What is DHCP Snooping?
- DHCP Snooping is a security feature found in network switches, used to filter DHCP messages received on untrusted ports. This helps prevent malicious or rogue DHCP servers from distributing IP addresses within the network.
- DHCP Snooping only inspects DHCP messages; non-DHCP traffic is not affected.
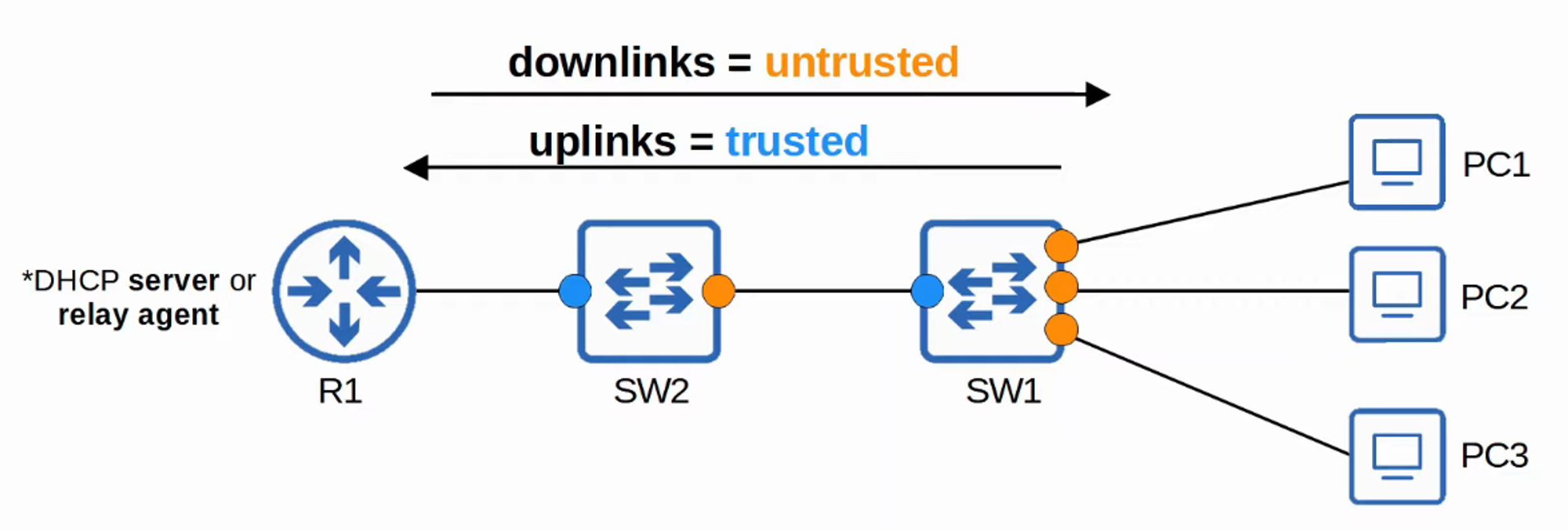
- By default, all ports are considered untrusted.
- Typically, uplink ports (those connecting to other trusted network devices) are configured as trusted, while downlink ports (those connecting to end-user devices) remain untrusted.
Attacks on DHCP
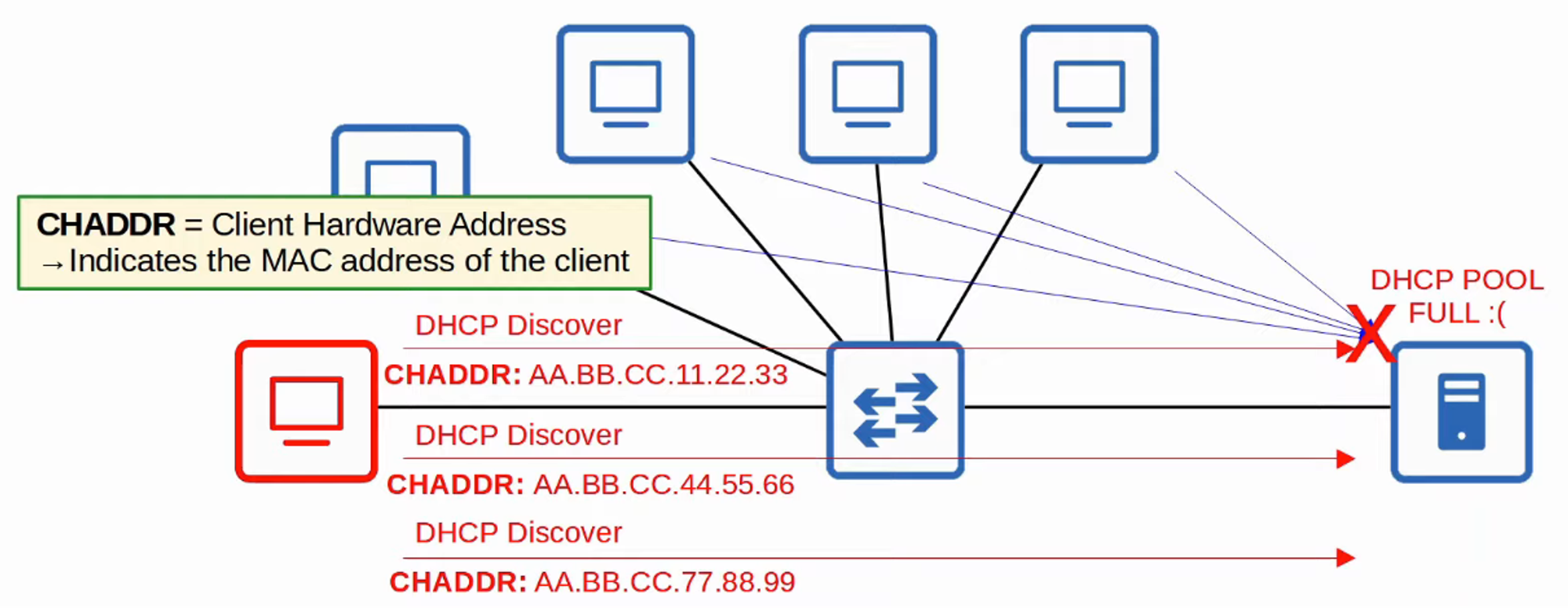
DHCP Starvation Attack
- In a DHCP Starvation Attack, an attacker floods the network with DHCP Discover messages using spoofed MAC addresses.
- This exhausts the available IP addresses in the DHCP server’s pool, leading to a Denial of Service (DoS) for legitimate devices trying to obtain an IP address.
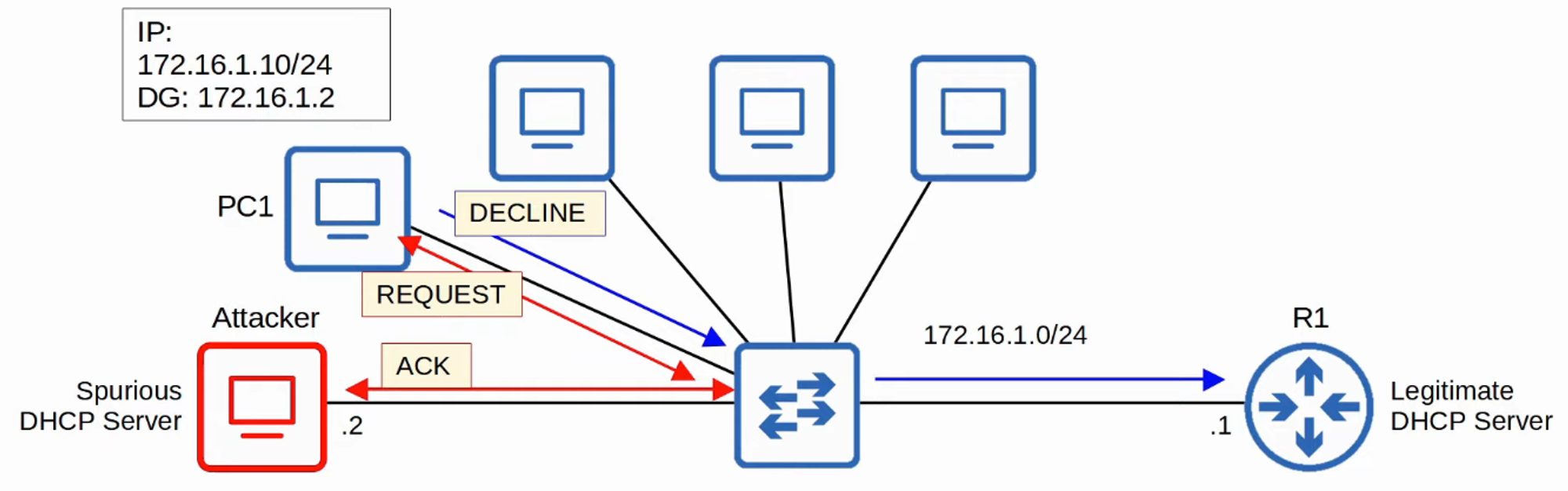
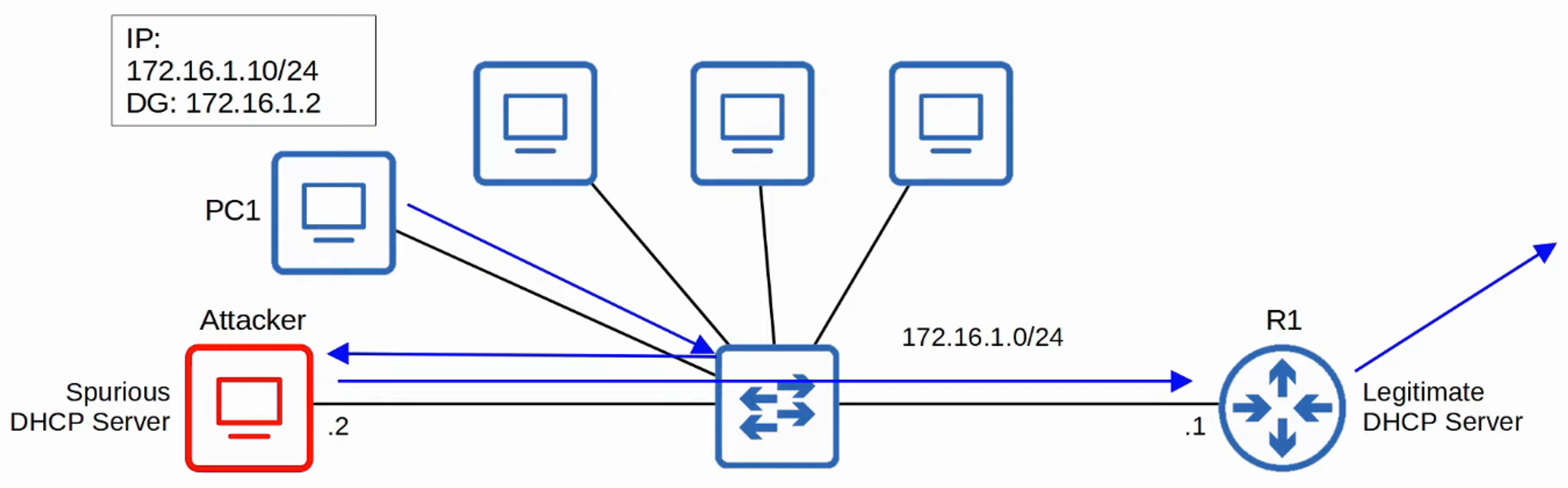
DHCP Poisoning (Man-in-the-Middle Attack)
- Similar to ARP Poisoning, a DHCP Poisoning attack allows an attacker to set up a rogue DHCP server.
- The rogue server responds to DHCP Discover messages, assigning the client an IP address with the attacker’s IP as the default gateway.
- As a result, the client sends all traffic to the attacker, enabling them to intercept or modify the traffic before forwarding it to the legitimate destination.
DHCP Messages
DHCP Snooping filters messages by identifying whether they originate from DHCP servers or clients:
-
DHCP Server Messages:
- OFFER: Server offers an IP address to a client.
- ACK: Server acknowledges the client’s request and assigns the IP.
- NAK: The server declines the client’s request for an IP (opposite of ACK).
-
DHCP Client Messages:
- DISCOVER: Client broadcasts a request to find available DHCP servers.
- REQUEST: Client requests the offered IP address from a server.
- RELEASE: Client informs the server it no longer needs the IP address.
- DECLINE: Client rejects an IP address offered by a server.
How Does DHCP Snooping Work?
-
Trusted Ports:
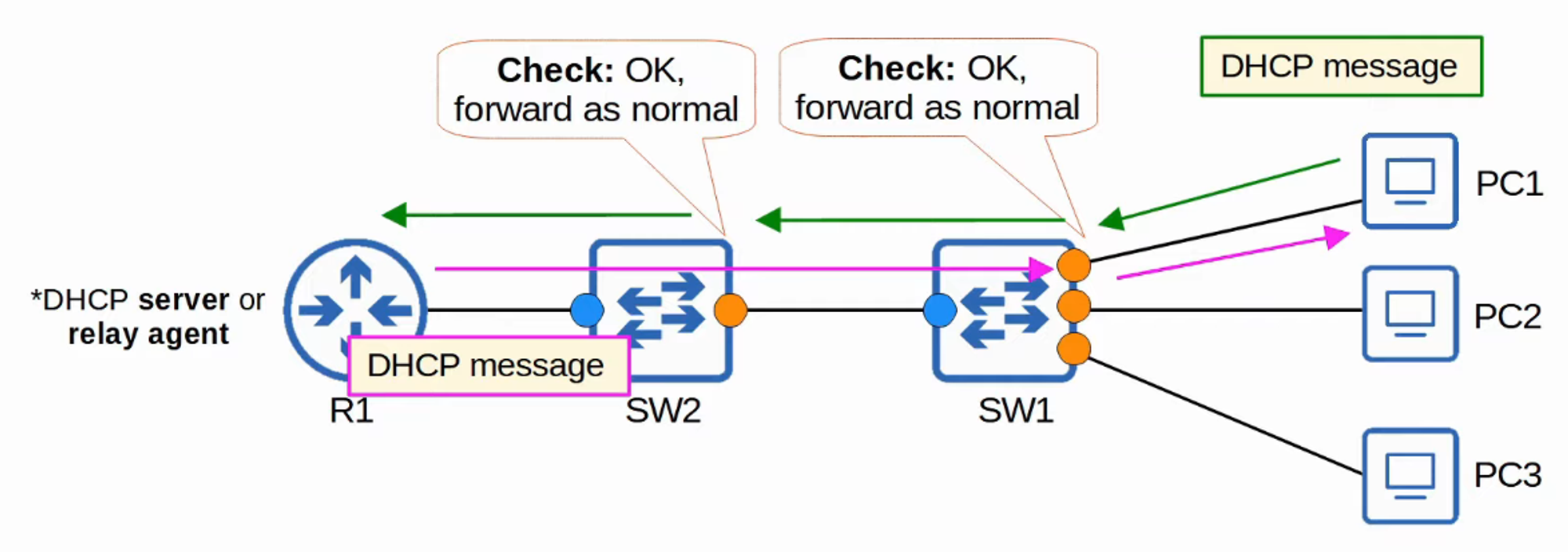
- If a DHCP message is received on a trusted port, the switch forwards the message without inspection.
-
Untrusted Ports:
- If a DHCP message is received on an untrusted port, the switch performs additional checks:
- DHCP Server Messages are discarded.
- DHCP Client Messages undergo these verifications:
- DISCOVER/REQUEST Messages:
Ensure the source MAC address in the Ethernet frame matches theCHADDRfield in the DHCP message.- Match: Forward the message.
- Mismatch: Discard the message.
- RELEASE/DECLINE Messages:
Check if the packet’s source IP and the receiving interface match the entry in the DHCP Snooping Binding Table.- Match: Forward the message.
- Mismatch: Discard the message.
- DISCOVER/REQUEST Messages:
- If a DHCP message is received on an untrusted port, the switch performs additional checks:
-
When a client successfully leases an IP address, an entry is created in the DHCP Snooping Binding Table.
DHCP Snooping Configuration
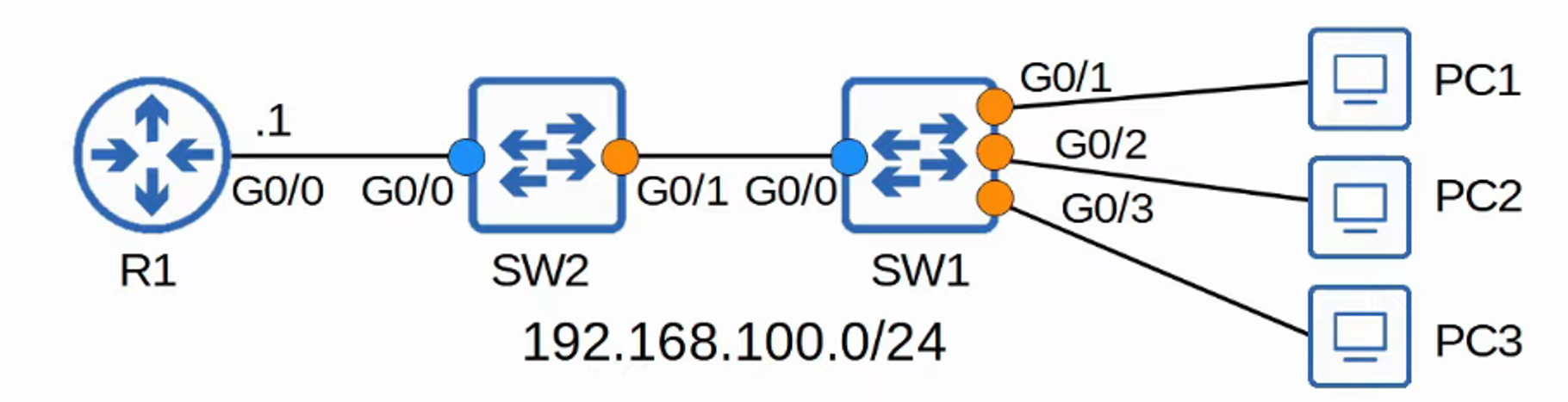
Switch 2 Configuration

Switch 1 Configuration

DHCP Snooping Rate-Limiting
- DHCP Snooping can also limit the rate at which DHCP messages are allowed to enter an interface. This prevents attacks that flood the network with DHCP traffic.
- If the message rate exceeds the configured limit, the interface is placed into an
err-disabledstate, much like in Port Security. - The interface can be re-enabled manually or configured to recover automatically using
errdisable recovery.
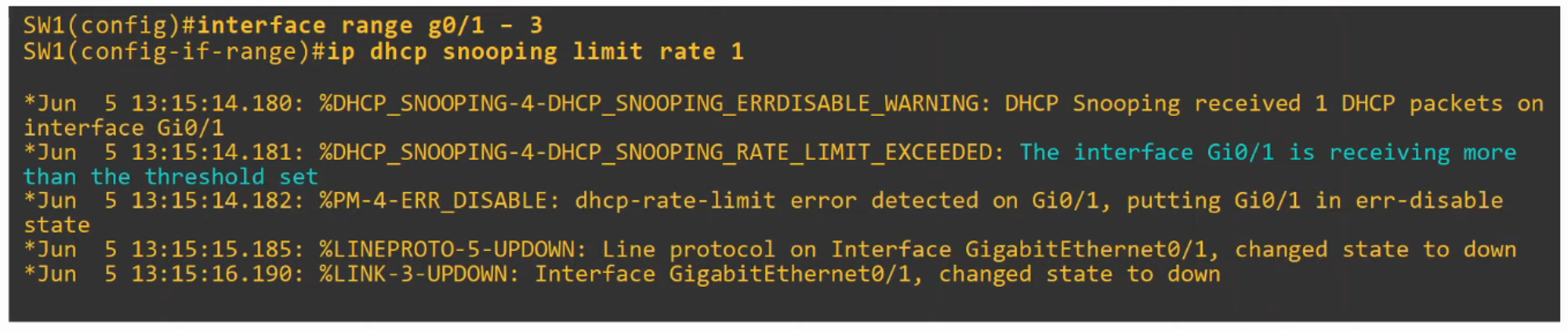
- For example, setting the limit rate to 1 would immediately shut down the port because a single DHCP message would trigger the limit, which demonstrates how rate-limiting works.
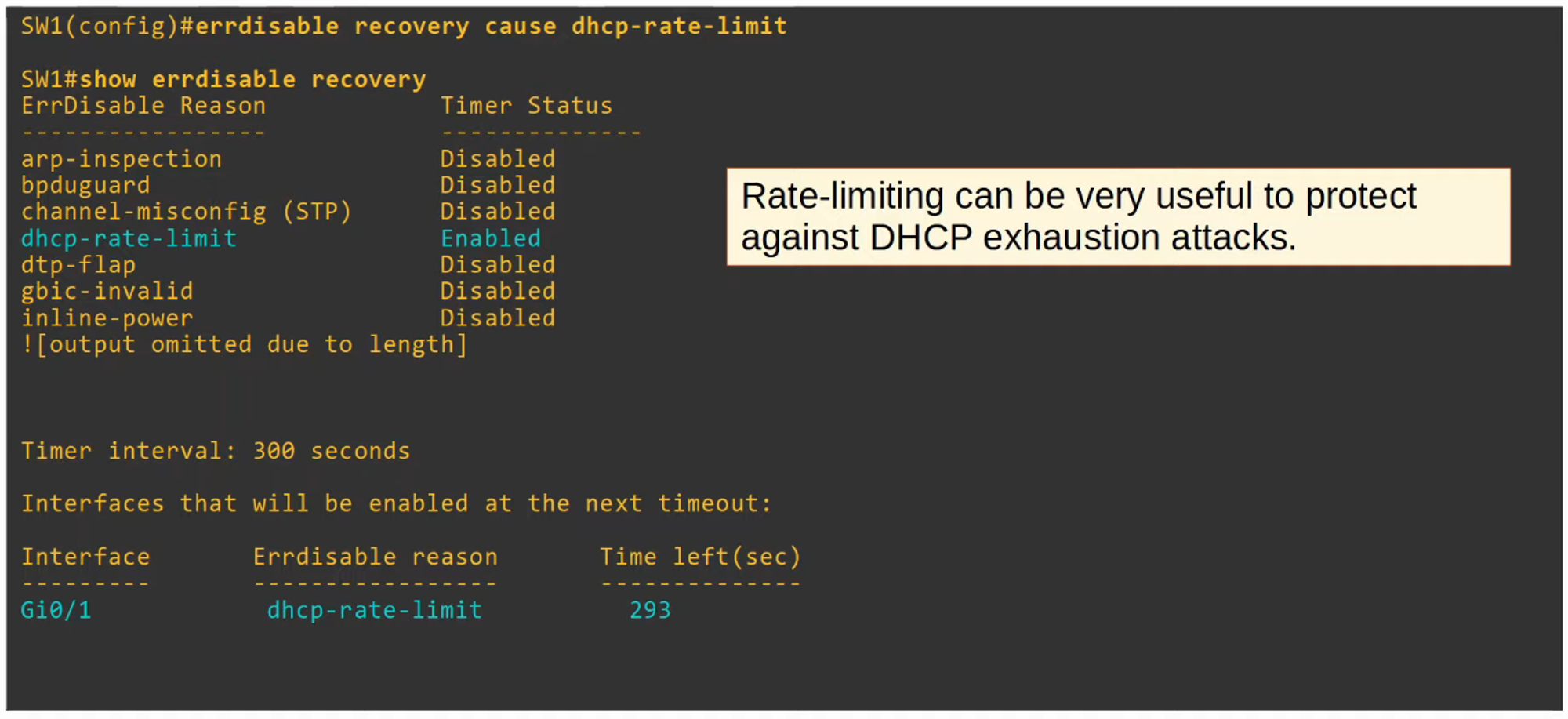
To automatically recover:
errdisable recovery cause dhcp-rate-limit
DHCP Option 82 (Information Option)
- Option 82, also known as the DHCP Relay Agent Information Option, is one of many DHCP options. It provides additional information about where a DHCP message was received, including which interface and VLAN it originated from.
- DHCP relay agents add Option 82 to messages forwarded to the remote DHCP server.
- With DHCP Snooping enabled, Cisco switches will add Option 82 to DHCP messages they receive from clients, even if they aren’t acting as a relay agent.
- By default, Cisco switches will drop DHCP messages with Option 82 received on an untrusted port.
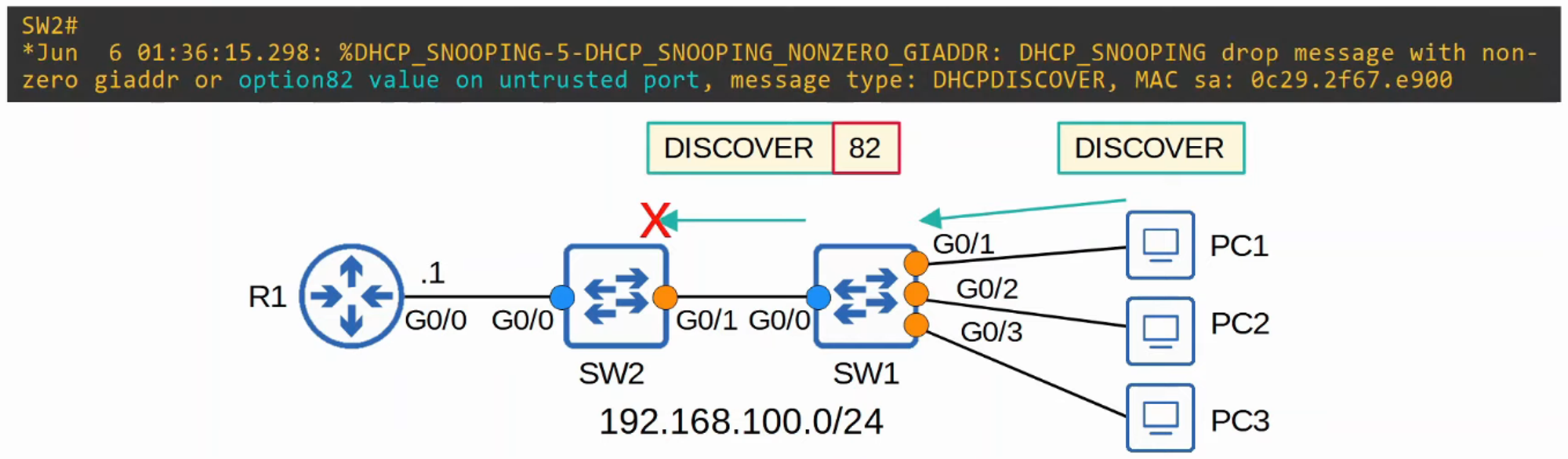
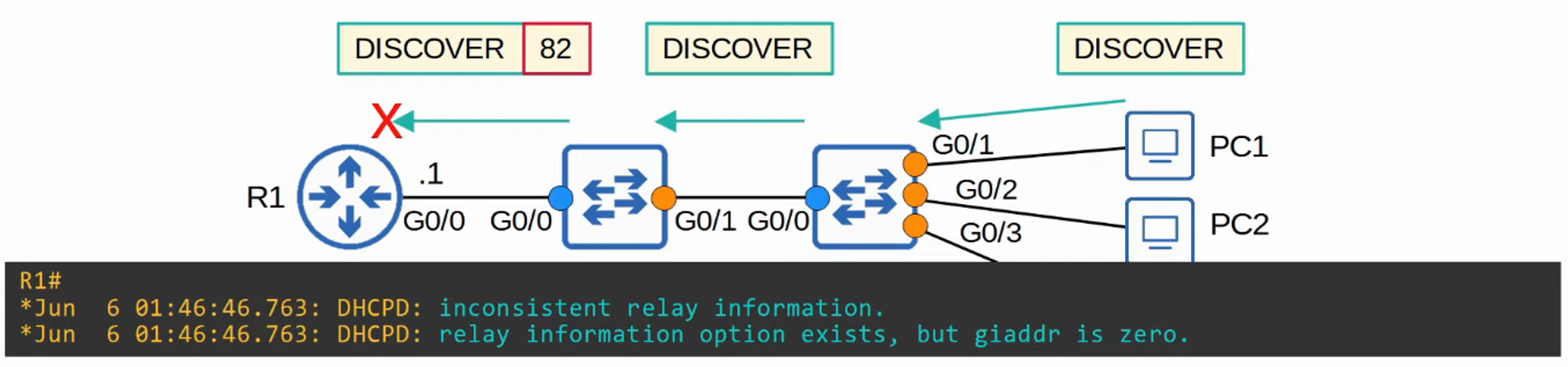
In the scenario below, disabling Option 82 on Switch 1 but not Switch 2 leads to traffic being dropped by Router 1 due to inconsistent relay information.

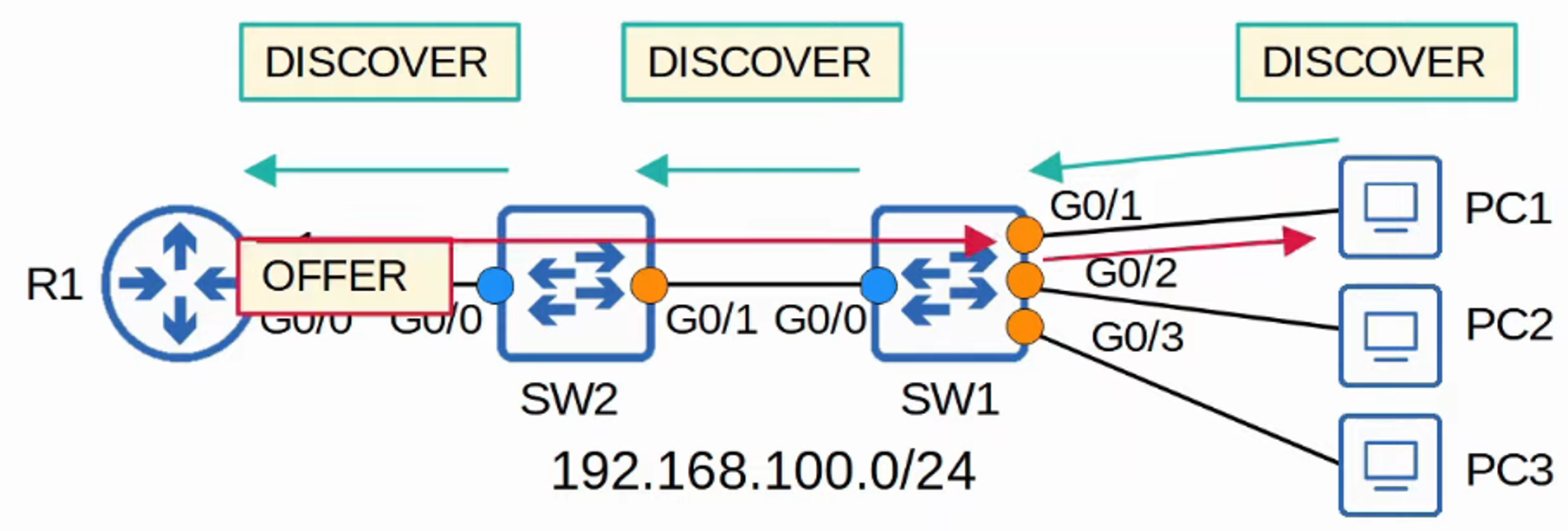
By enabling Option 82 on both switches, DHCP traffic flows correctly, with Router 1 successfully responding to PC1’s DHCP Discover message.

Command Summary
