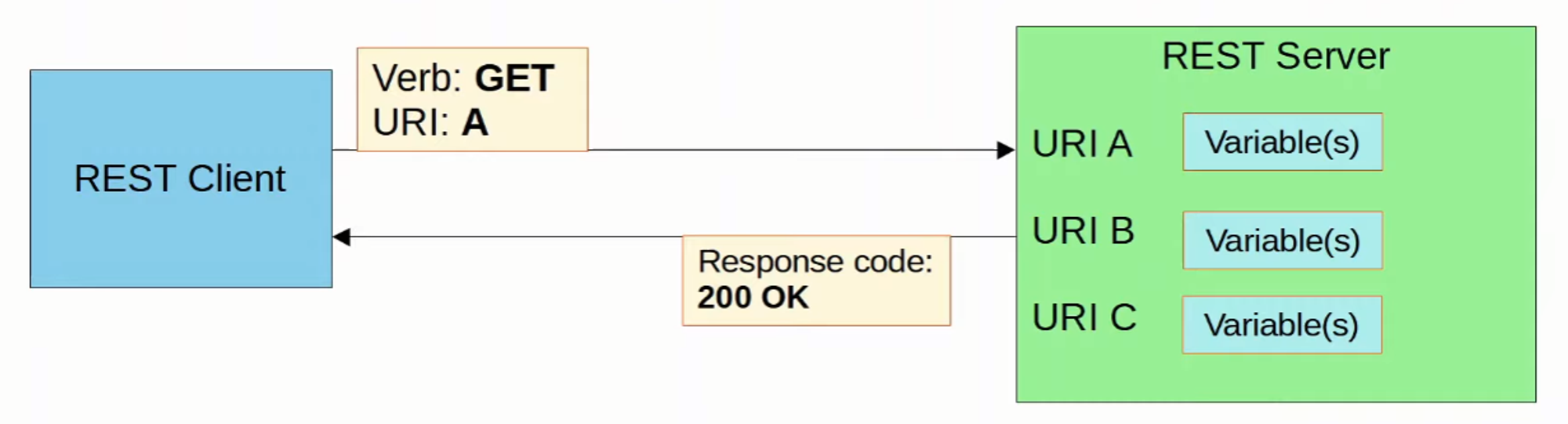
When a REST client makes an API call (request) to a REST server, it will send an HTTP request like the one above
💡 REST APIs do NOT have to use HTTP for communication, although HTTP is the most common choice
HTTP RESPONSE :
- The server’s response will include a STATUS CODE indicating if the request succeeded or failed, as well as other details
- The FIRST digit indicates the class of the response:
- 1xx : Informational - request was received, continuing process
- 2xx : Successful - request was successfully received, understood, and accepted
- 3xx : Redirection - further action needs to be taken in order to complete the request
- 4xx : Client Error - request contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled
- 5xx : Server Error - server failed to fulfill an apparently valid request

Examples of each HTTP Response class:
-
1xx Informational
- 102 Processing indicates that the server received the request and is processing it but the response is not available yet
-
2xx Successful
- 200 OK **indicates that the request succeeded
- 201 Created indicates the request succeeded and a new resource was created
-
3xx Redirection
- 301 Moved Permanently indicates that the request resource has been moved and the server indicates its new location
-
4xx Client Error
- 403 Unauthorized means the client must authenticate to get a response
- 404 Not Found means the requested resource was not found
-
5xx Server Error
- 500 Internal Server Error means the server encountered something unexpected that it doesn’t know how to handle
REST APIs
-
REST stands for Representational State Transfer
-
REST APIs are also know as REST-based APIs or RESTful APIs
- REST isn’t a specific API. Instead it describes a set of rules about how the API should work
-
The SIX constraints of RESTful architecture are:
- Stateless
- Layered system
- Uniform Interface
- Client-Server
- Cacheable or non-cacheable
- Code-on-Demand (optional)
-
For applications to communicate over a network, networking protocols must be used to facilitate those communications
- For REST APIs, HTTP(S) is the most common choice
REST: Client-Server
- REST APIs use a client-server architecture
- The client uses API calls (HTTP requests) to access the resources on the server
- The separation between the client and server means they can both change and evolve independently of each other
- When the client application changes or the server application changes, the interface between them must not break
REST: Stateless
- REST APIs exchanges are STATELESS
- This means that each API exchange is a separate event, independent of all past exchanges between the client and server
- The server does not store information about previous requests from the client to determine how it should respond to new requests
- If authentication is required, this means that the client must authenticate with the server for each request it makes
- TCP is an example of a STATEFUL protocol
- UDP is an example of STATELESS protocol
** Although REST APIs use HTTP, which uses TCP (STATEFUL) as it’s LAYER 4 protocol, HTTP and REST APIs themselves aren’t STATEFUL. The functions of each layer are separate !
REST: Cacheable or Non-Cacheable
- REST APIs must support caching of data
- Caching refers to storing data for future use
- Example :
- Your computer might cache many elements of a web page so it doesn’t have to retrieve the entire page every time you visit. This improves performance for the client and reduces load on the server
- Example :
- Not all resources have to be cacheable but cacheable resources MUST be declared as cacheable
FOR THE CCNA

REST API CALLS USING CISCO DEVNET
-
“Cisco DevNet is Cisco’s developer program to help developers and IT professionals who want to write applications and develop integrations with Cisco products, platforms, and API’s”
-
DevNet offers lots of free resources such as courses, tutorials, labs, sandboxes, documentation, etc to learn about AUTOMATION and develop your skills
-
There is also a DevNet certification track that you can pursue if you are interested in AUTOMATION
-
We will use their Cisco DNA Center Sandbox to send a REST API call using Postman
- DNA Center is one of Cisco’s SDN Controllers (covered in more detail later)
- Postman is a platform for building an using APIs
TO START:
- Make an account on developer.cisco.com (Used my NetAcademy login)
- Make an accounts on postman.com and download the desktop app (https://www.postman.com/downloads) - Used my gmail.com account