What is Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI)?
ARP Review
- ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is used to learn the MAC address of another device when its IP address is known.
- Example: A PC utilizes ARP to determine the MAC address of its default gateway for communication with external networks.
- ARP typically consists of a two-message exchange:
- ARP Request: Sent to inquire about a device’s MAC address.
- ARP Reply: Response that provides the requested MAC address.
Gratuitous ARP (GARP)
- A Gratuitous ARP message is an ARP reply sent without an accompanying ARP request.
- It is broadcasted to the broadcast MAC address.
- Purpose:
- Allows other devices on the network to learn the MAC address of the sending device without needing to send ARP requests.
- Some devices automatically send GARP messages when:
- An interface is enabled.
- An IP address is changed.
- A MAC address is changed.
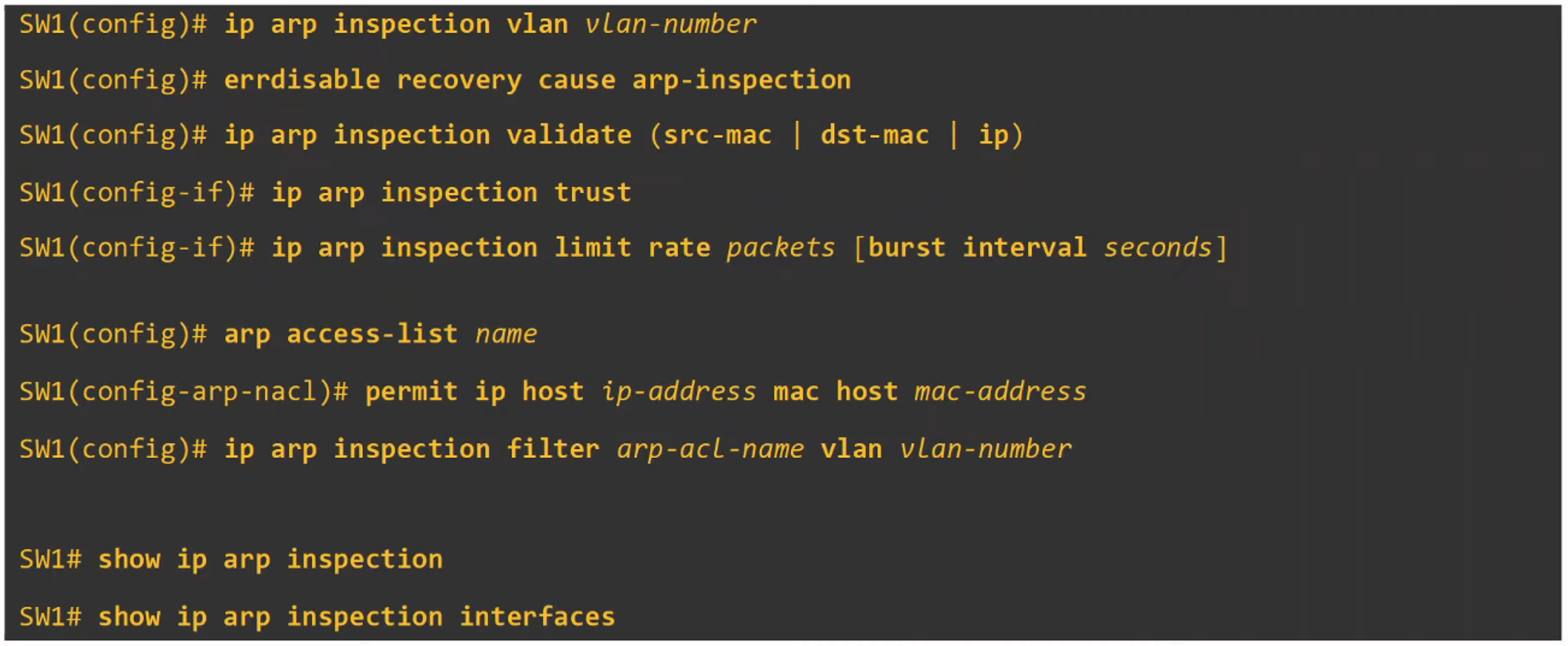
Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI)
- DAI is a security feature on switches that filters ARP messages received on untrusted ports.
- It only filters ARP messages; non-ARP messages are not affected.
- By default, all ports are considered untrusted.
- Typically, ports connected to network devices (e.g., switches, routers) should be configured as trusted, while interfaces connected to end hosts should remain untrusted.
ARP Poisoning (Man-in-the-Middle Attack)
- Similar to DHCP poisoning, ARP poisoning involves an attacker manipulating the target’s ARP tables, redirecting traffic to themselves.
- To execute this, the attacker can send gratuitous ARP messages using the IP address of another device.
- Other devices in the network receive the GARP, leading them to update their ARP tables, which results in sending traffic to the attacker instead of the legitimate destination.
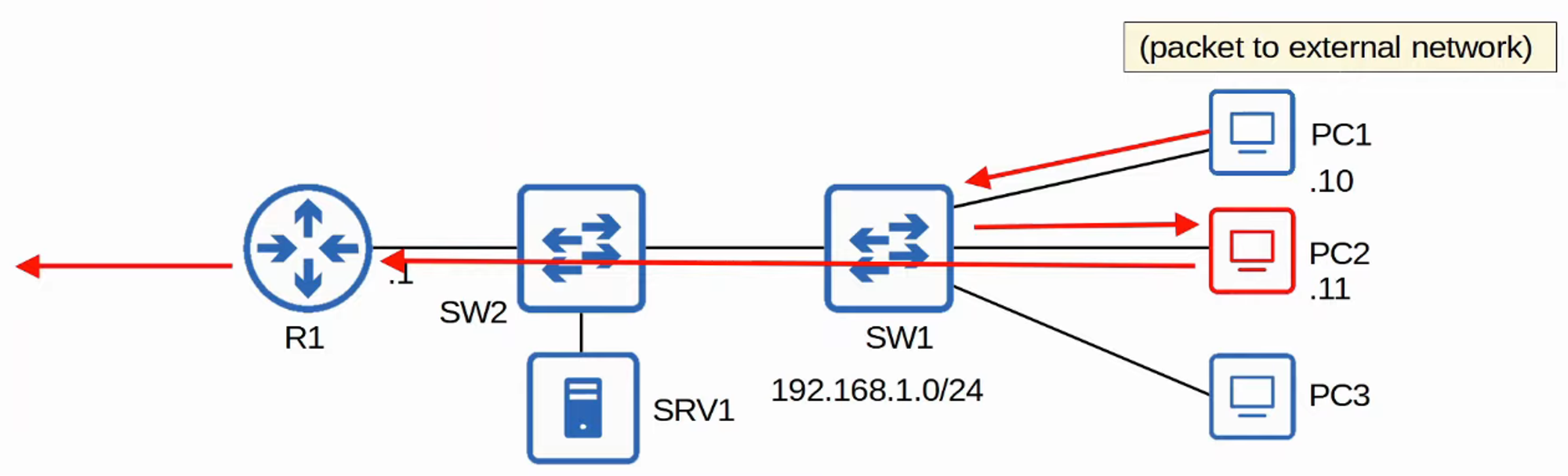
DAI Operations
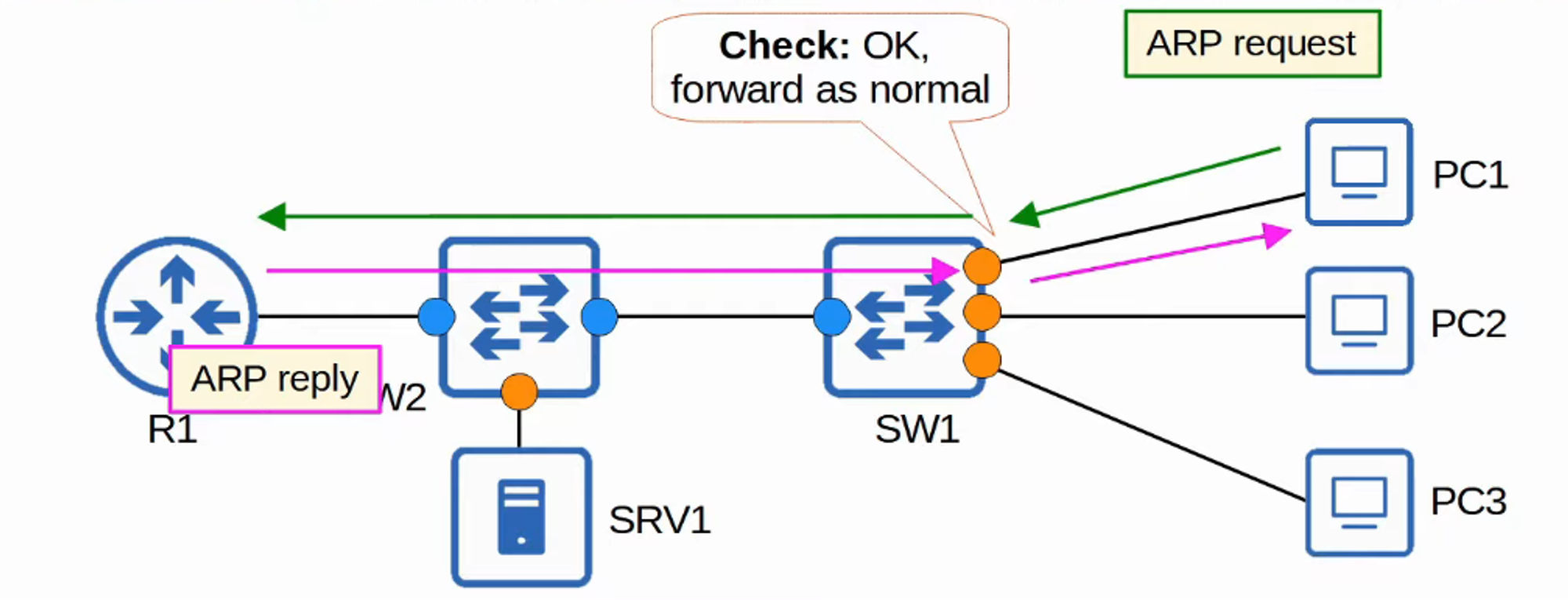
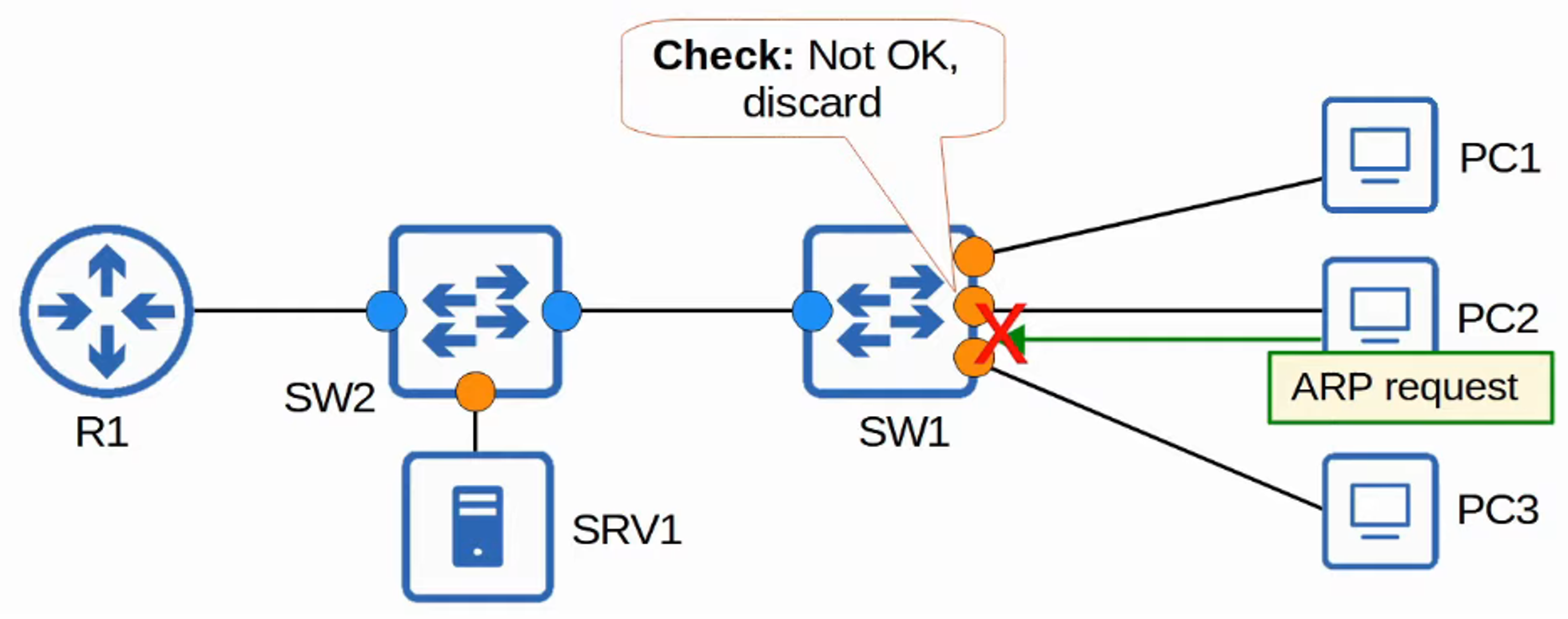
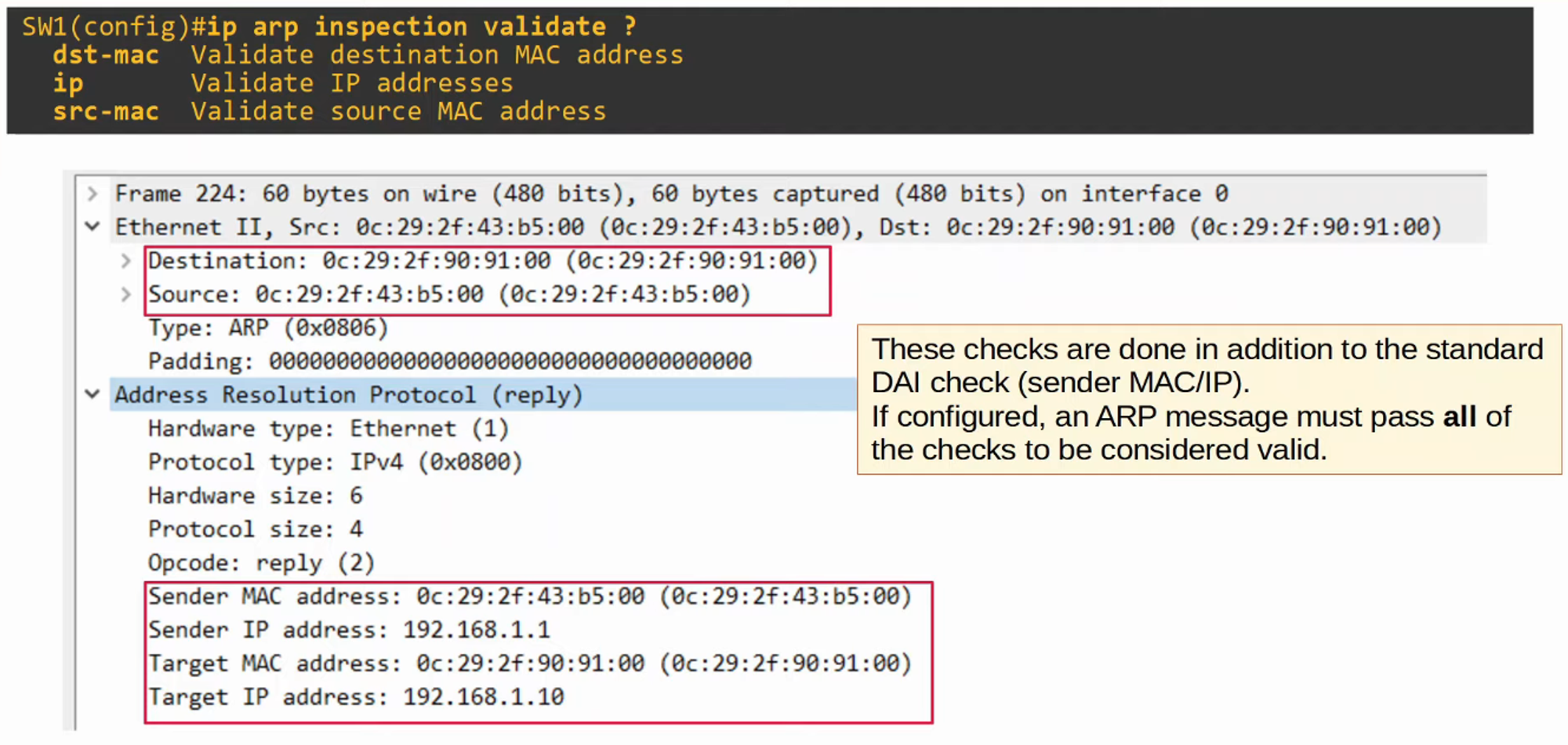
- DAI inspects the Sender MAC and Sender IP fields of ARP messages received on untrusted ports and checks for a matching entry in the DHCP Snooping Binding Table.
- If there is a match, the ARP message is forwarded.
- If there is no match, the ARP message is discarded.
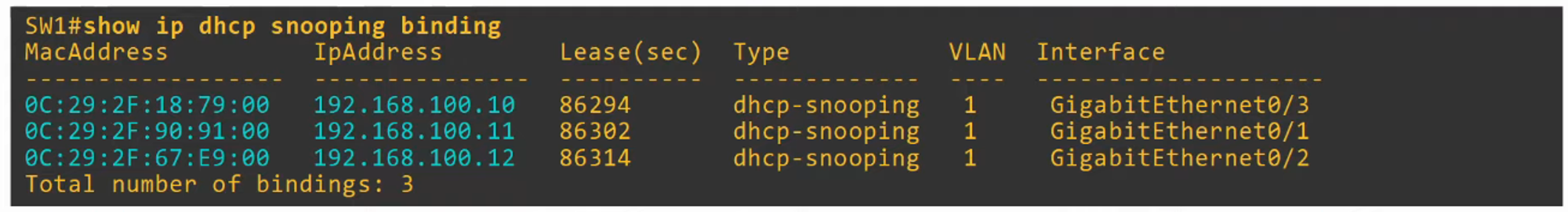
- DAI does not inspect messages received on trusted ports; they are forwarded normally.
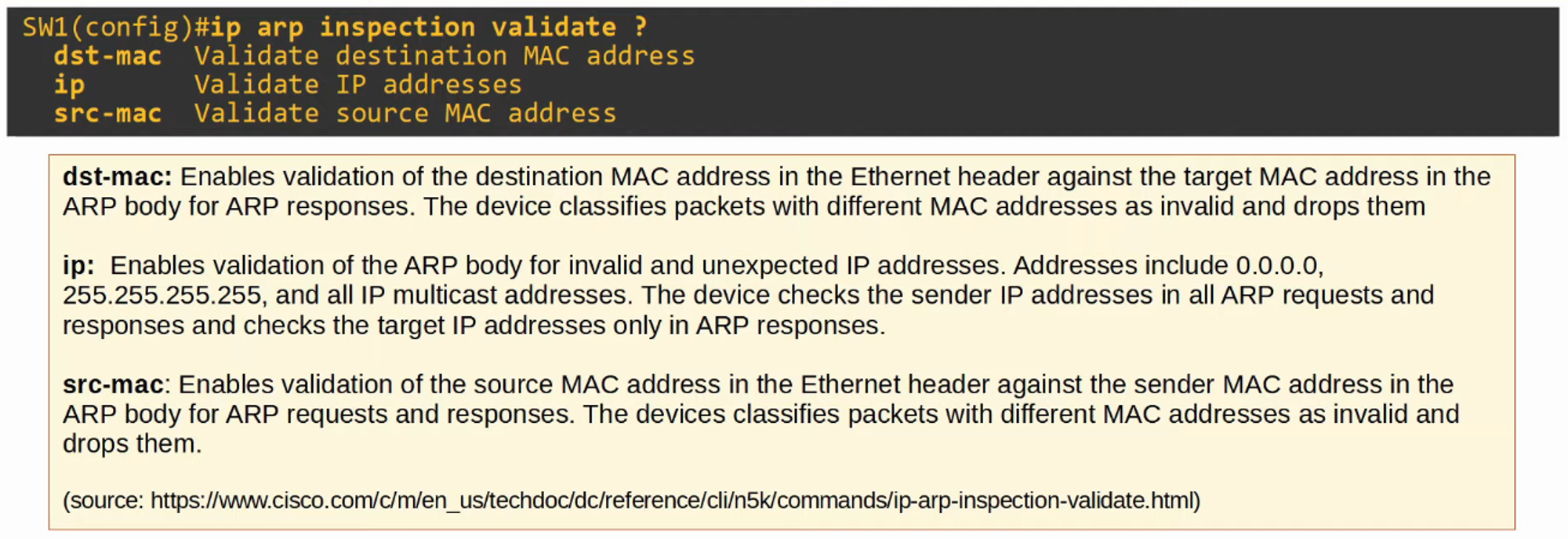
- ARP ACLs (Access Control Lists) can be manually configured to map specific IP addresses to MAC addresses for DAI to check.
- This is useful for hosts that do not use DHCP.
- DAI can also be configured for more in-depth checks, although these are optional.
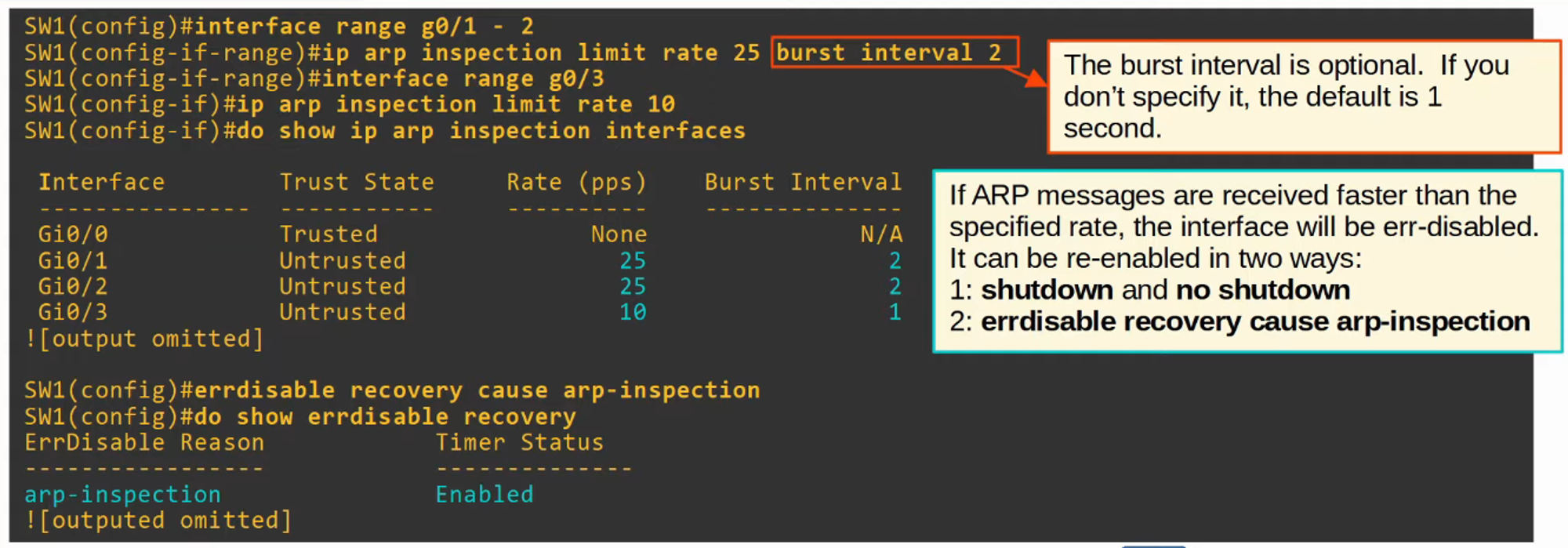
- Similar to DHCP Snooping, DAI supports rate-limiting to prevent attackers from overwhelming the switch with ARP messages.
- Both DHCP Snooping and DAI require processing power from the switch’s CPU.
- Even if the attacker’s messages are blocked, they can still overload the switch’s CPU with ARP messages.
Dynamic ARP Inspection Configuration
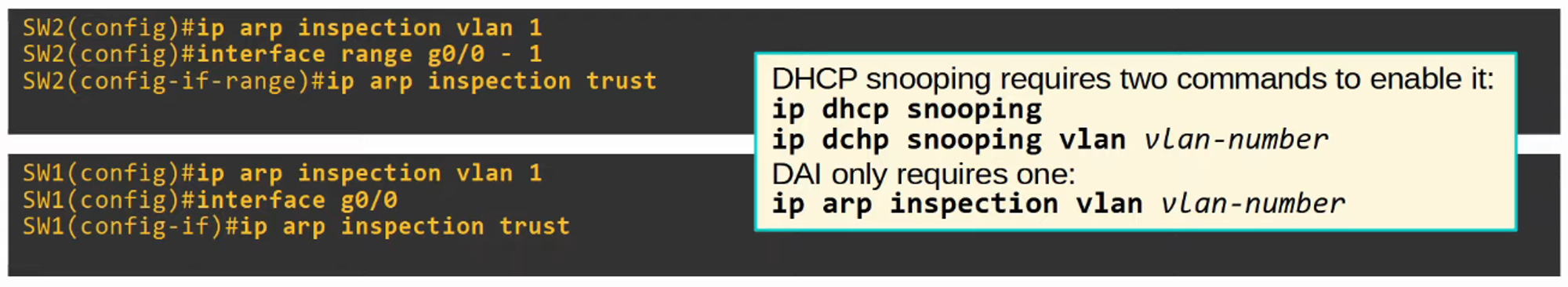
Command:
show ip arp inspection interfaces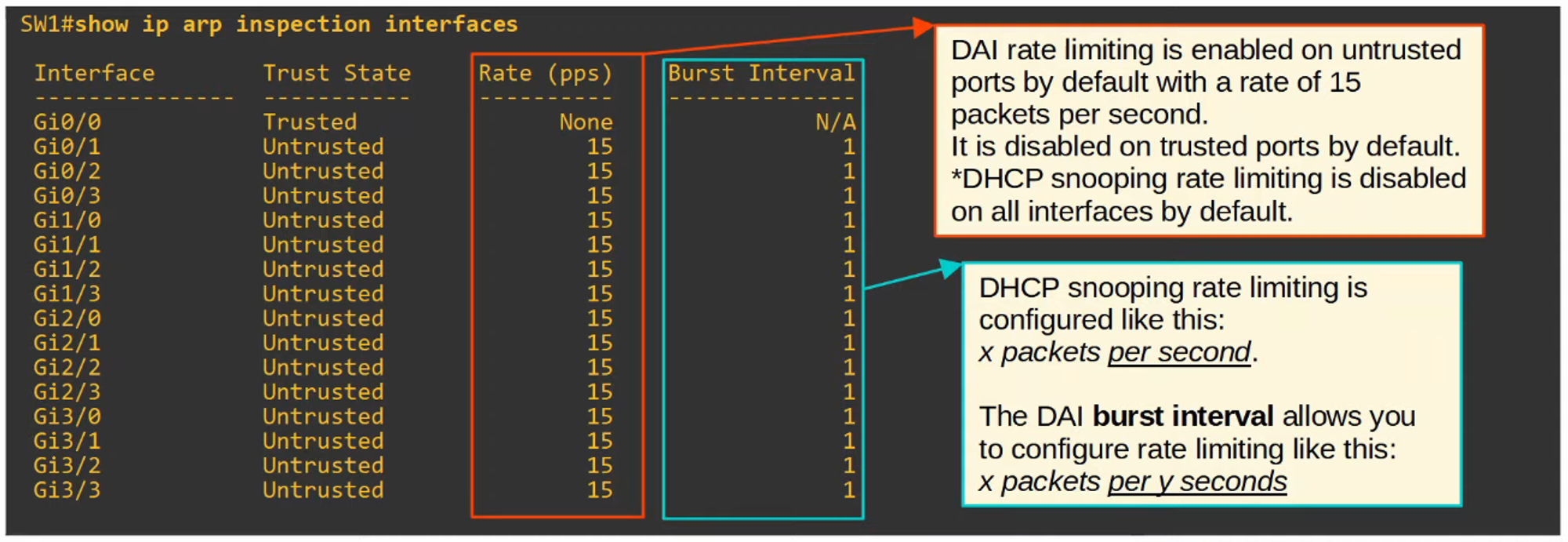
DAI Rate Limiting
DAI Optional Checks
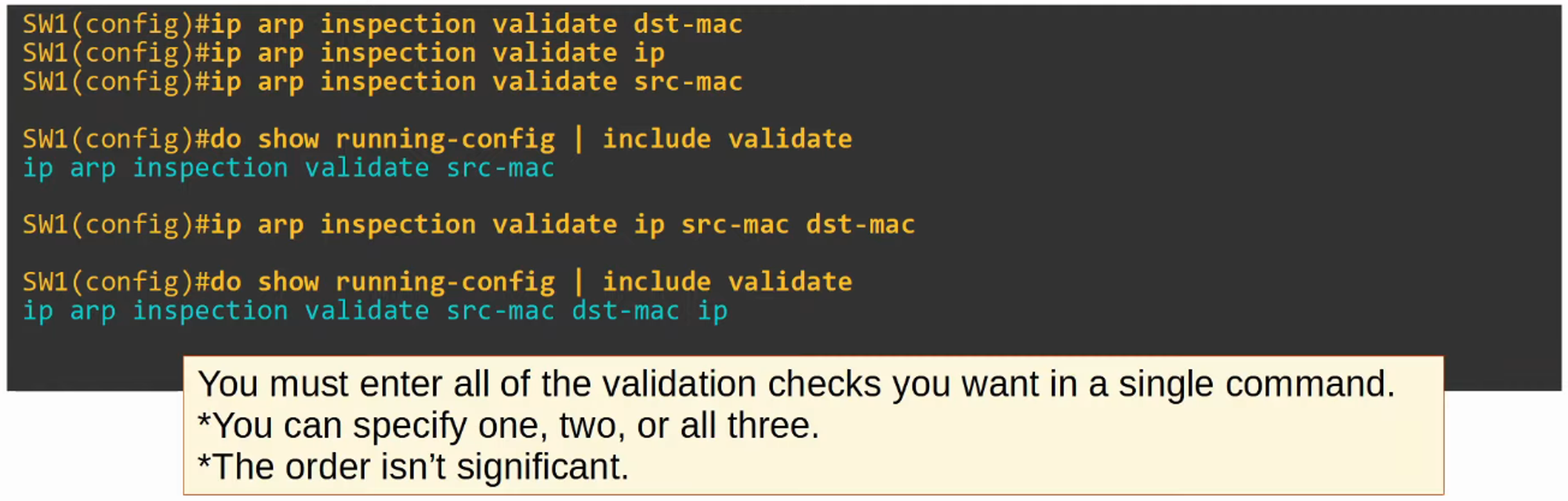
ARP ACLs (Advanced Topic Beyond CCNA Scope)
Create an ARP ACL for SRV1
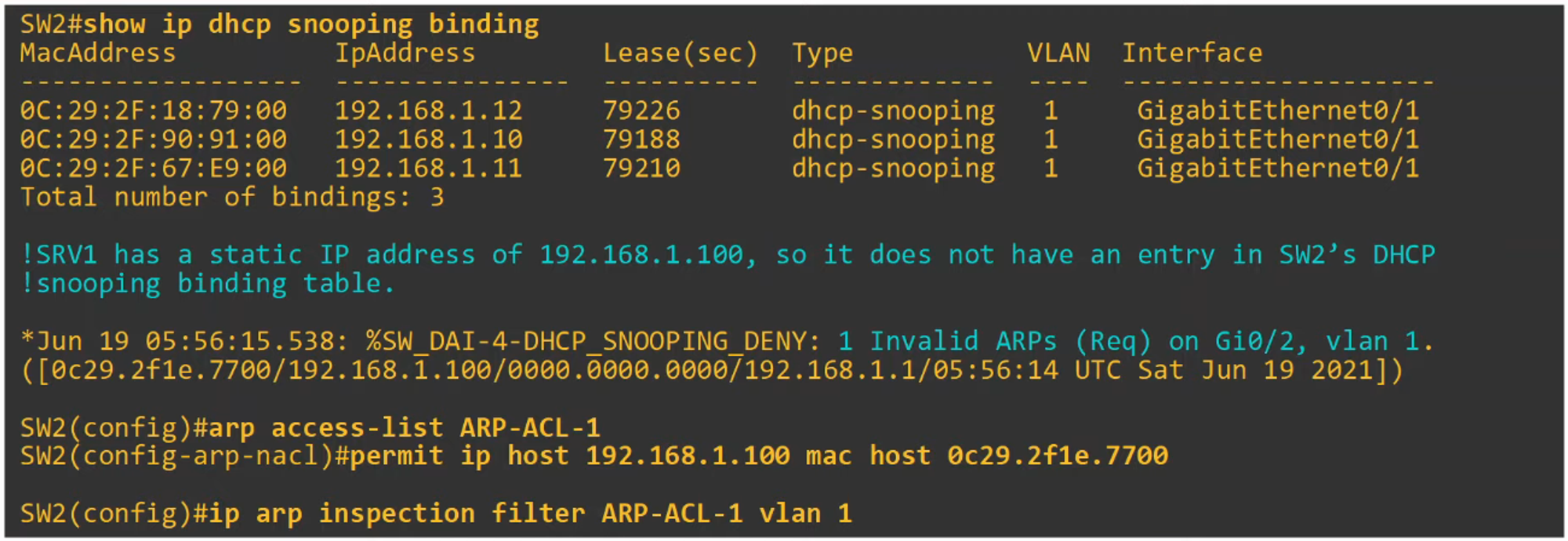
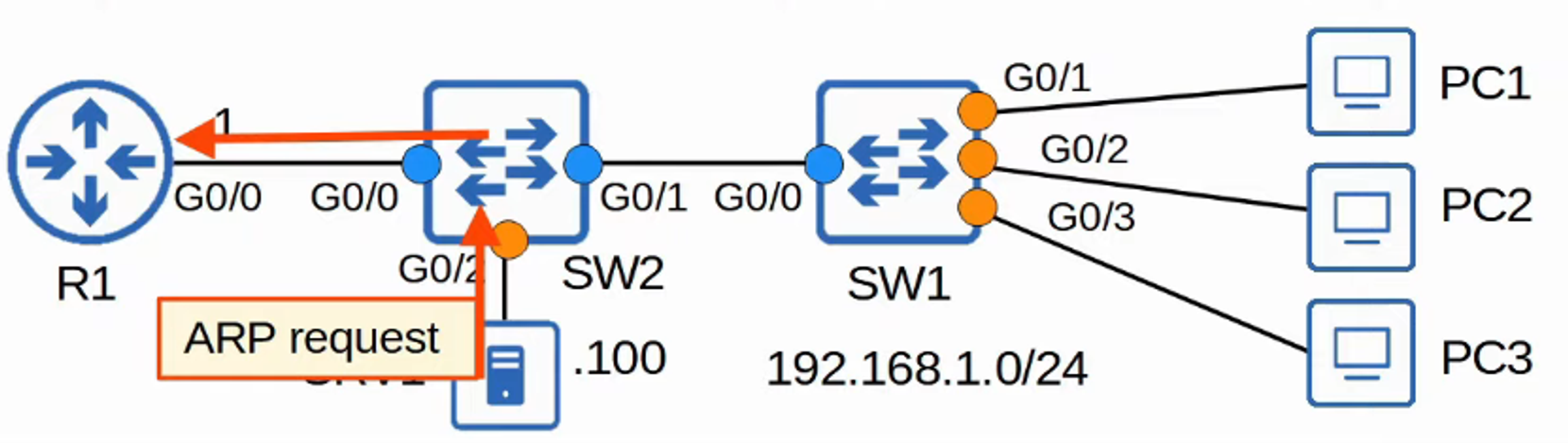
After applying it to Switch 2, SRV1 can successfully send an ARP request to R1.
Command:
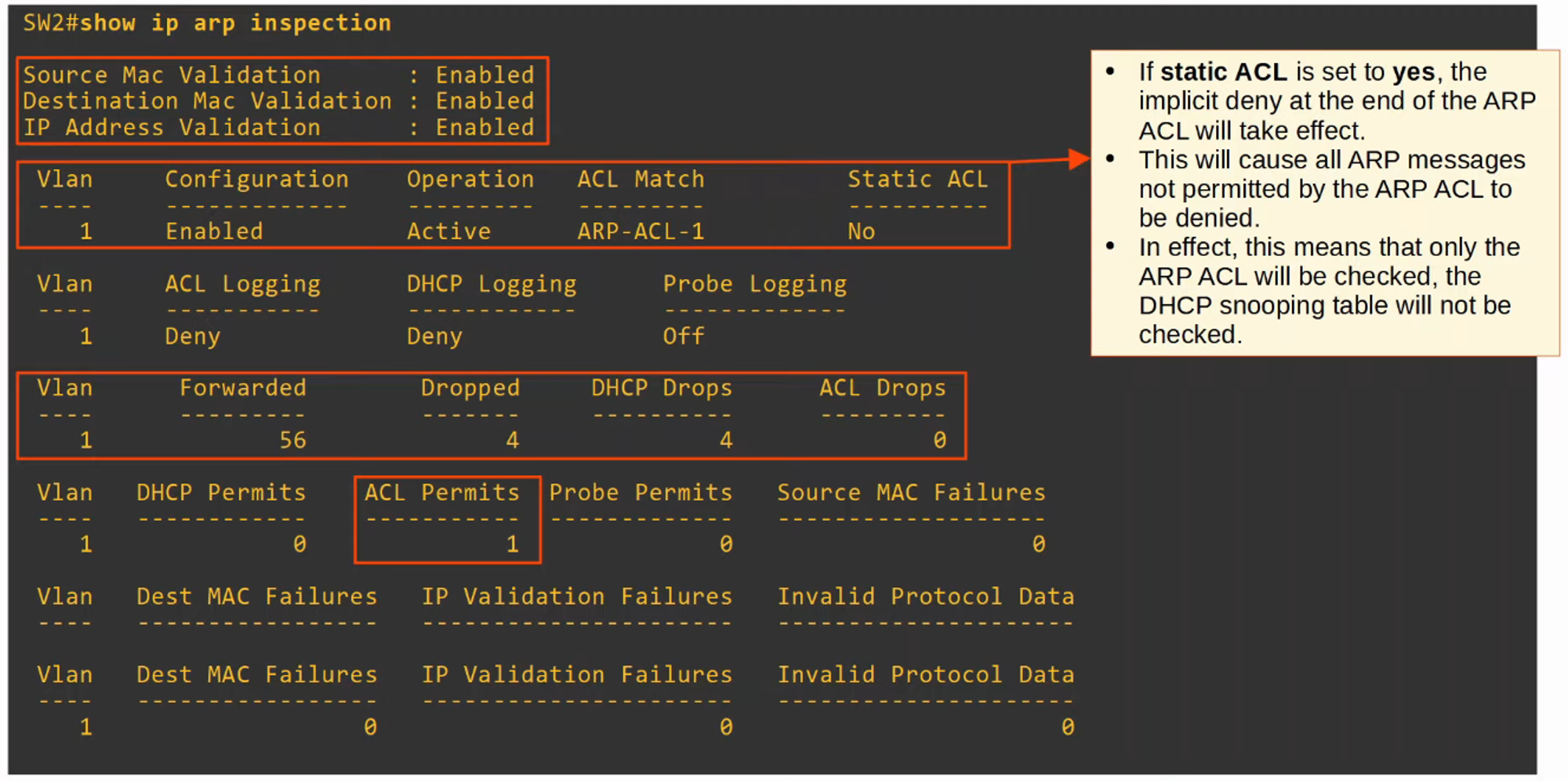
show ip arp inspectionThis command displays a summary of the DAI configuration and statistics.
Command Review