Purpose of FTP and TFTP
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) and TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) are industry-standard protocols used for transferring files over a network. Both utilize a client-server model:
- Clients can:
- Copy files from a server
- Copy files to a server
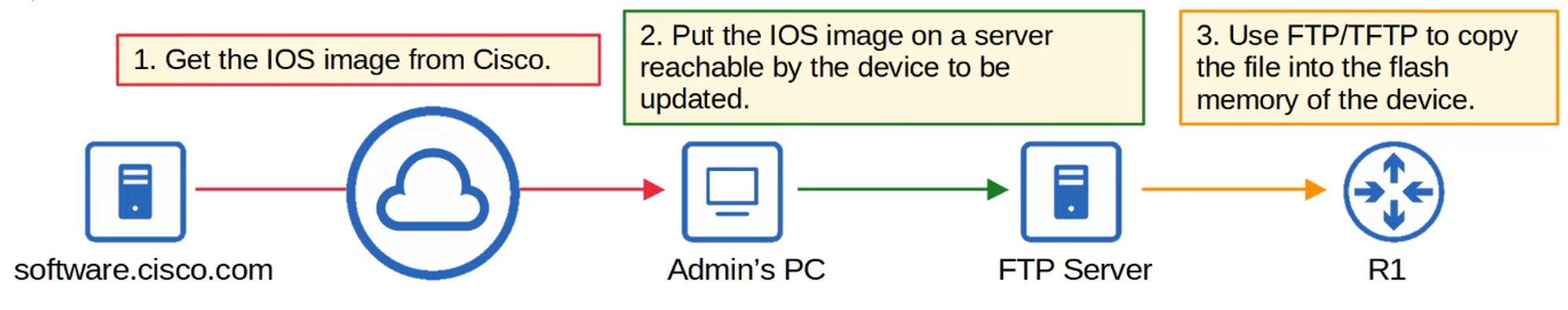
As a network engineer, one of the most common applications for FTP and TFTP is during the operating system upgrade process of a network device. You can download the newer version of IOS from a server and then reboot the device with the updated IOS image.
TFTP and FTP: Functions and Differences
TFTP
- Standardization: First standardized in 1981.
- Simplicity: Named “Trivial” due to its minimalistic design and basic functionality, allowing clients to copy files to and from a server.
- Not a Replacement: Released after FTP, it serves as an alternative when lightweight simplicity is prioritized over functionality.
- No Authentication: Lacks username/password authentication; servers respond to all requests.
- No Encryption: All data is sent in plain text, which can pose security risks.
- Use Case: Best suited for controlled environments to transfer small files quickly.
- Listening Port: TFTP servers listen on UDP Port 69.
- Connectionless: Utilizes UDP, which does not provide reliability through retransmissions. However, TFTP incorporates built-in features for acknowledgment.
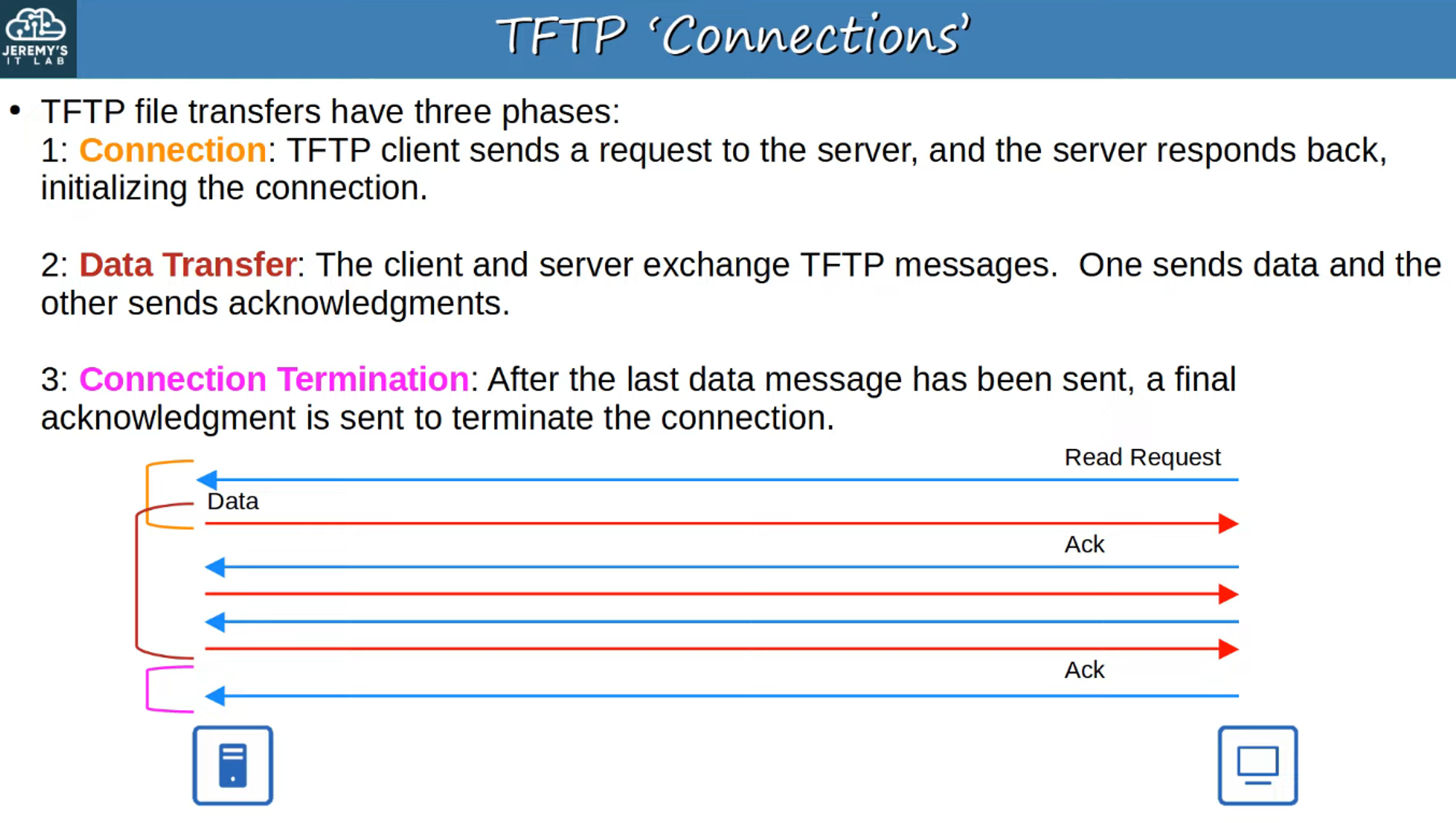
TFTP Reliability
- Every TFTP data message is acknowledged:
- If a client is sending a file to the server, the server sends acknowledgment (ACK) messages.
- Conversely, if the server is sending a file to the client, the client sends ACK messages.
- Timers: If an expected message isn’t received in a timely manner, the waiting device will resend its previous message.

TFTP “Connections”
Transfer Identifier (TID) (Not in the CCNA Exam)
- When a client sends the first message to the server, the destination port is UDP 69, and the source port is a random ephemeral port.
- This “random port” is referred to as a Transfer Identifier (TID), which identifies the data transfer.
- The server also selects a random TID to use as a source port when replying, rather than using UDP 69.
- In subsequent messages, the destination port will be the server’s TID.
Note: UDP Port 69 (TFTP) is only used for the initial request message.

FTP
- Standardization: First standardized in 1971.
- Ports: Uses TCP Ports 20 and 21.
- Authentication: Requires usernames and passwords, although there is no encryption.
- Secure Alternatives: For greater security, consider using FTPS (FTP over SSL/TLS) or SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol).
- Complexity: More complex than TFTP, allowing clients to:
- Navigate file directories
- Add or remove files
- List files, etc.
- Commands: Clients send FTP commands to the server to perform these functions.
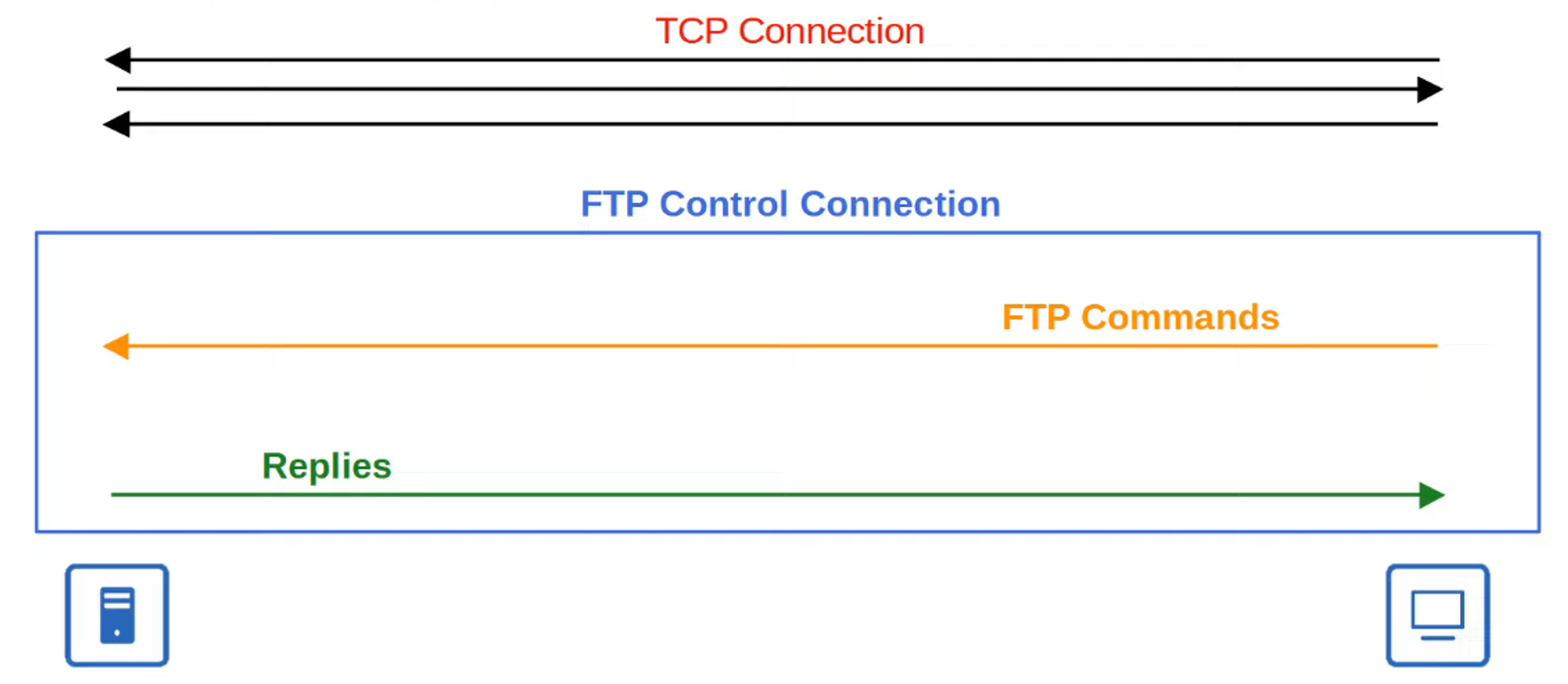
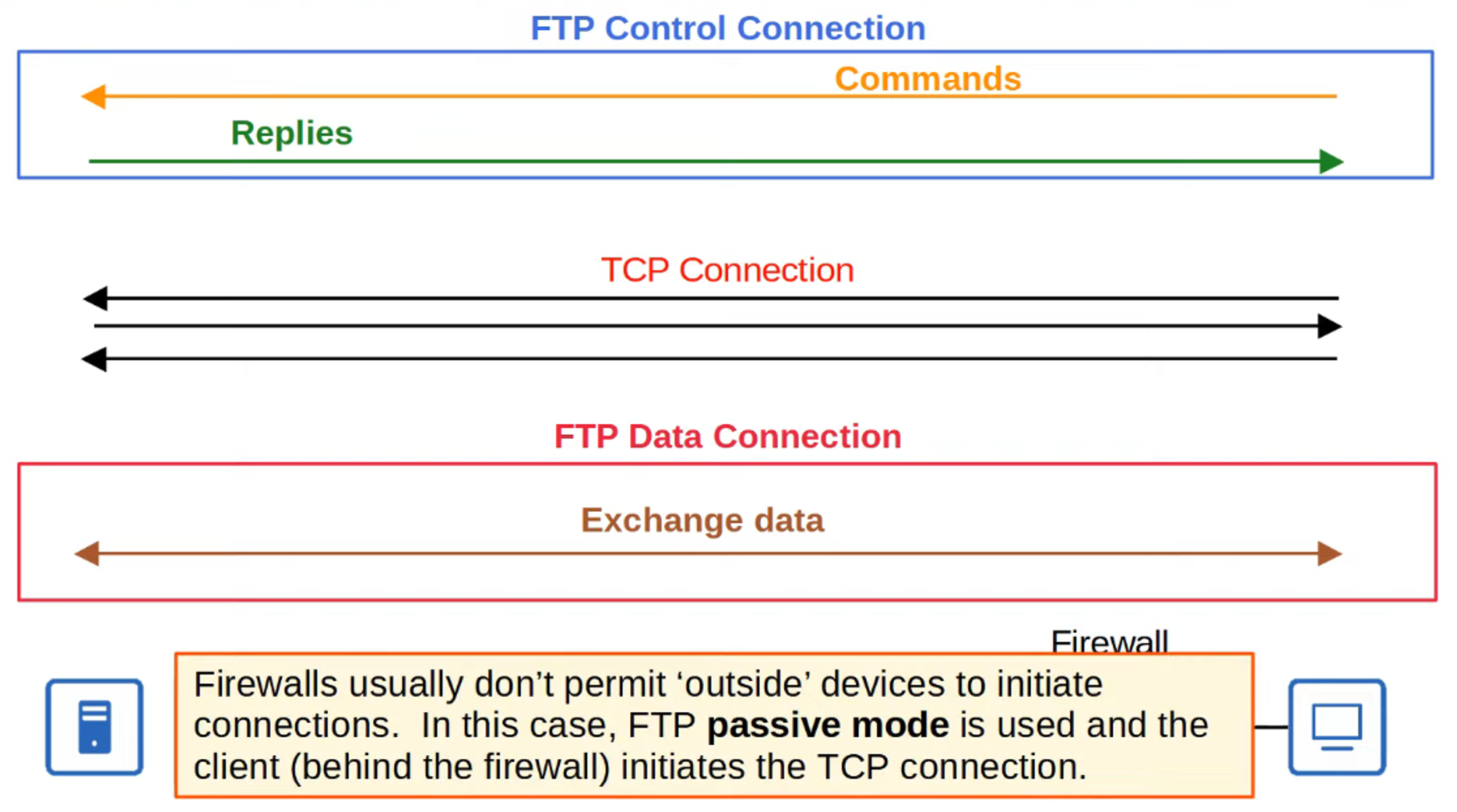
FTP Control Connections
- FTP utilizes two types of connections:
- Control Connection: Established over TCP Port 21 to send FTP commands and replies.
- Data Connection: Separate TCP connections over TCP Port 20 are established for transferring files.
Active Mode FTP Data Connections
- The default method for establishing FTP data connections is Active Mode, where the server initiates the TCP connection.
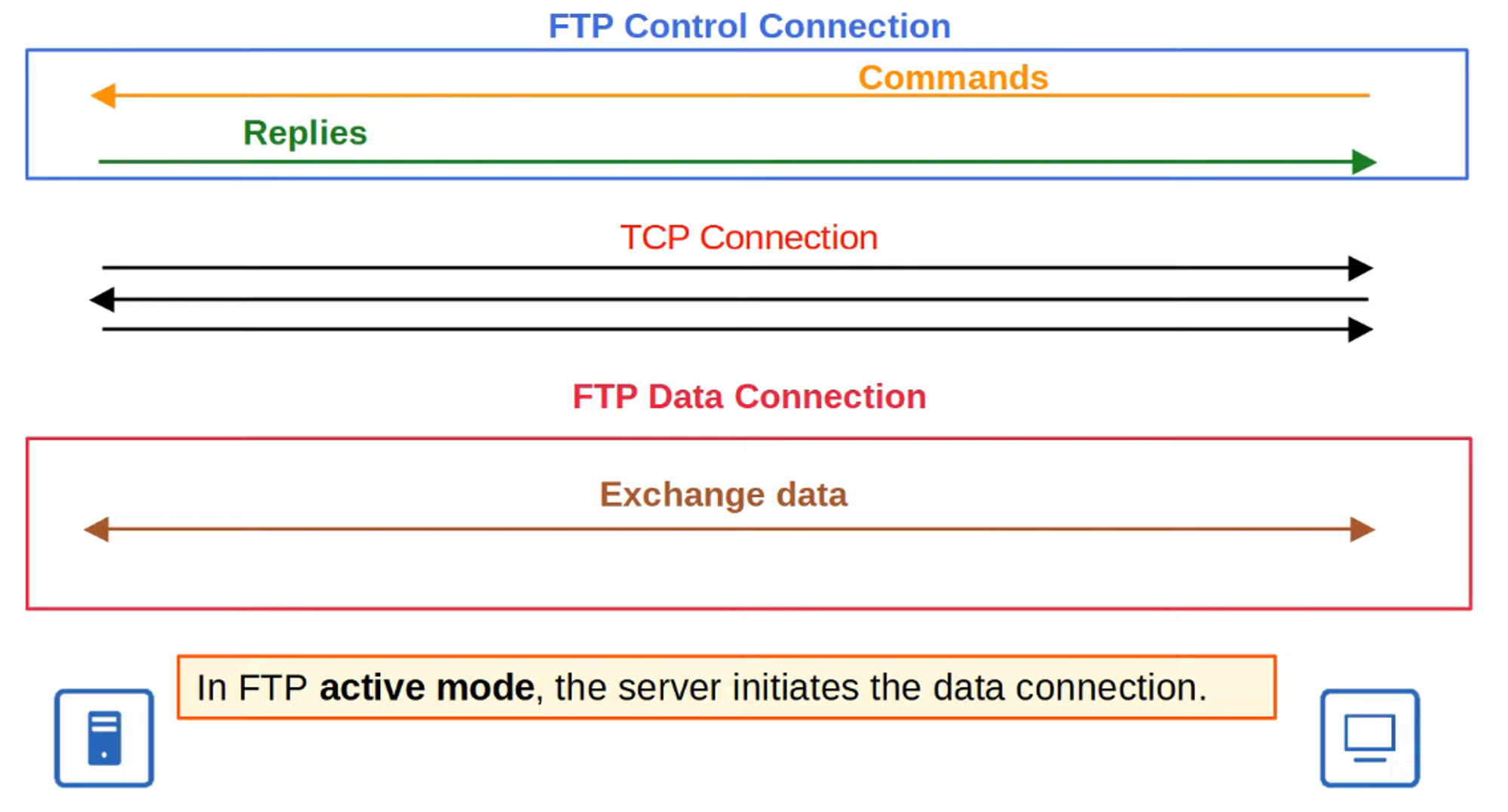
- In Passive Mode, the client initiates the data connection. This is often necessary when the client is behind a firewall that may block incoming connections from the server.
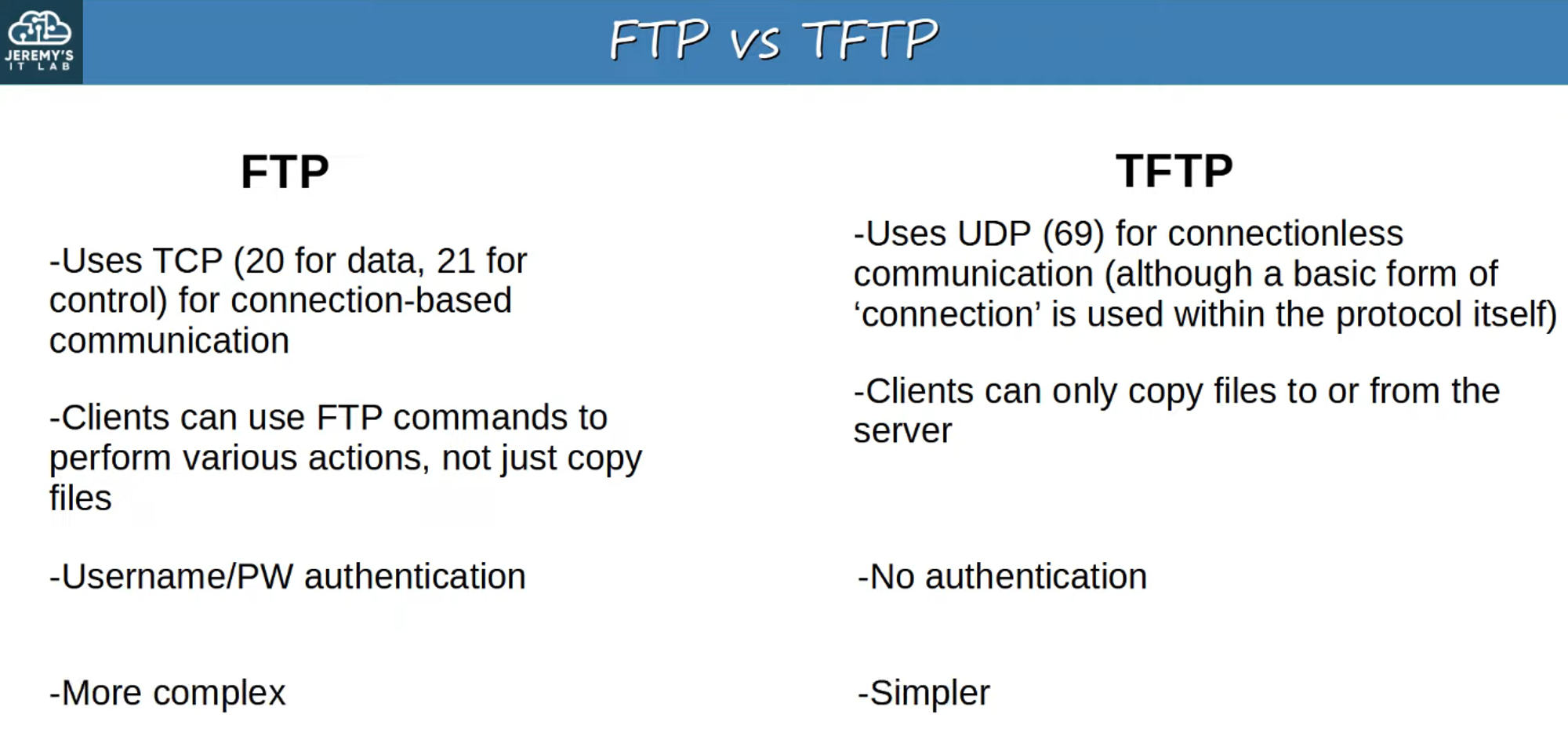
FTP vs. TFTP
A comparison between FTP and TFTP highlighting key differences.
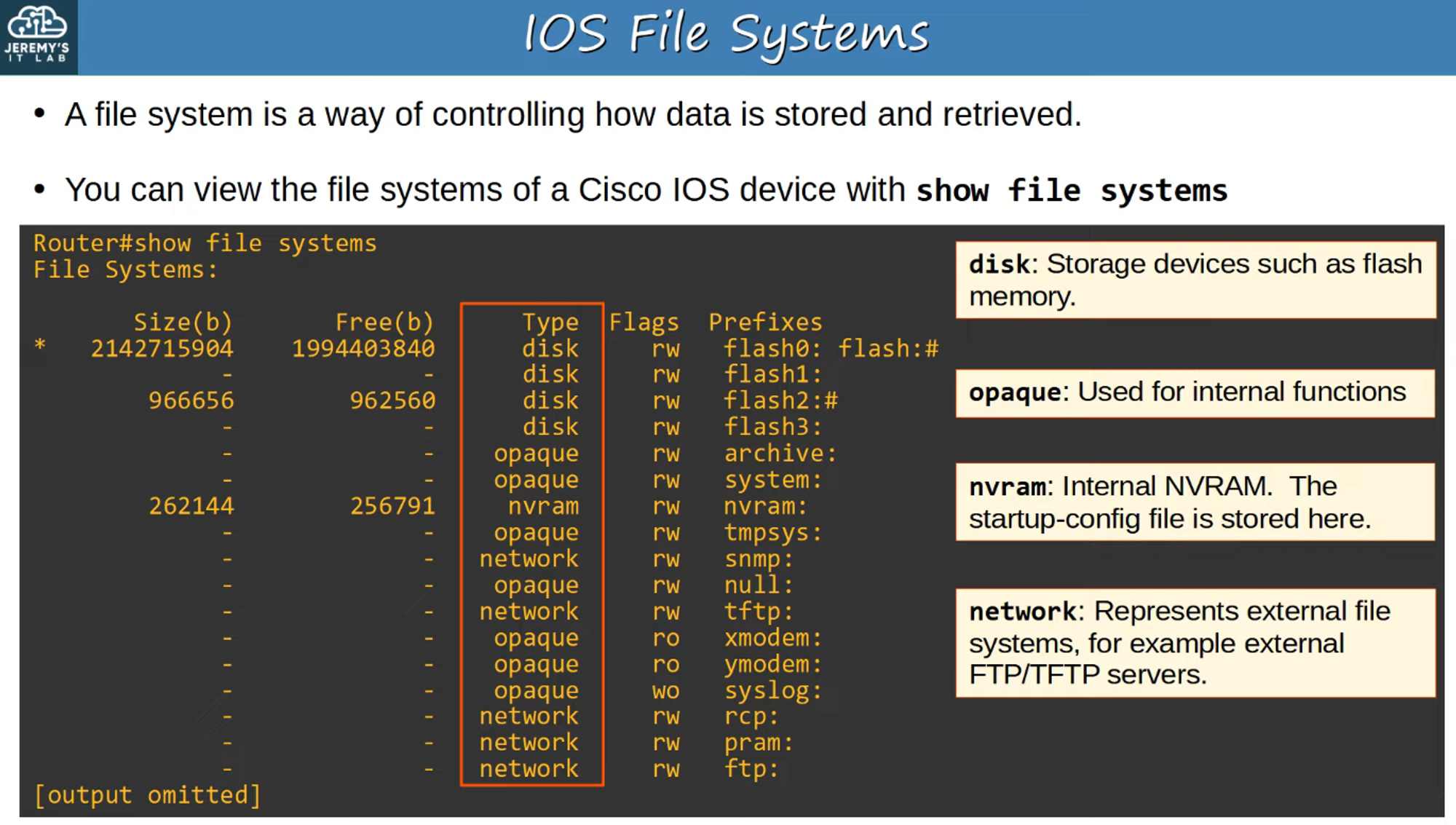
IOS File Systems
A file system is a method of controlling how data is stored and retrieved. You can view the file system of a Cisco IOS device using the command:
show file systems
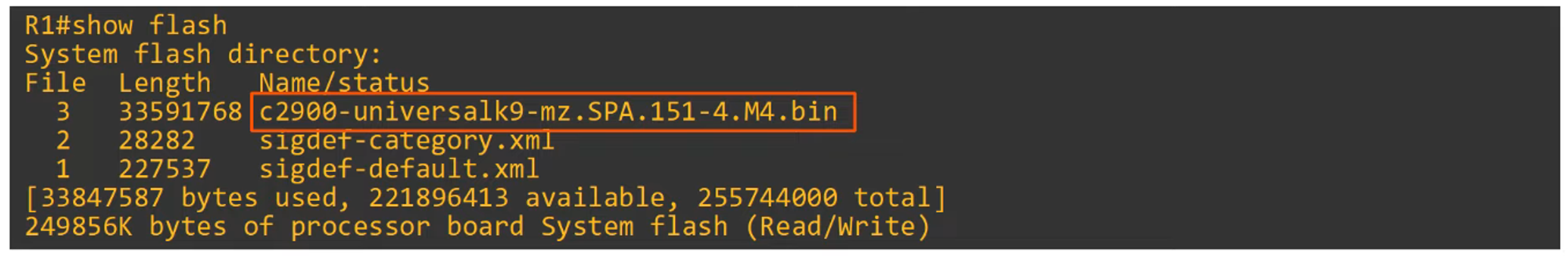
Using FTP/TFTP in IOS
To manage your IOS version and file system, the following commands can be utilized:
- View the current version of IOS:
show version
- View the contents of flash memory:
show flash

Copying Files with TFTP
Step 1
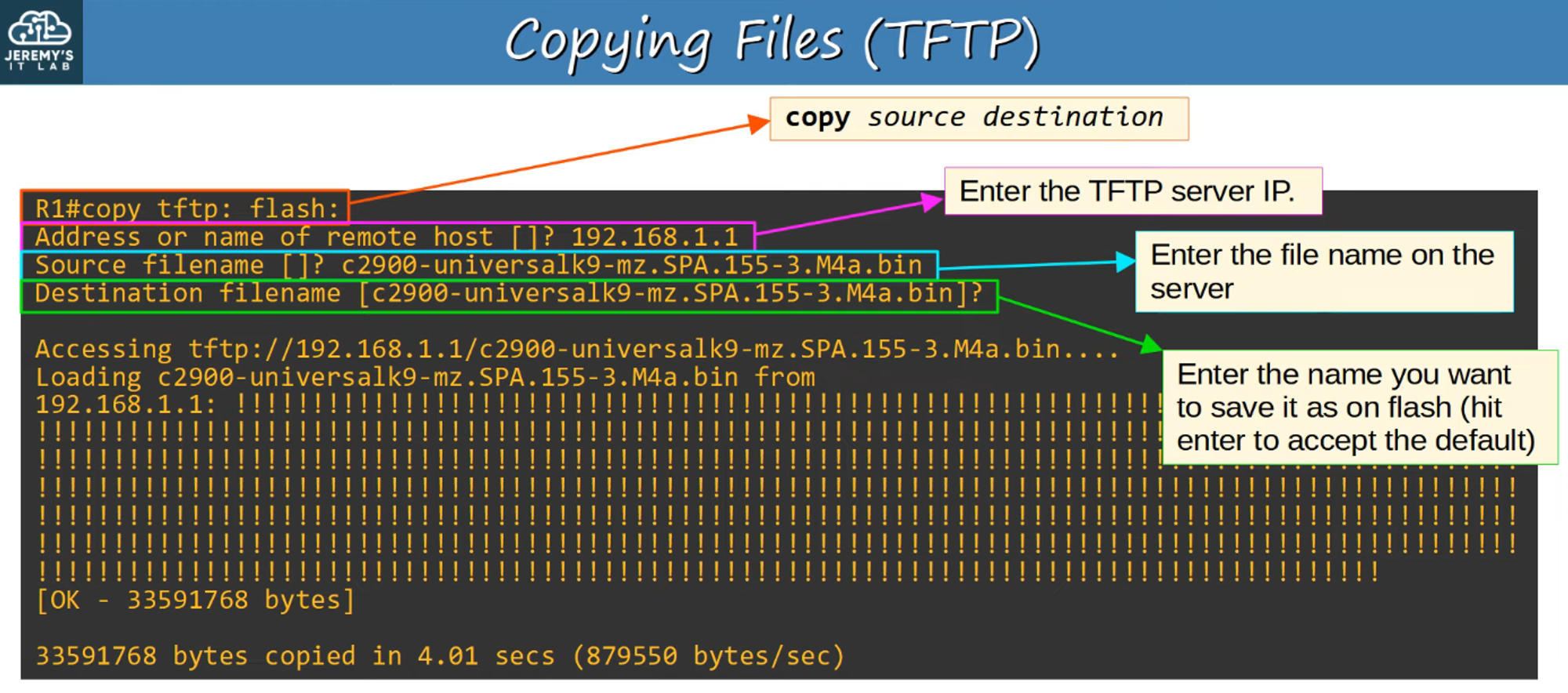
Step 2
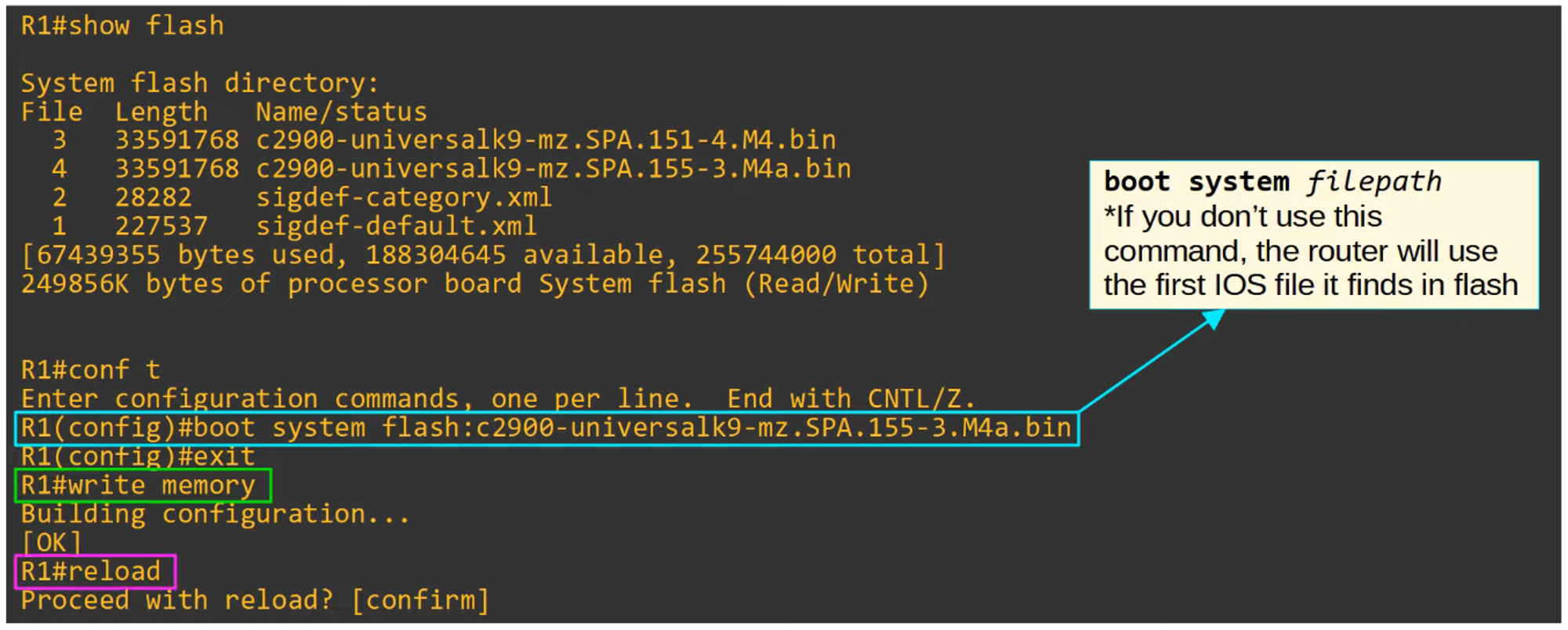
Step 3
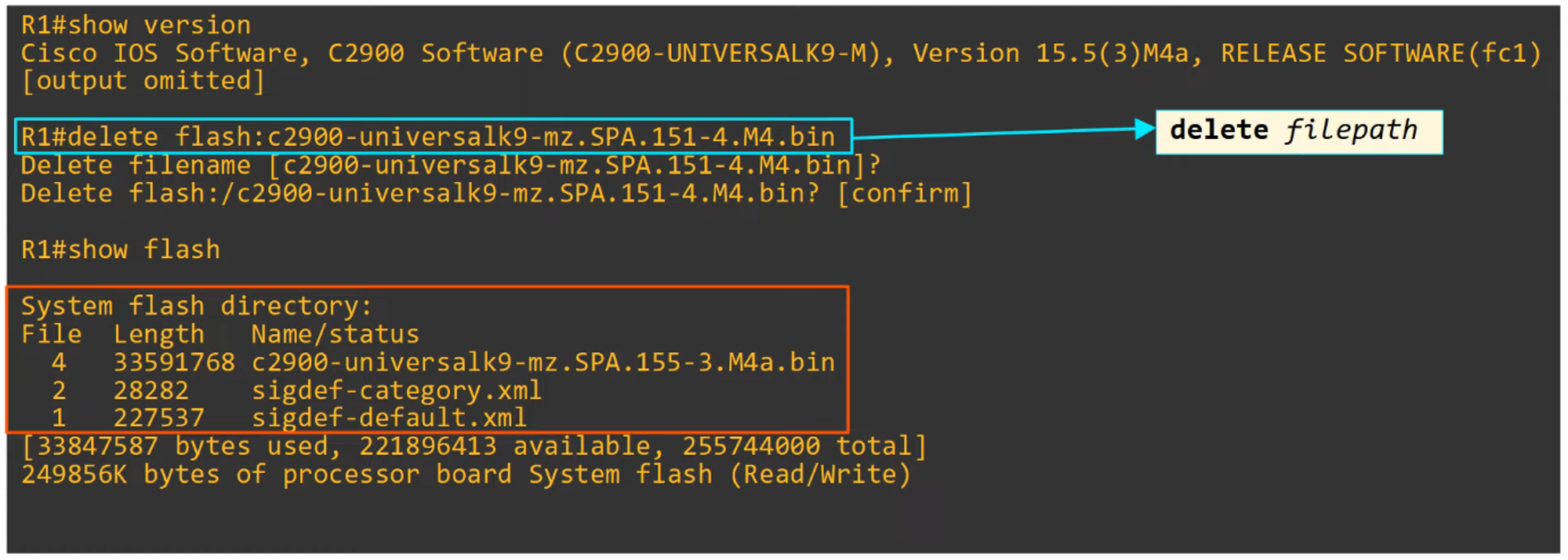
Copying Files with FTP
Step 1
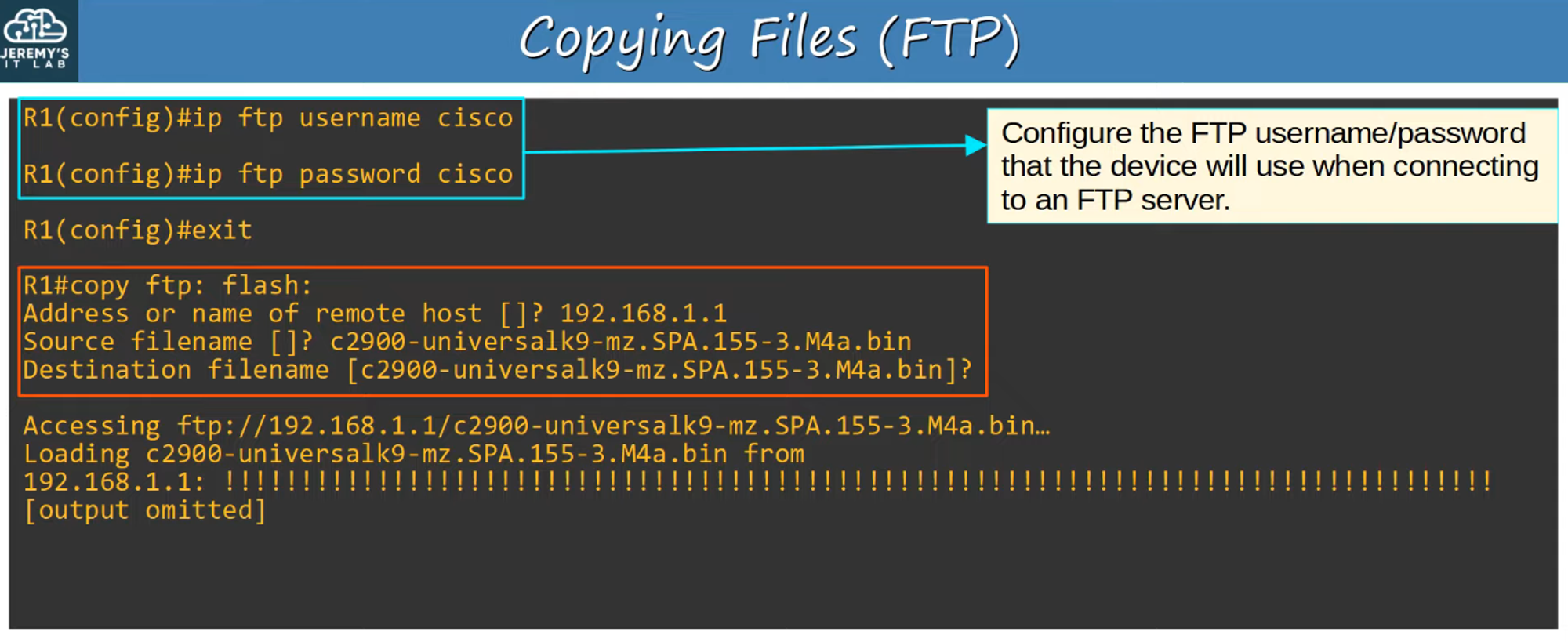
Steps 2 and 3
Steps are identical to TFTP as described above.
Command Summary
A summary of key commands for FTP and TFTP operations.
