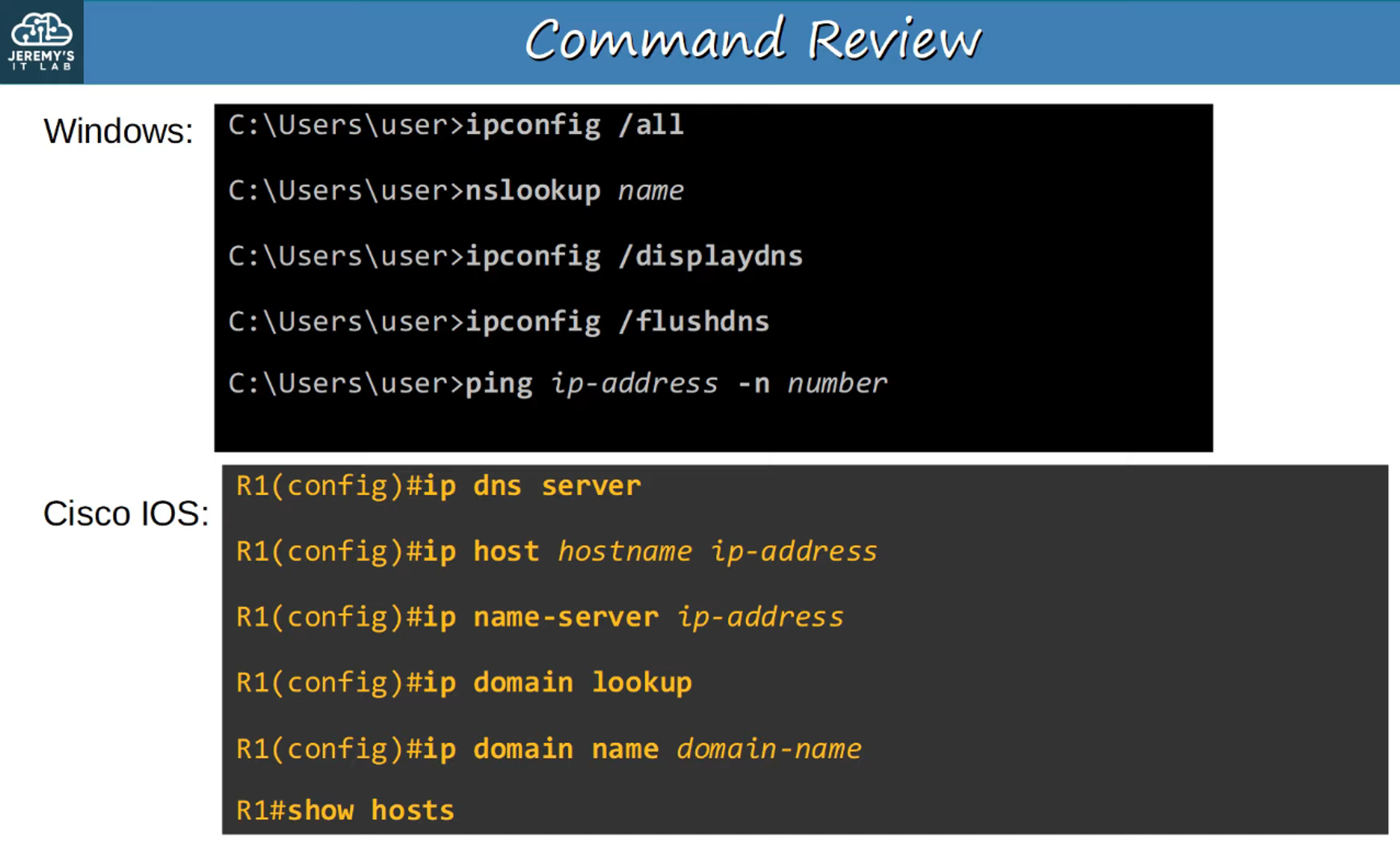
Purpose of DNS
- DNS (Domain Name System) is used to resolve human-readable domain names (like
google.com) into IP addresses. - Machines (such as PCs) do not use names; they use IP addresses (IPv4 or IPv6).
- Domain names are much easier for humans to use and remember compared to IP addresses.
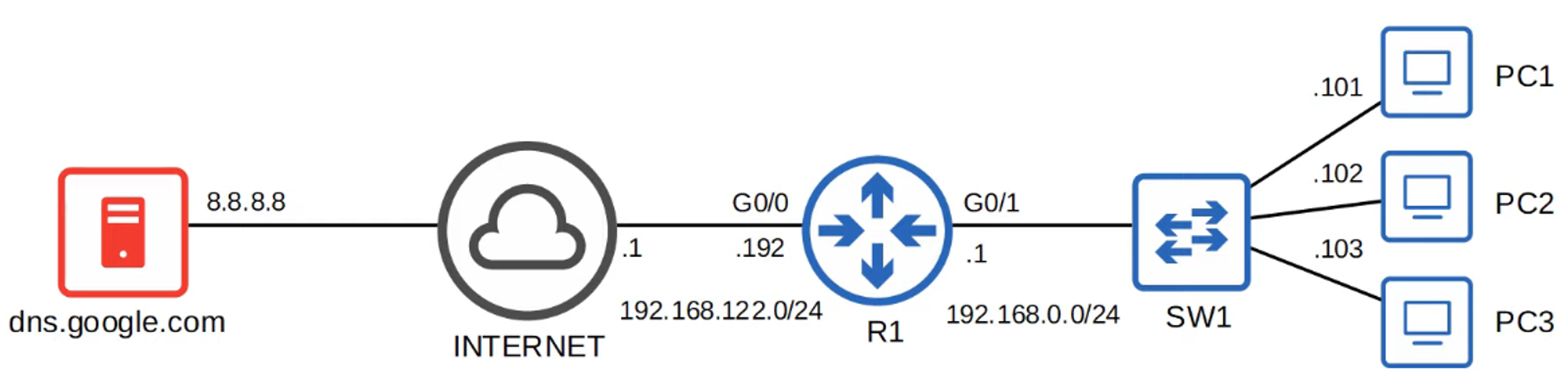
- Example: What is the IP address of
youtube.com?
- Example: What is the IP address of
- When you type
youtube.cominto a web browser, your device queries a DNS server for the IP address ofyoutube.com. - The DNS servers your device uses can be:
- Manually configured.
- Learned automatically through DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
Basic Functions of DNS
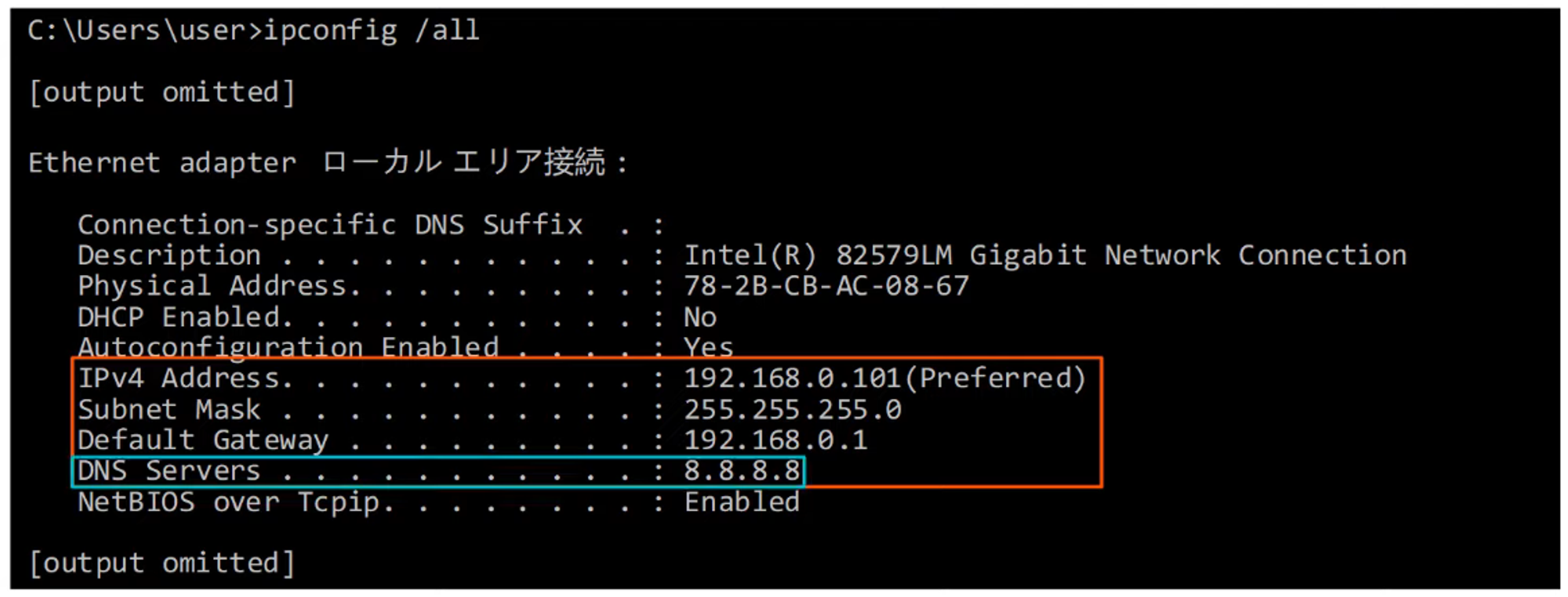
Viewing Local IP Configuration
-
Use the
ipconfig /allcommand to display the local IP configuration of the current device.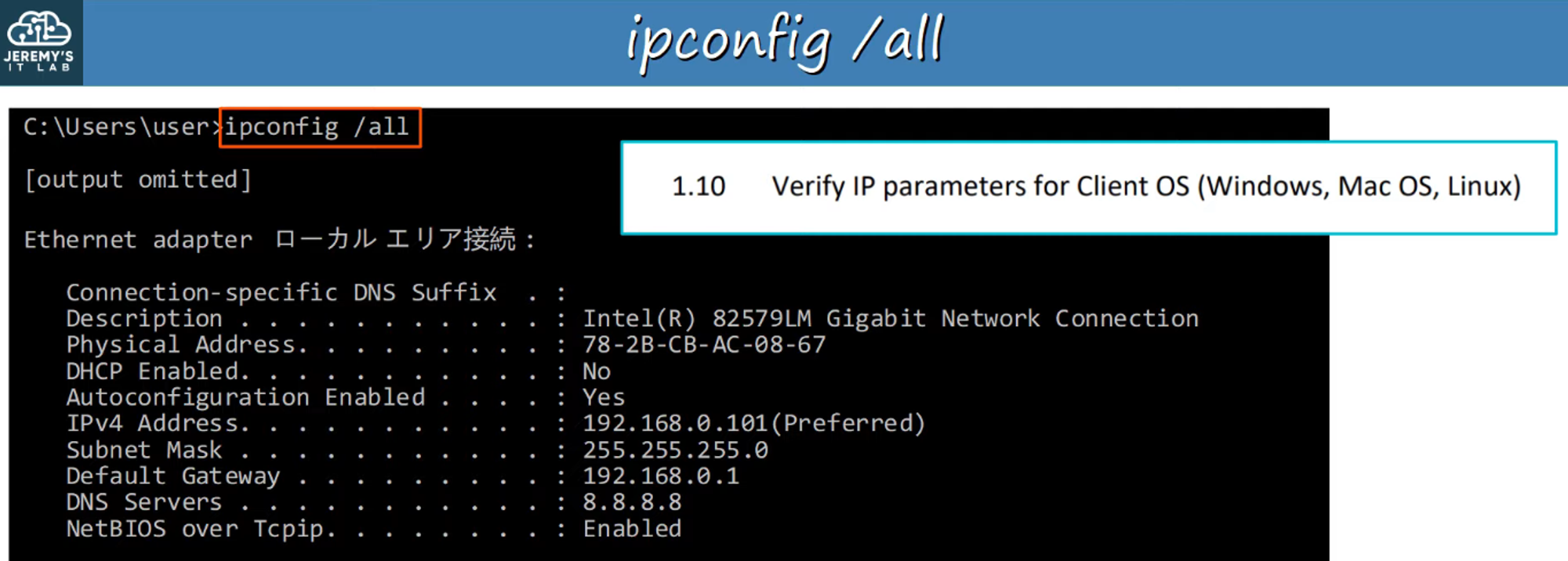
Using nslookup
-
The
nslookupcommand shows the IP address information for a given DNS entry (domain name).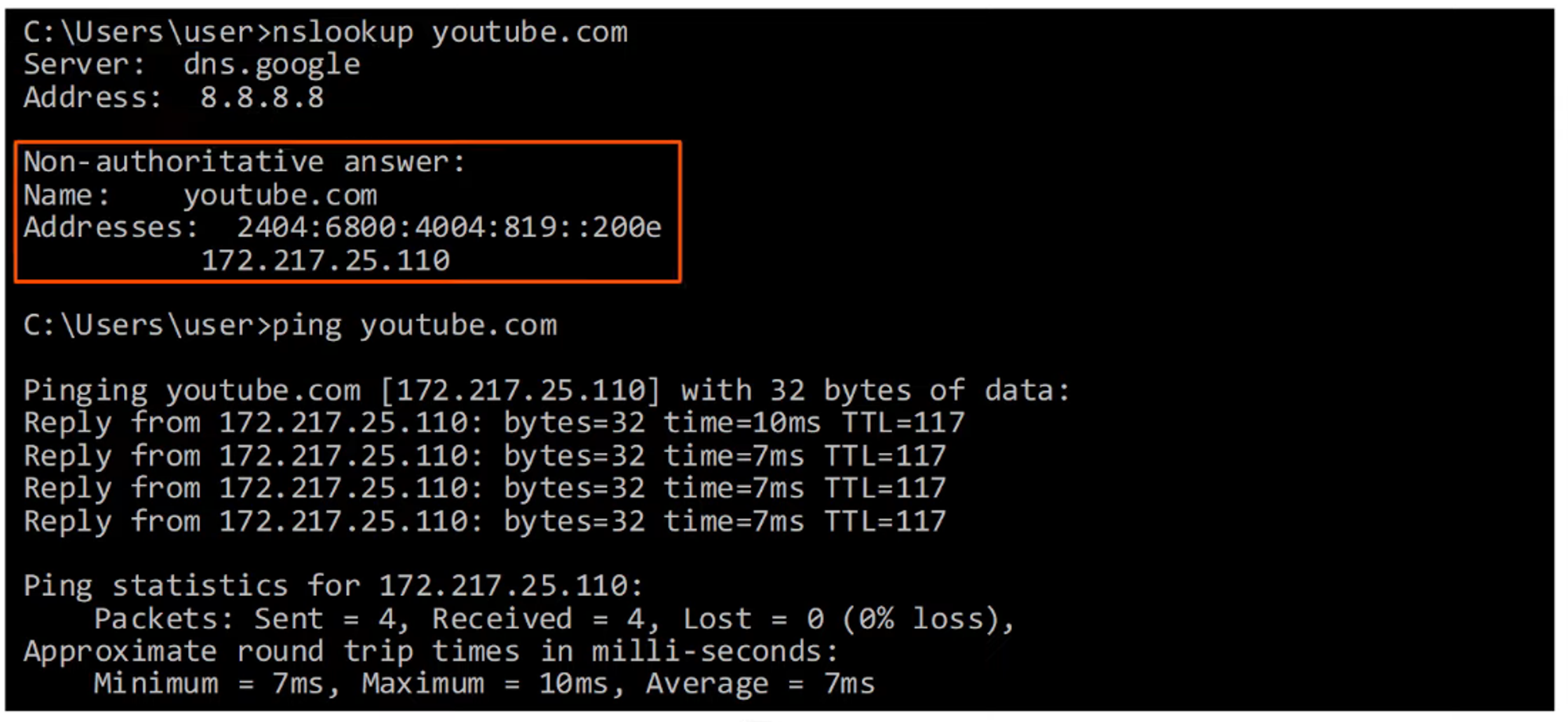
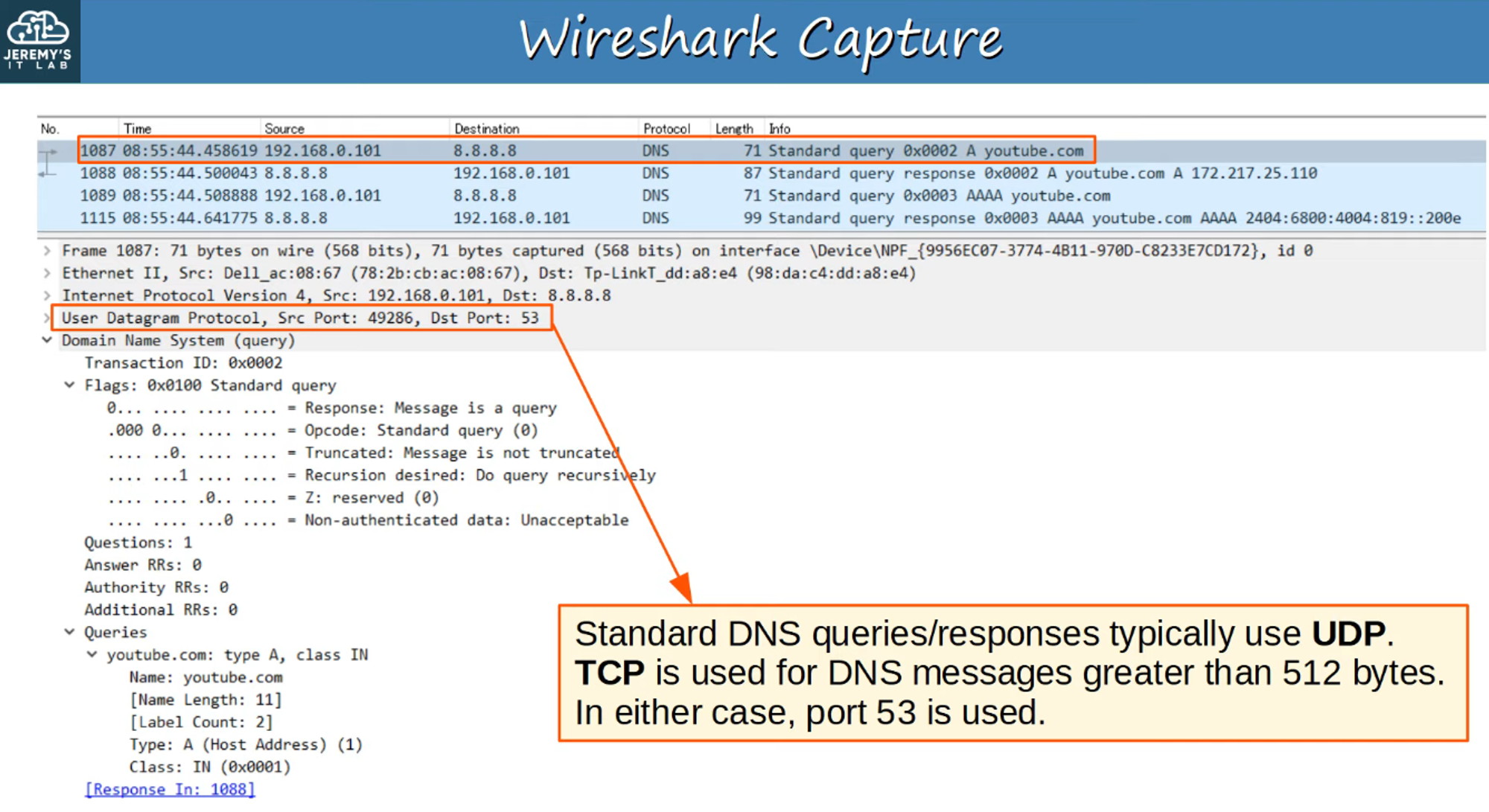
DNS Packet Capture (Wireshark)
-
The results of using commands like
ipconfigandnslookupcan be captured and analyzed with Wireshark.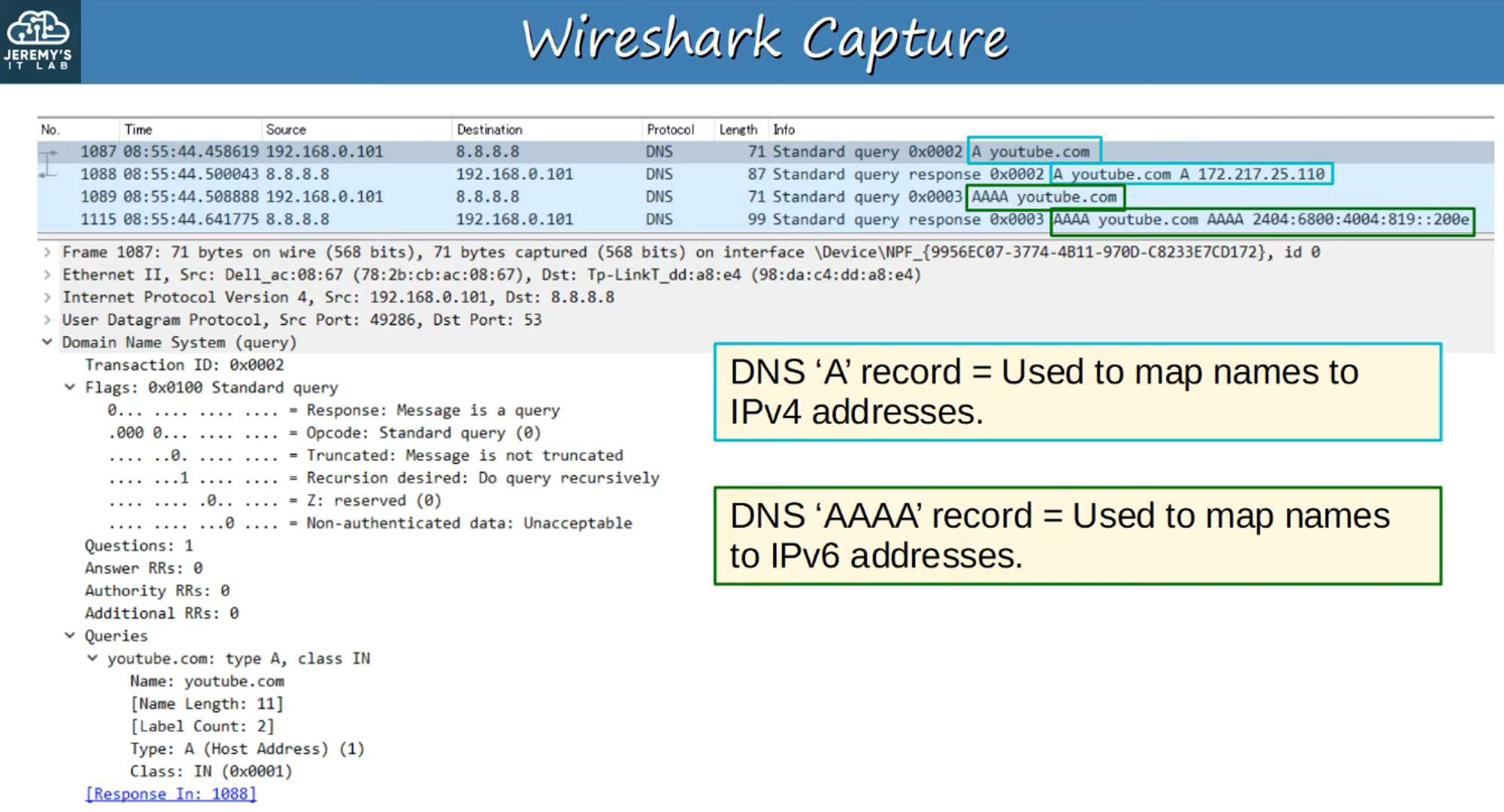
Managing DNS Cache
-
ipconfig /displaydnsshows the DNS cache stored on the device.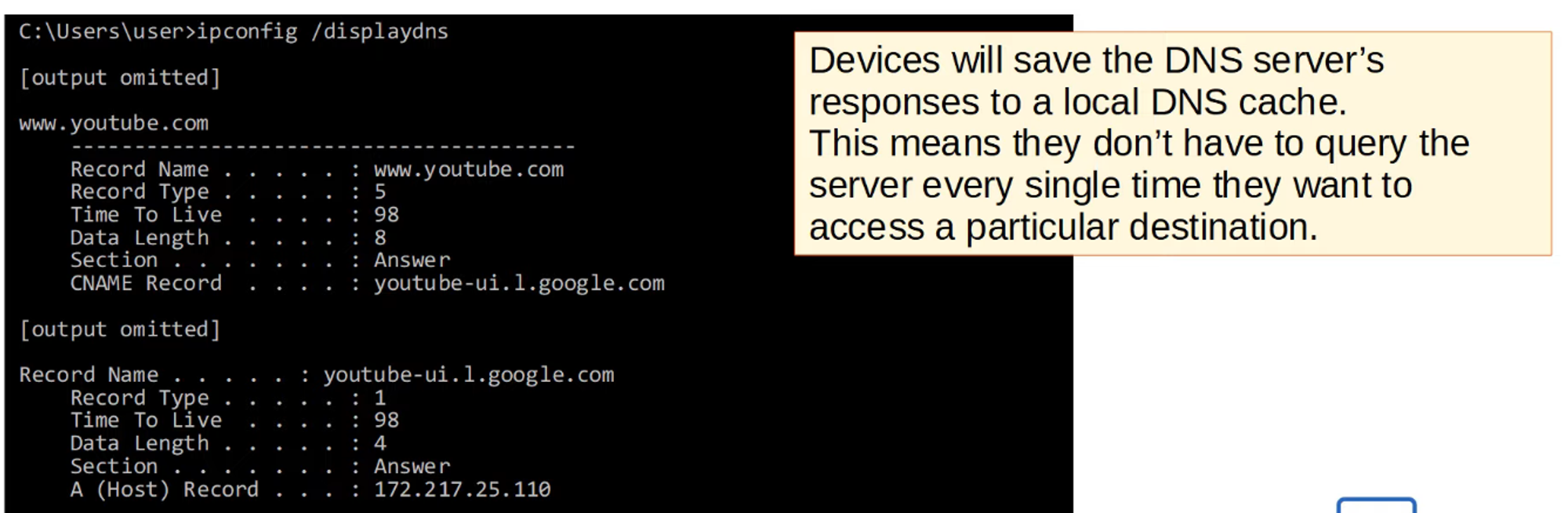
-
ipconfig /flushdnsclears the DNS cache, forcing the device to fetch fresh DNS information.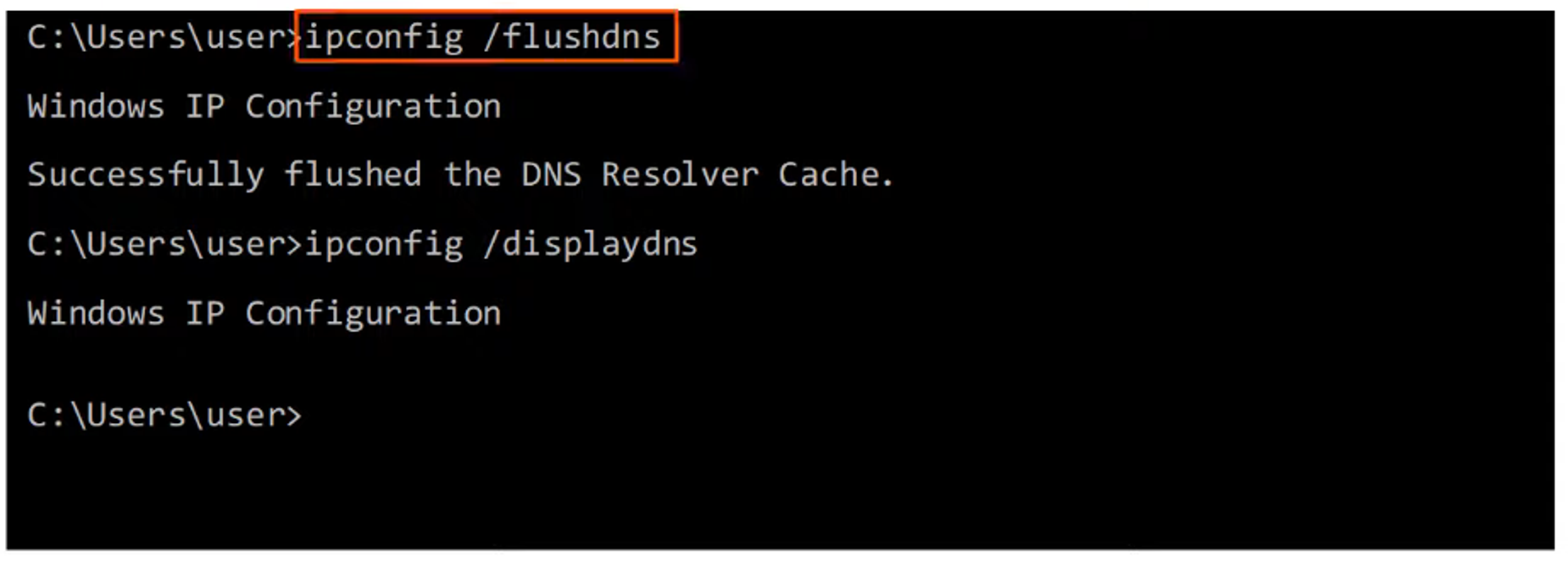
Hosts File
-
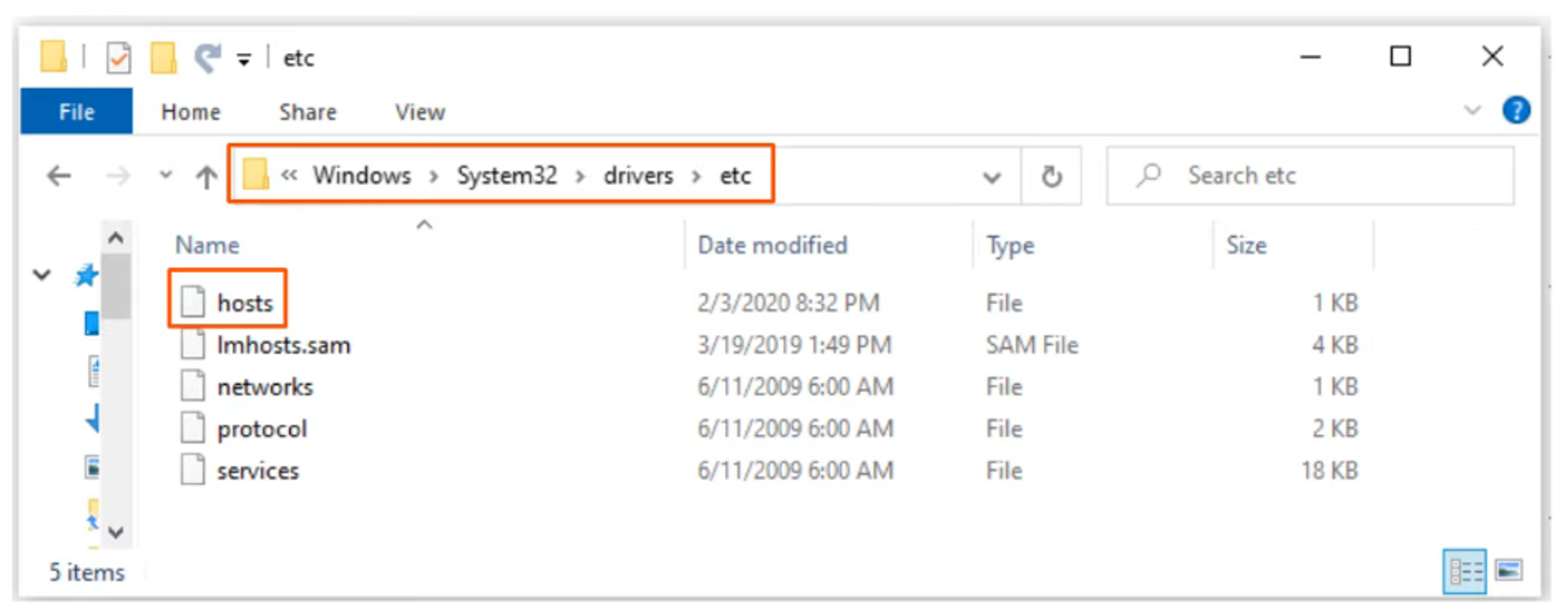
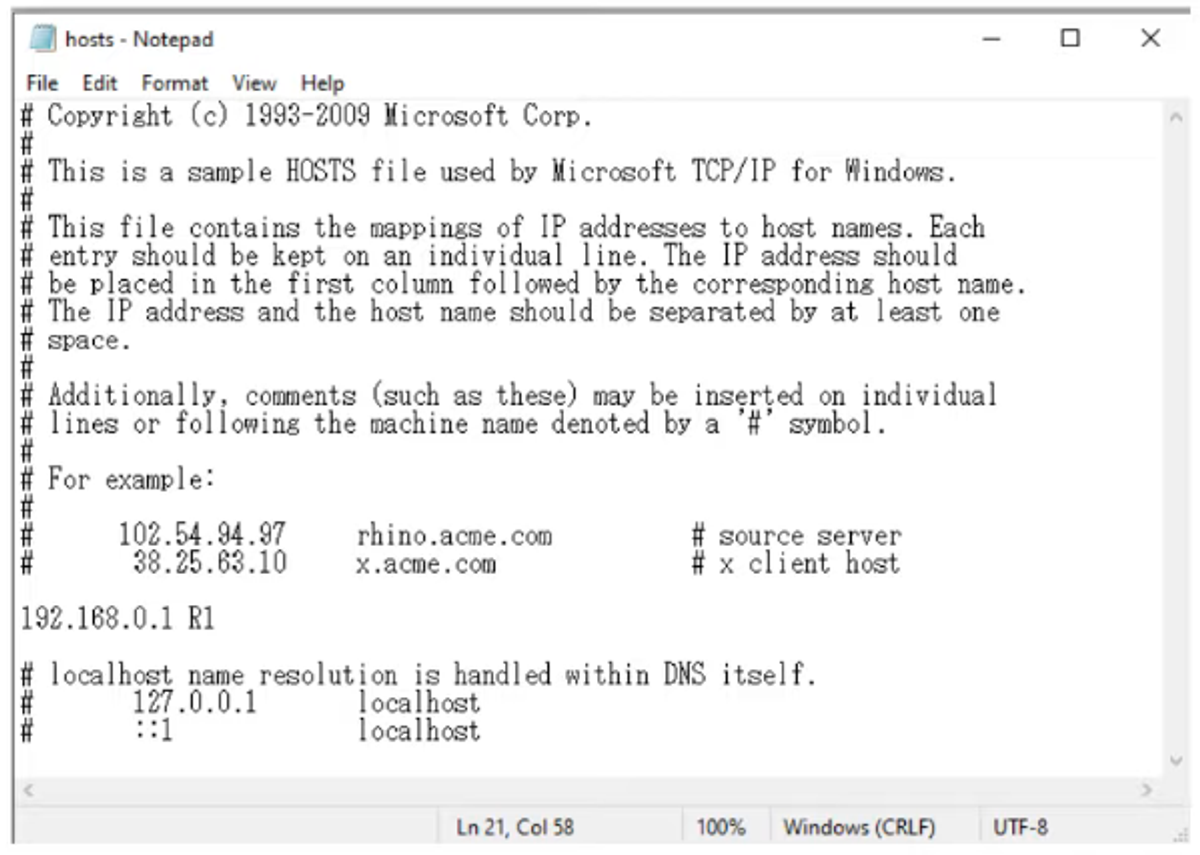
Devices can use a hosts file to map domain names to IP addresses locally, bypassing DNS.
-
For Windows, the hosts file is located here:
Configuring DNS in Cisco IOS
- Devices on a network don’t need DNS to be configured on routers to use DNS:
- Routers forward DNS requests like any other packet.
- However, a Cisco router can be configured as a DNS server, although this is not common practice.
- Typically, Windows or Linux servers act as internal DNS servers.
- Cisco routers can also function as DNS clients.
DNS Commands in Cisco IOS
-
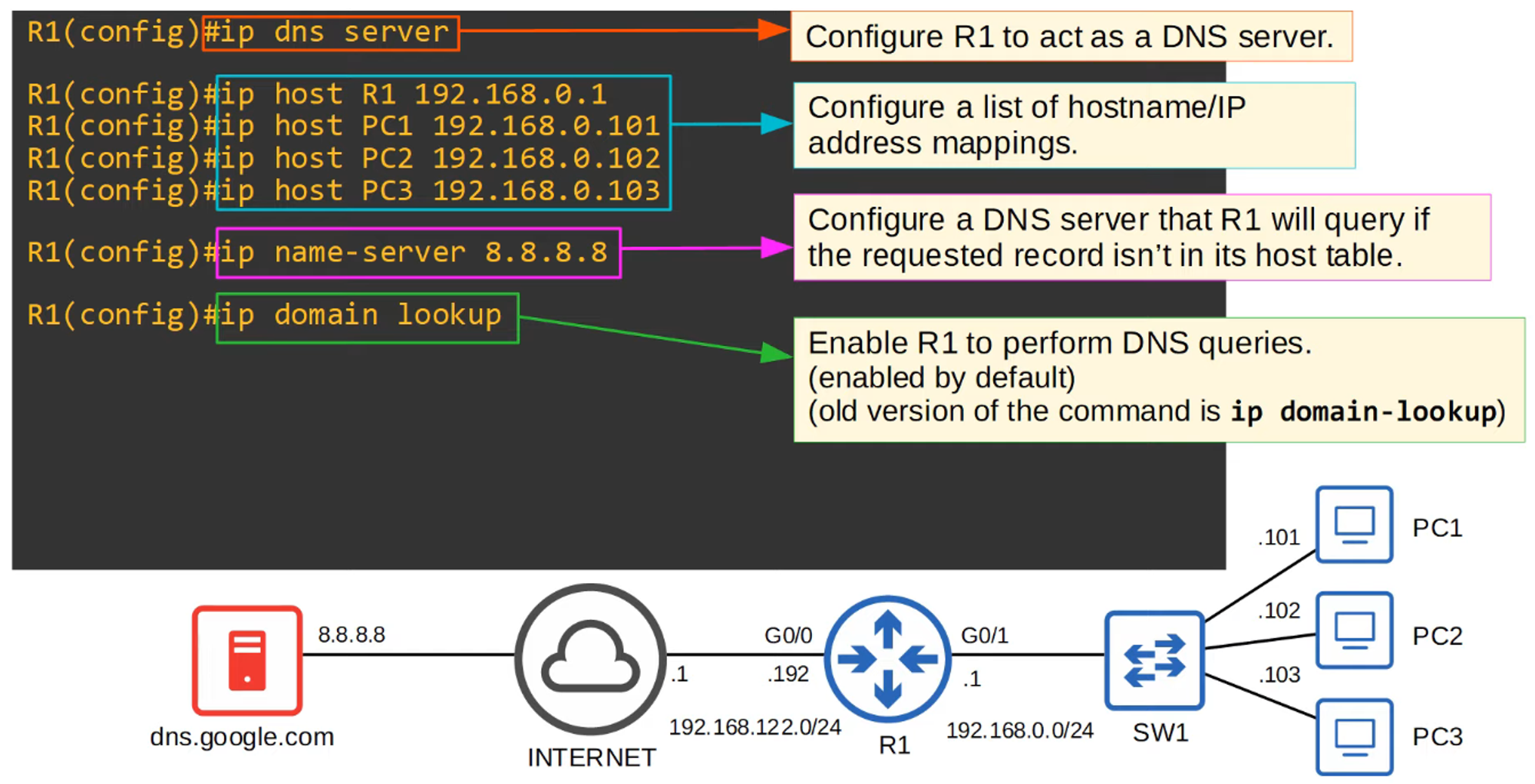
To configure a Cisco router as a DNS server, use the following commands:
ip dns server— Enables DNS server functionality on the router.ip host <hostname> <ip address>— Manually assigns a hostname to an IP address.
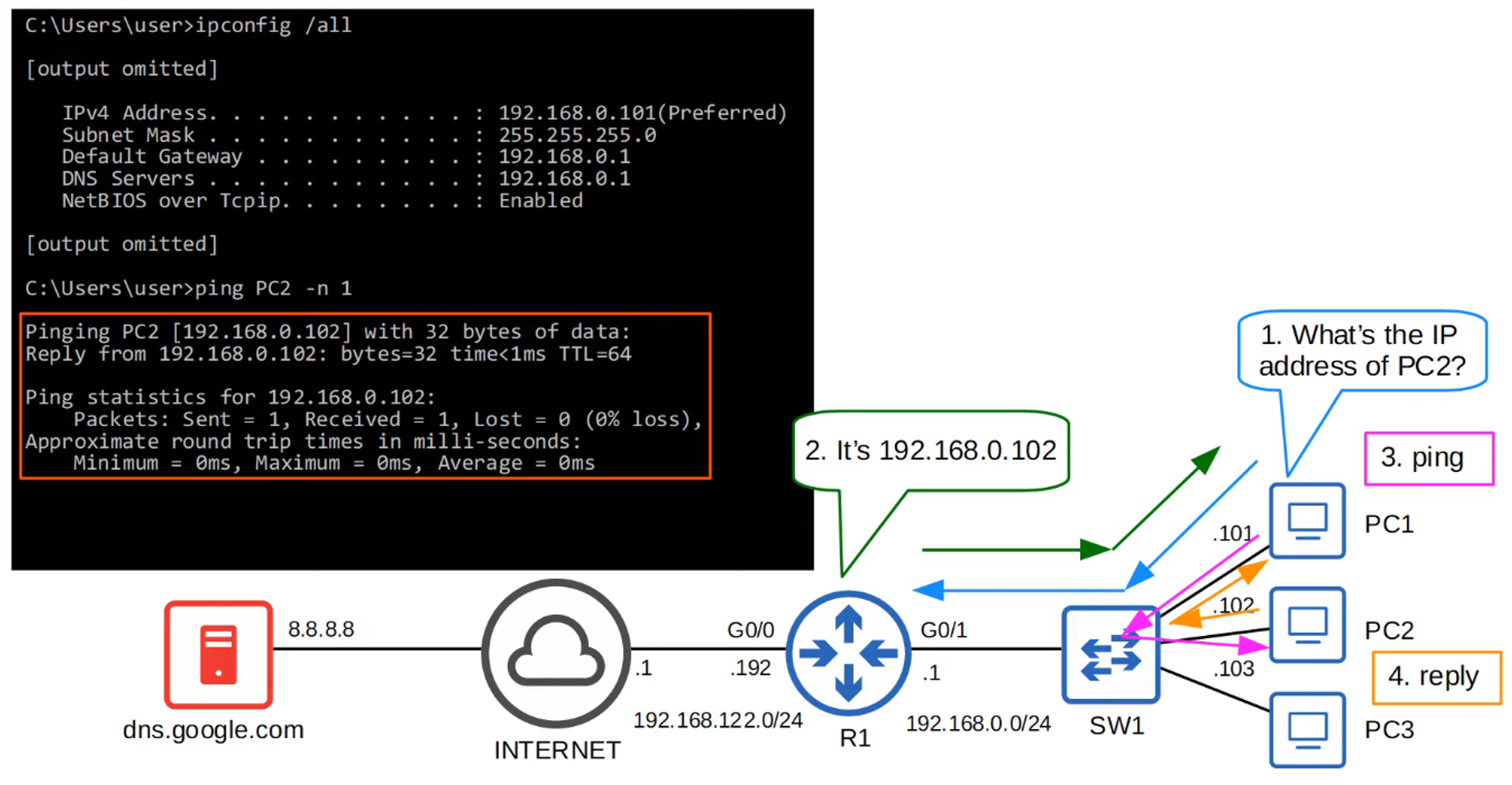
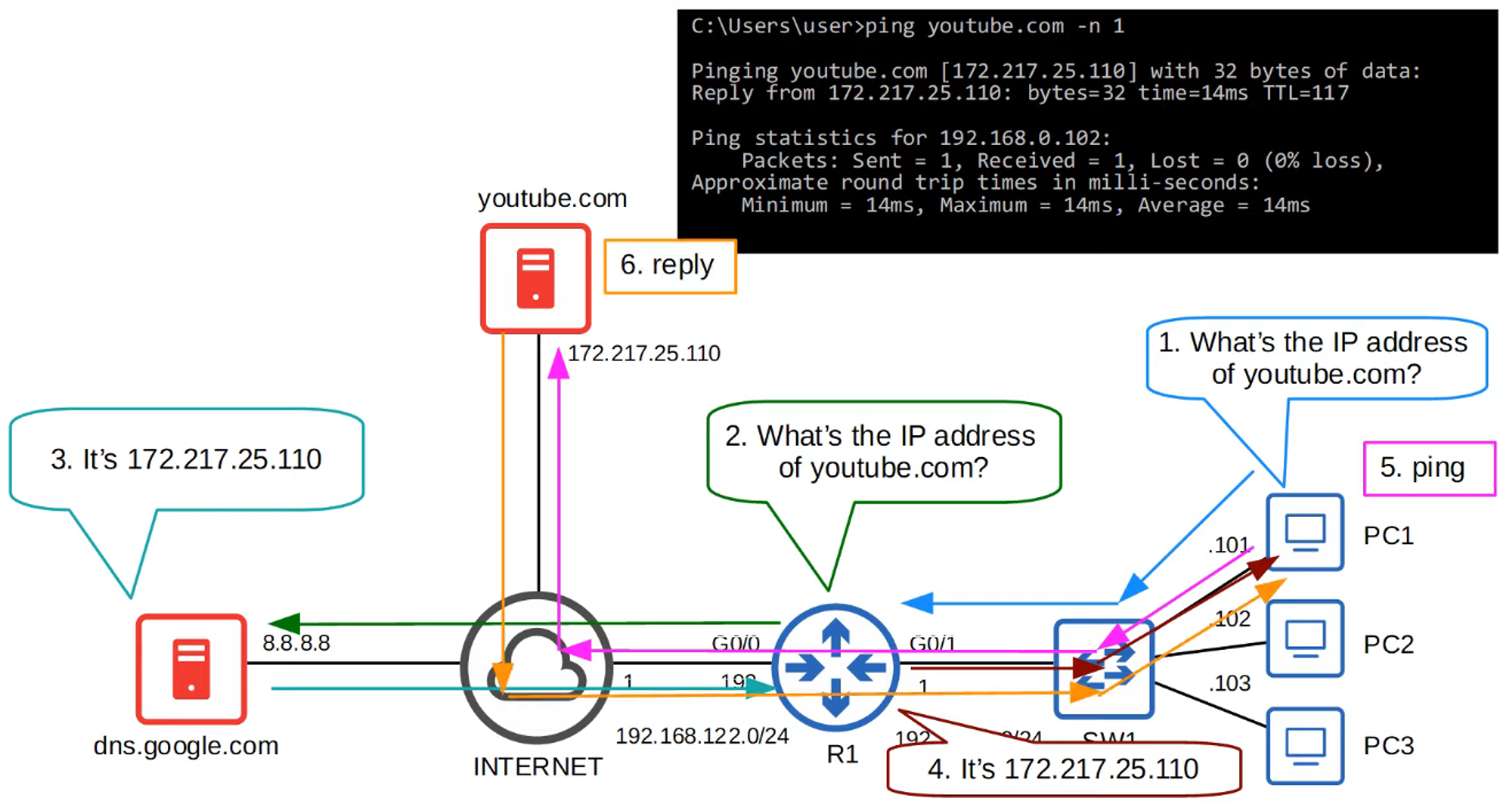
-
To view the list of manually configured hostnames, use the
show hostscommand.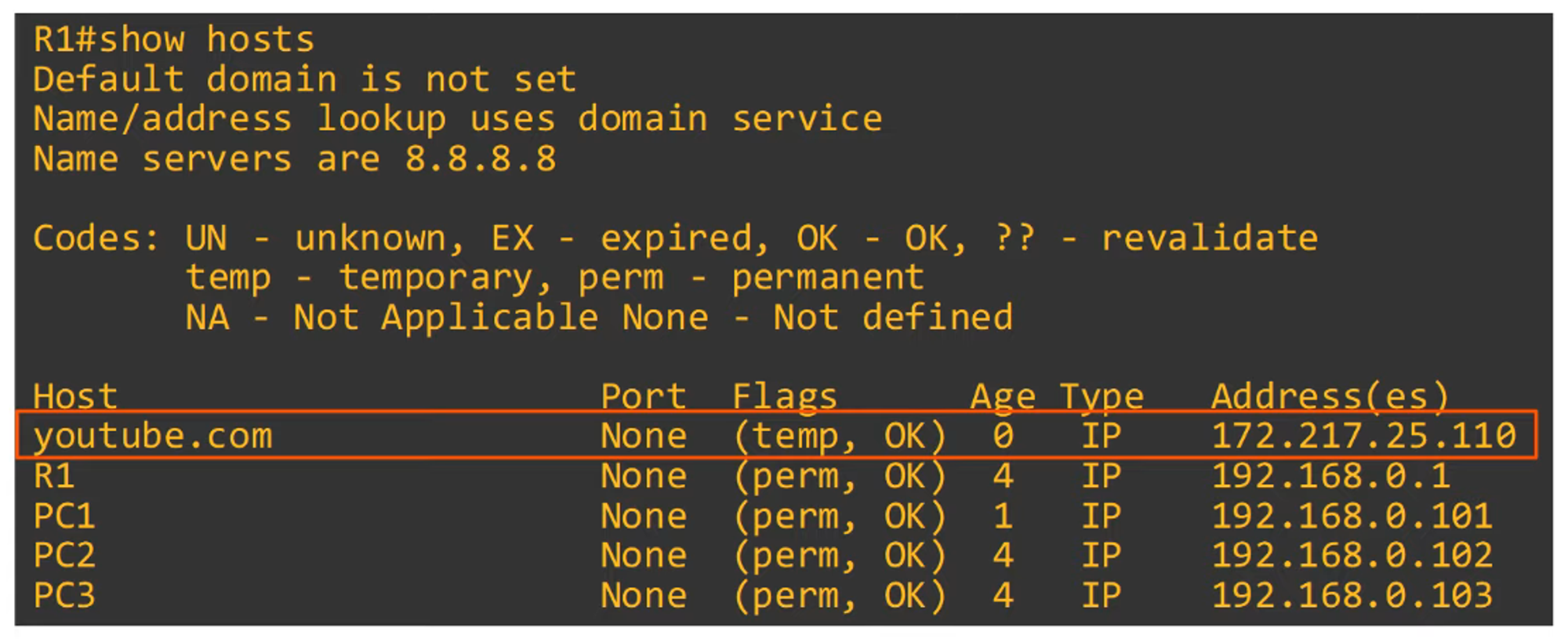
-
You can also configure DNS name resolution using the following commands:
ip name-server <ip>— Specifies the DNS server(s) the router will use for DNS lookups.ip domain lookup— Enables DNS lookup on the router.
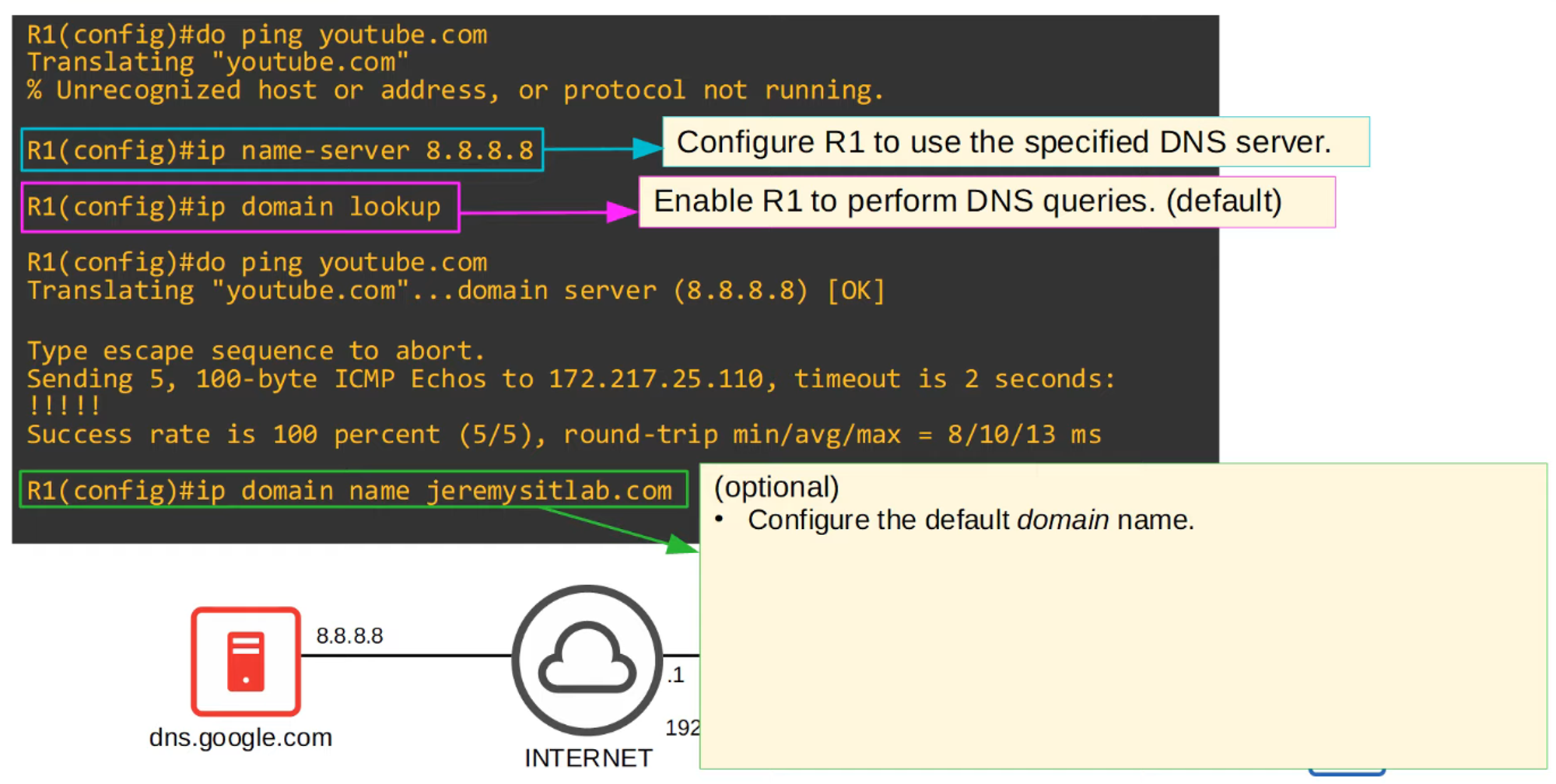
DNS Command Review