DATA SERIALIZATION
-
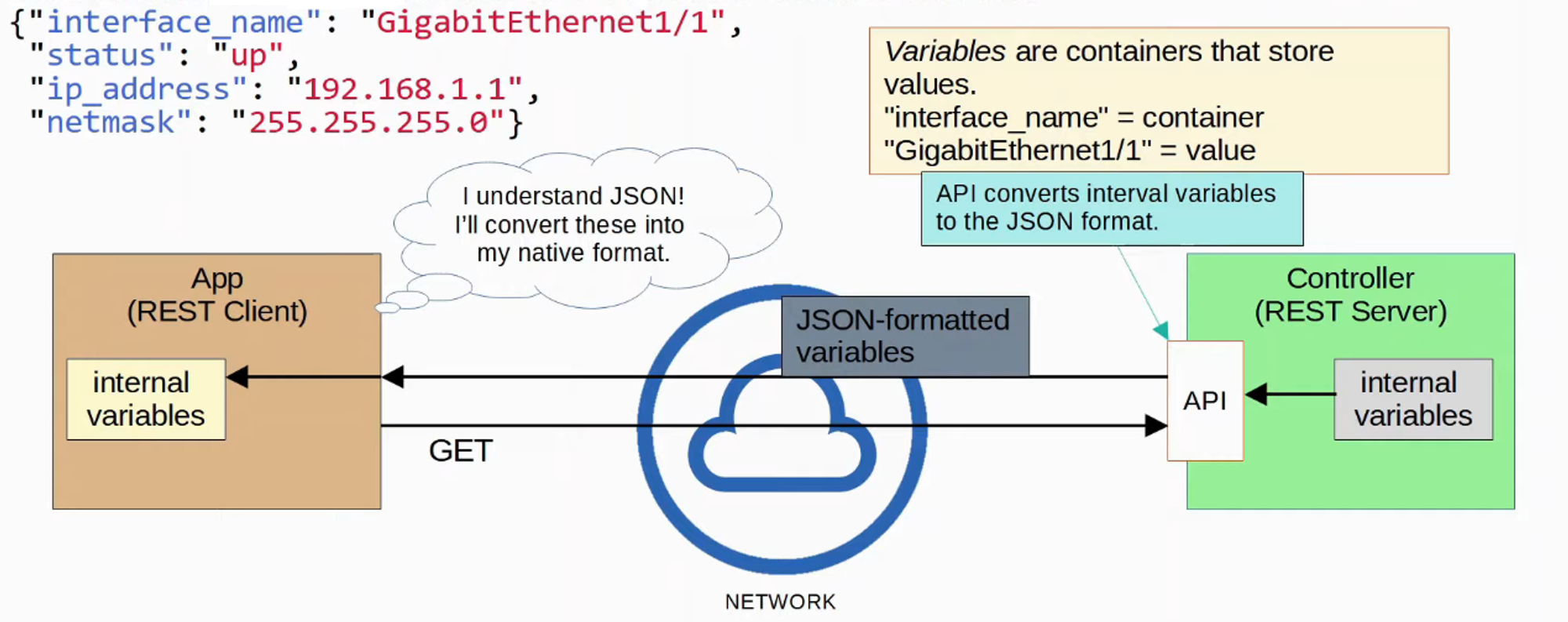
DATA SERIALIZATION is the process of converting DATA into a standardized format/structure that can be stored (in a file) or transmitted (over a network) and reconstructed later (ie: by a different application)
- This allows the DATA to be communicated between applications in a way both APPLICATIONS understand.
-
DATA SERIALIZATION languages allow us to represent variables with text
JSON (JAVASCRIPT OBJECT NOTATION)
-
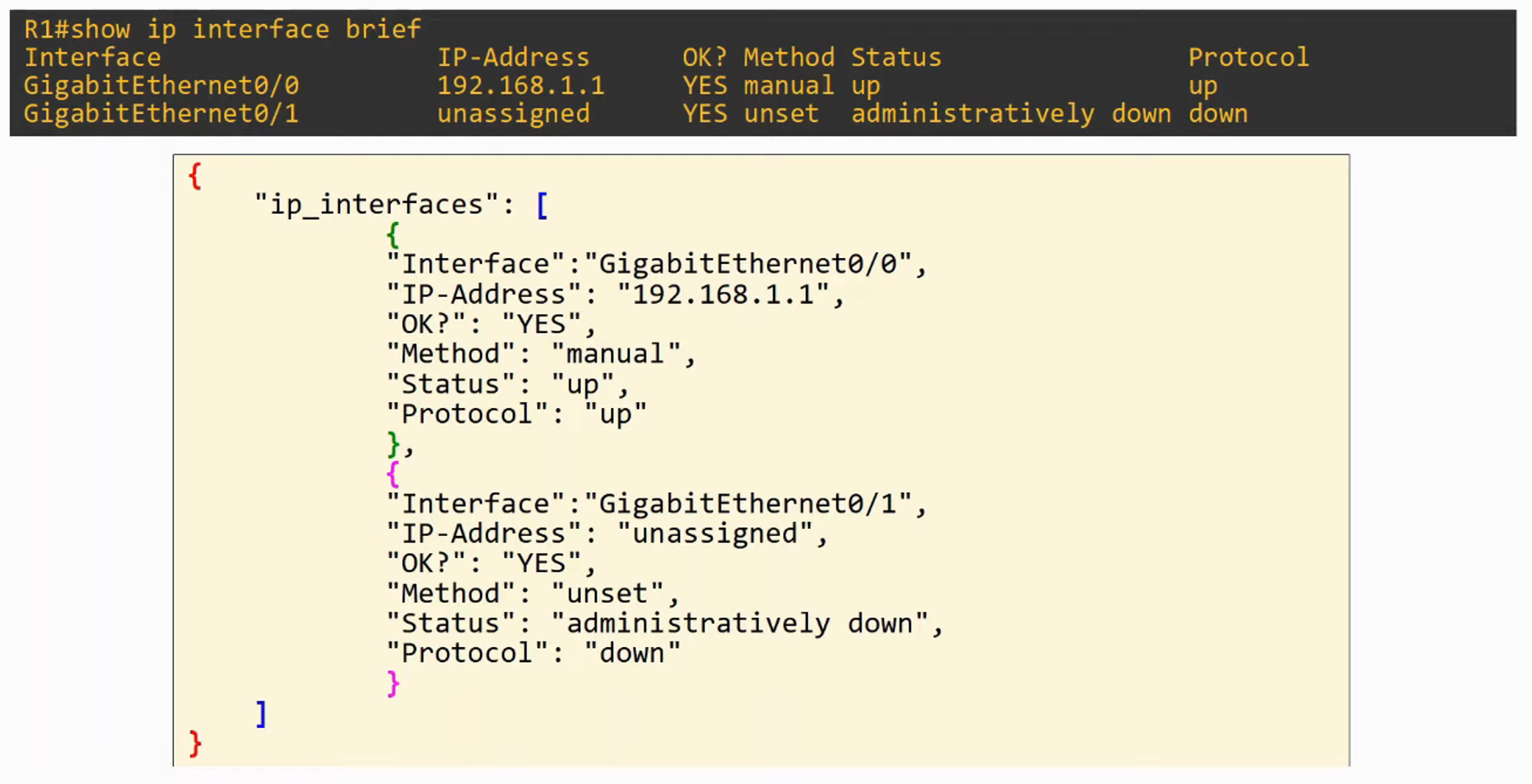
JSON (JAVASCRIPT OBJECT NOTATION) **is an open standard FILE FORMAT and DATA INTERCHANGE FORMAT that uses human-readable text to store and transmit data objects
-
It is standardized in RFC 8259 (https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc8259)
-
It was derived from JavaScript, but it is language-independent and many modern programming languages are able to generate and read JSON data
- REST APIs often use JSON
-
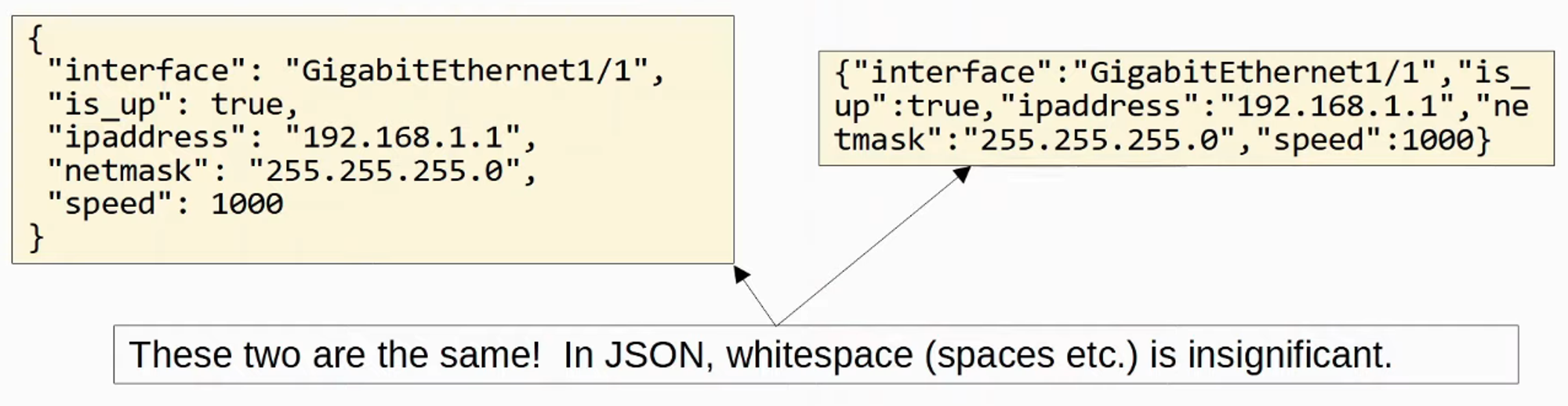
Whitespace is insignificant
-
JSON can represent FOUR “primitive” DATA Types:
- String
- Number
- Boolean
- Null
-
JSON also has TWO “structured” DATA Types:
- Object
- Array
JSON PRIMITIVE DATA TYPES:
-
A STRING is a text value. It is surrounded by double quotes “ “
- “Hello”
- “Five”
- “5”
-
A NUMBER is a numeric value. It is NOT surrounded by quotes
- 5
- 100
-
A BOOLEAN is a DATA Type that has only TWO possible values, not surrounded by quotes
- true
- false
-
A NULL value represents the intentional absence of any object value. It is not surrounded by quotes
- null
JSON STRUCTURED DATA TYPES:
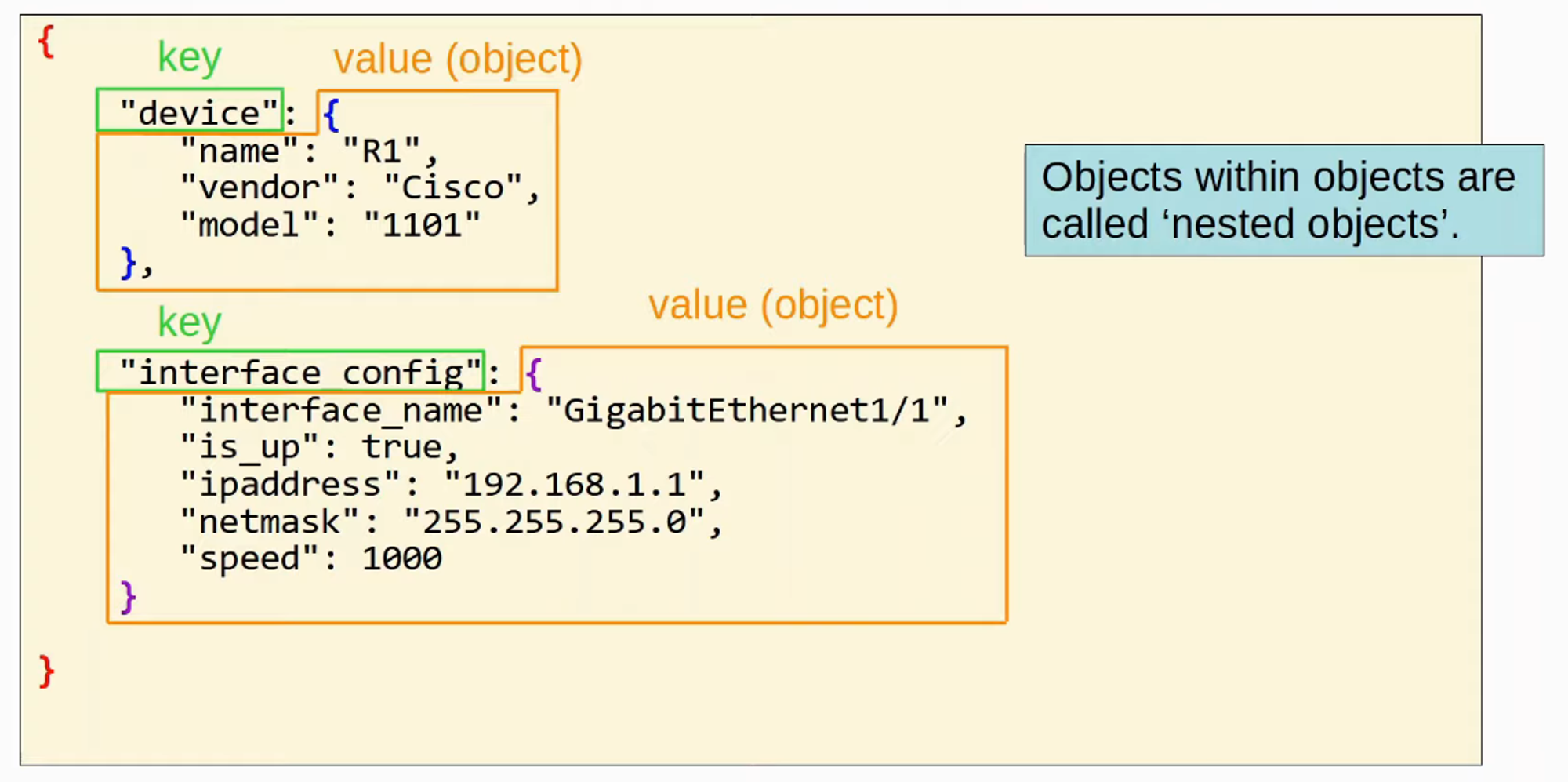
- An OBJECT is an unordered list of key-value pairs (variables)
- Sometimes called a DICTIONARY
- OBJECTS are surrounded by curly brackets {}
- The key is a STRING
- The value is any valid JSON DATA Type (string, number, boolean, null, object, array)
- The key and value are separated by a colon :
- If there are multiple key-value pairs, each pair is separated by a comma

- An ARRAY is a series of values separated by commas
- Not key-value pairs
- The values do NOT have to be the same DATA Type

XML (EXTENSIBLE MARKUP LANGUAGE)
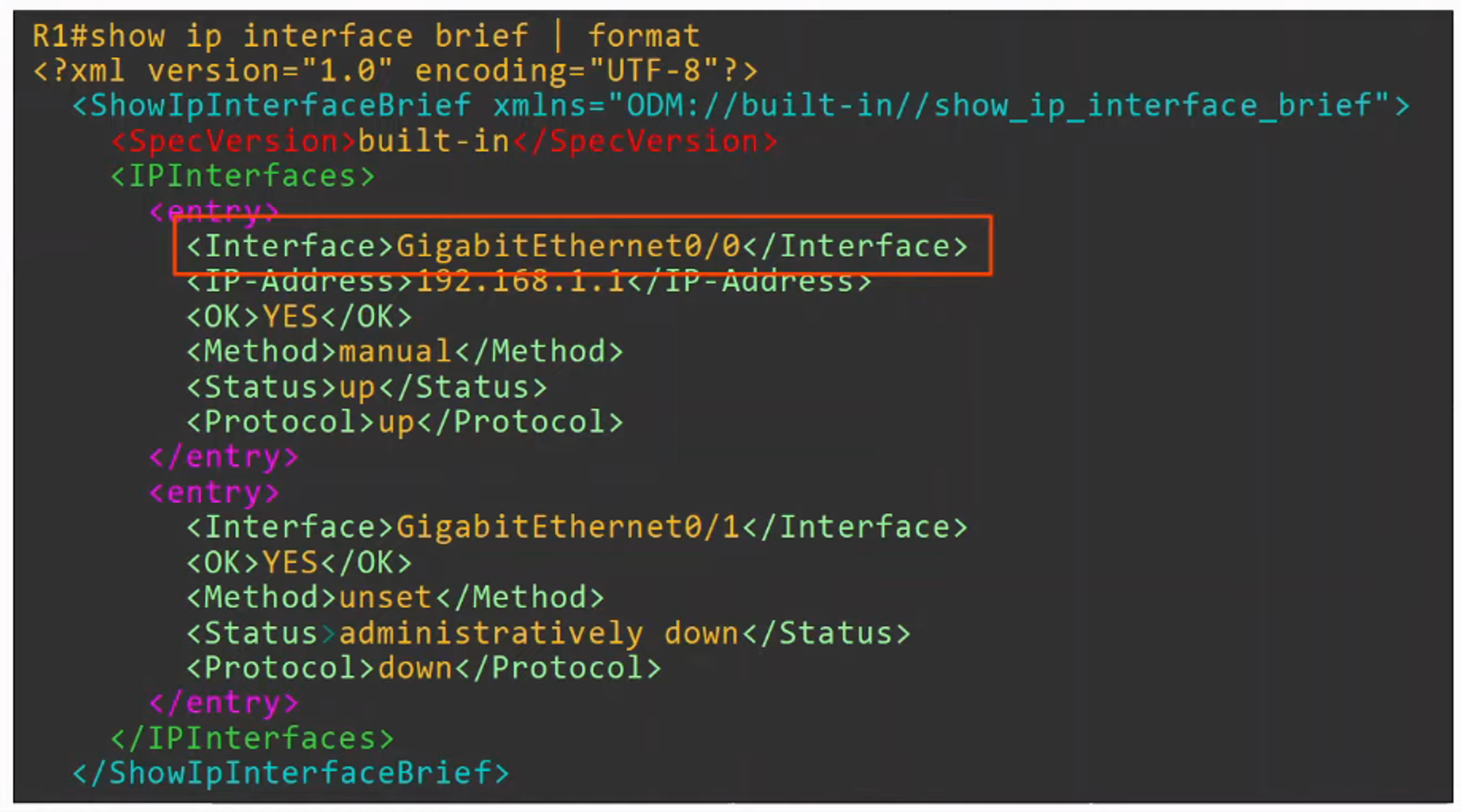
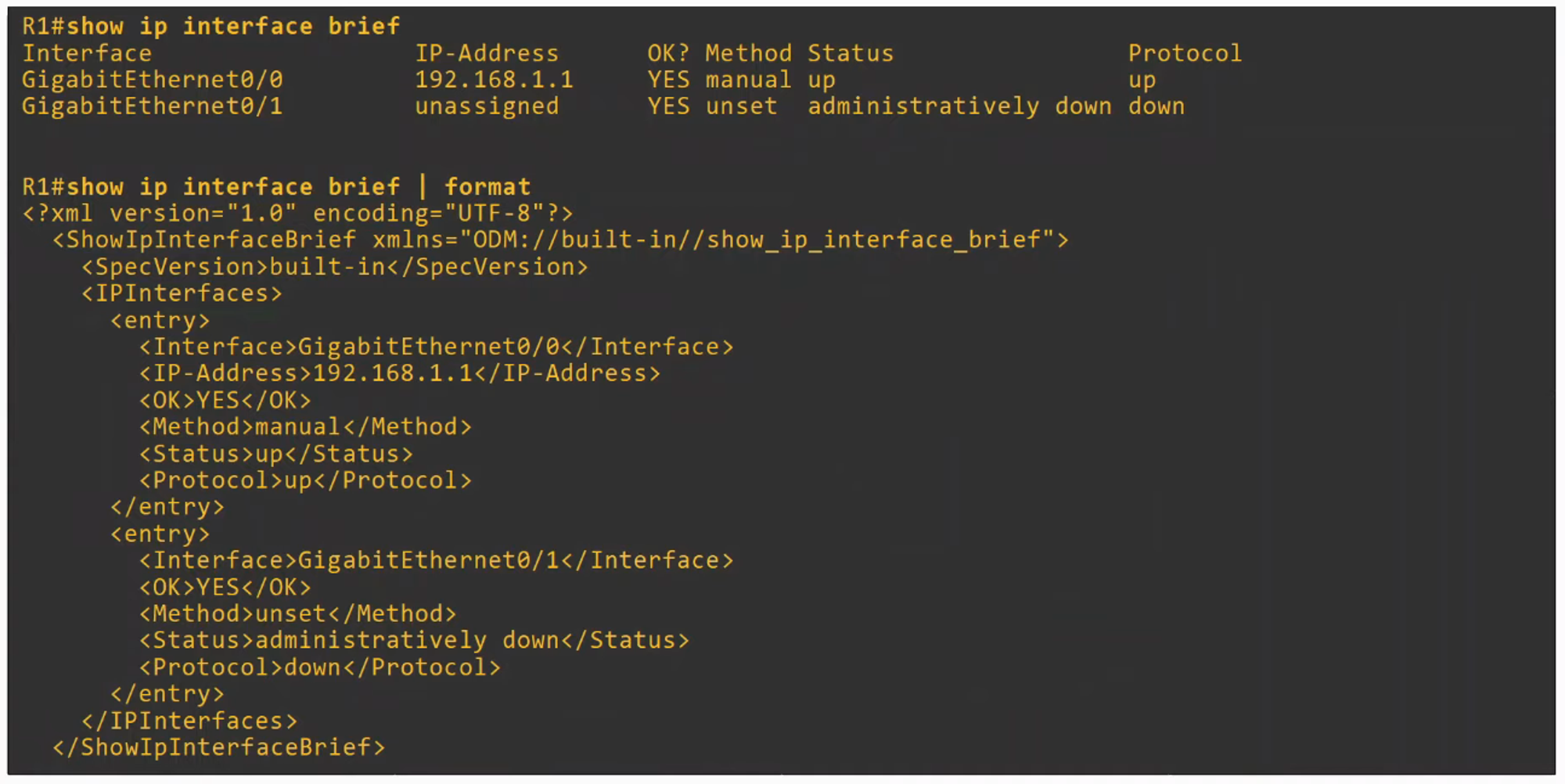
- XML (EXTENSIBLE MARKUP LANGUAGE) was developed as a MARKUP language, but is now used as a general data serialization language
- Markup languages (ie: HTML) are used to format text (font, size, color, headings, etc)
- XML is generally less human-readable than JSON
- Whitespace is insignificant
- Often used by REST APIs
value (similar to HTML)
YAML (YAML AIN’T MARKUP LANGUAGE)
- YAML originally meant YET ANOTHER MARKUP LANGUAGE but to distinguish its purpose as a data-serialization language rather than a markup language, it was repurposed to YAML AINT MARKUP LANGUAGE
- YAML is used by the network automation tool ANSIBLE (covered later in the course)
- YAML is VERY Human-Readable
- Whitespace is significant (unlike JSON and XML)
- Indentation is very important
- YAML files start with - - - (three dashes)
-
- is used to indicate a list
- Keys and Values are represented as key : value
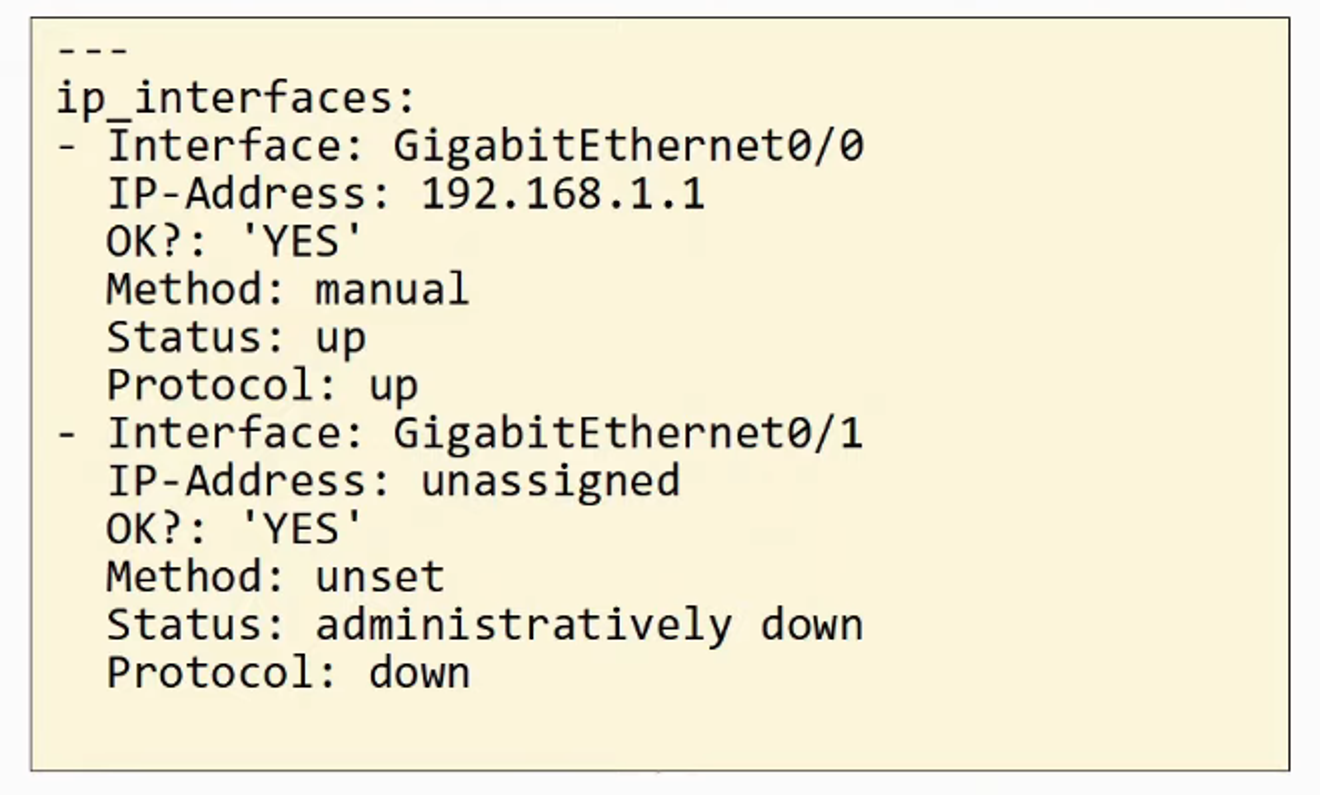
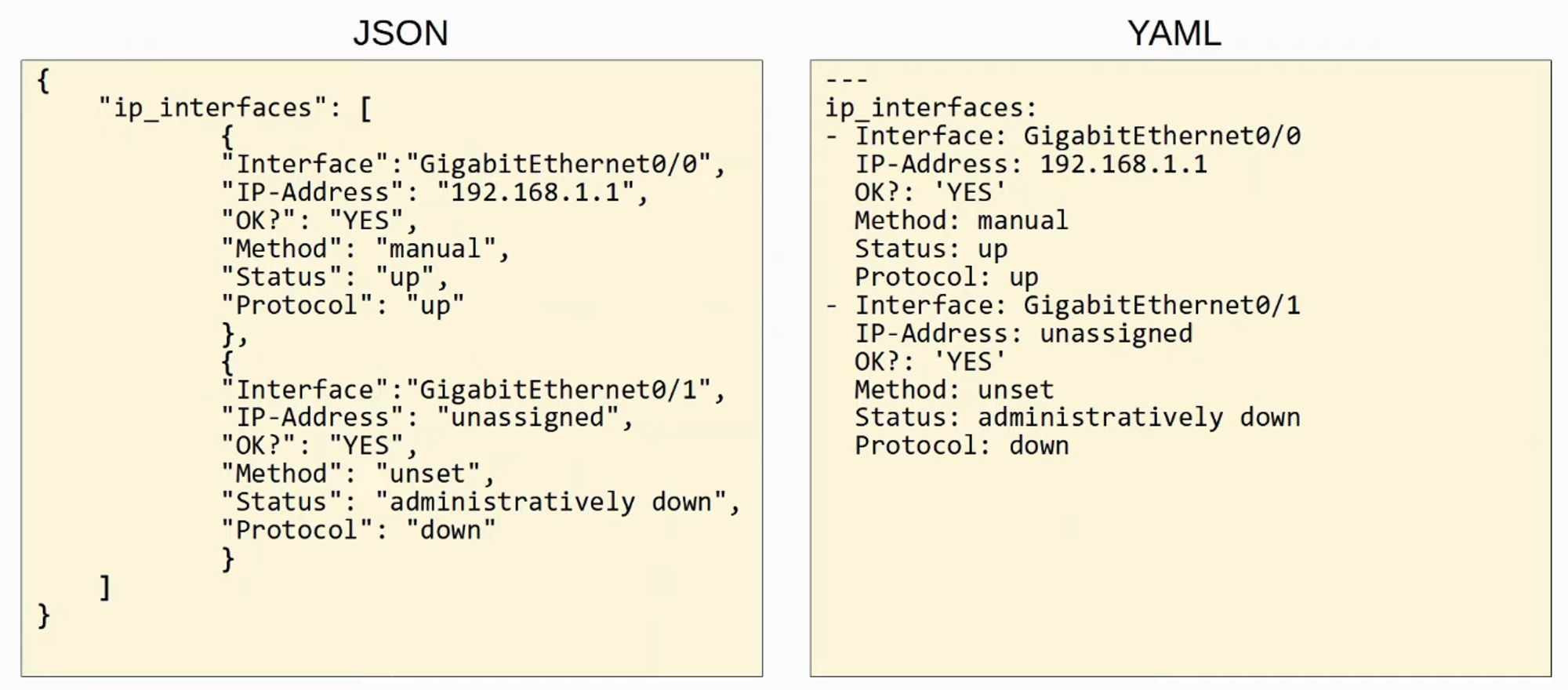
COMPARISON BETWEEN JSON and YAML using the same DATA